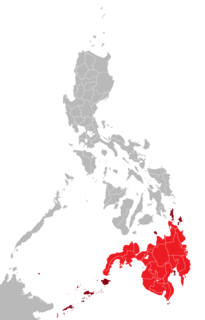
Mindanao is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. As of 2015 census, Mindanao has 25,700,000 inhabitants, while the entire island group has an estimated population of 27,021,036 as of 2021.

Northern Mindanao is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region X. It comprises five provinces: Bukidnon, Camiguin, Misamis Occidental, Misamis Oriental, and Lanao del Norte, and two cities classified as highly urbanized, all occupying the north-central part of Mindanao island, and the island-province of Camiguin. The regional center is Cagayan de Oro. Lanao del Norte was transferred to Northern Mindanao from Region XII by virtue of Executive Order No. 36 in September 2001.

Zamboanga del Sur, officially the Province of Zamboanga del Sur, is a province in the Philippines located in the Zamboanga Peninsula region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Pagadian. Statistically grouped with Zamboanga del Sur is the highly urbanized city of Zamboanga, which is geographically separated and a chartered city and governed independently from the province.

Cotabato, officially the Province of Cotabato and formerly but still colloquially known as North Cotabato, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Soccsksargen region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Kidapawan. Some of its barangays are under the jurisdiction of the nearby Bangsamoro Autonomous Region.

The Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao was an autonomous region of the Philippines, located in the Mindanao island group of the Philippines, that consisted of five predominantly Muslim provinces: Basilan, Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao, Sulu, and Tawi-Tawi. It was the only region that had its own government. The region's de facto seat of government was Cotabato City, although this self-governing city was outside its jurisdiction.

The kampilan also known as talong is a type of single-edged sword, traditionally used by various ethnic groups in the Philippine archipelago. It has a distinct profile, with the tapered blade being much broader and thinner at the point than at its base, sometimes with a protruding spikelet along the flat side of the tip. The design of the pommel varies between ethnic groups, but it usually depicts either a buaya (crocodile), a kalaw (hornbill), or a kakatua (cockatoo).

The Bisayan languages or the Visayan languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken in the Philippines. They are most closely related to Tagalog and the Bikol languages, all of which are part of the Central Philippine languages. Most Bisayan languages are spoken in the whole Visayas section of the country, but they are also spoken in the southern part of the Bicol Region, islands south of Luzon, such as those that make up Romblon, most of the areas of Mindanao and the province of Sulu located southwest of Mindanao. Some residents of Metro Manila also speak one of the Bisayan languages.

The Tausūg or Suluk, are an ethnic group of the Philippines and Malaysia, small population can also be found in the northern part of North Kalimantan, Indonesia. The Tausūg are part of the wider political identity of Muslims of Mindanao, Sulu and Palawan. Most of the Tausugs have converted into the religion of Islam whose members are now more known as the Moro group, who constitute the third largest ethnic group of Mindanao, Sulu and Palawan. The Tausugs originally had an independent state known as the Sultanate of Sulu, which once exercised sovereignty over the present day provinces of Basilan, Palawan, Sulu, Tawi-Tawi, Zamboanga City, North Kalimantan and the eastern part of the Malaysian state of Sabah.

The malong is a traditional Filipino rectangular or tube-like wraparound skirt bearing a variety of geometric or okir designs. The malong is traditionally used as a garment by both men and women of the numerous ethnic groups in the mainland Mindanao and parts of the Sulu Archipelago. They are wrapped around at waist or chest-height and secured by tucked ends, with belts of braided material or other pieces of cloth, or are knotted over one shoulder. They were traditionally hand-woven, with the patterns usually distinctive to a particular ethnic group. However, modern malong are usually machine-made or even imported, with patterns that mimic the traditional local designs.

The collective term Moro people or Bangsamoro people refers to the 13 Islamized ethnolinguistic groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan, native to the region known as the Bangsamoro. As Muslim-majority ethnic groups, they form the largest non-Christian population in the Philippines, and comprise about 5% of the country's total population, or 5 million people.

The Philippines is inhabited by more than 175 ethnolinguistic groups, the majority of whose languages fall under the Austronesian language family, along with some historical migrant groups throughout the country's history.

The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous people in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad, the autonym officially adopted by the delegates of the Lumad Mindanao Peoples Federation (LMPF) founding assembly on 26 June 1986 at the Guadalupe Formation Center, Balindog, Kidapawan, Cotabato, Philippines. Usage of the term was accepted in Philippine jurisprudence when President Corazon Aquino signed into law Republic Act 6734, where the word was used in Art. XIII sec. 8(2) to distinguish Lumad ethnic communities from the Bangsamoro.

The Cebuano people are the largest subgroup of the larger ethnolingustic group Bisaya, who constitute the largest Filipino ethnolinguistic group in the country. Their primary language is the Cebuano language, an Austronesian language. They originated in the province of Cebu in the region of Central Visayas, but then later spread out to other places in the Philippines, such as Siquijor, Bohol, Negros Oriental, southwestern Leyte, western Samar, Masbate, and large parts of Mindanao. It may also refer to the ethnic group who speak the same language as their native tongue in different parts of the archipelago. The term Cebuano also refers to the demonym of permanent residents in Cebu island regardless of ethnicity.

The gunong is a knife from Mindanao and the Visayas islands of the Philippines. In ancient past, it was called bunong by the Tagalog people. It is essentially a diminutive form of the larger kalis or kris. The gunong serves both as a utility knife and as a thrusting weapon used for close quarter fighting—usually as a last defense. It is most often associated with the Maranao, among whom the gunong was traditionally carried by both sexes, although it exists in other cultures throughout Mindanao and the Visayas. The weapon is generally tucked into the back of a waist sash.
Shariff Muhammed Kabungsuwan was the first Sultan of Maguindanao in the Philippines. A native of Johore in Maritime Southeast Asia, Kabungsuwan re-settled in Mindanao in the Philippines where he preached Islam to the native tribes around the region.
Ahmed Harris Ramuros Pangcoga, best known as Tommy Pangcoga, is a writer and non-government organization worker based in Mindanao, the Philippines.
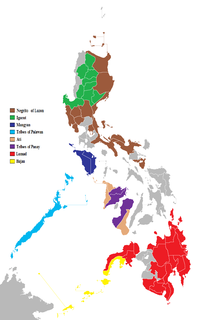
The Philippines consist of numerous upland and lowland indigenous ethnolinguistic groups living in the country, with Austronesians making up the overwhelming majority, while full or partial Negritos scattered throughout the archipelago. The highland Austronesians and Negrito have co-existed with their lowland Austronesian kin and neighbor groups for thousands of years in the Philippine archipelago. The primary difference is that they were not absorbed by centuries of Spanish and United States colonization of the Philippines, and in the process have retained their customs and traditions. This is mainly due to the rugged inaccessibility of the mountains and established headhunting and warrior cultures, which discouraged Spanish and American colonizers from coming into contact with the highlanders.

Malay is spoken by a minority of Filipinos, particularly in the Palawan, Sulu Archipelago and parts of Mindanao, mostly in the form of trade and creole languages, such as Sabah Malay.

Malays played a significant role in pre-Hispanic Philippine history. Malay involvement in Philippine history goes back to the Classical Era with the establishment of Rajahnates as well as the Islamic era, in which various sultanates and Islamic states were formed in Mindanao, the Sulu Archipelago, and around Manila.
Pangasi, also known as pangase or gasi, are various traditional Filipino rice wines from the Visayas Islands and Mindanao. They could also be made from other native cereals like millet and job's tears. Pangasi and other native Filipino alcoholic beverages made from cereal grains were collectively referred to by the Spanish as pitarrillos.















