Sir Joshua Reynolds was an English painter who specialised in portraits. John Russell said he was one of the major European painters of the 18th century. He promoted the "Grand Style" in painting, which depended on idealisation of the imperfect. He was a founder and first president of the Royal Academy of Arts and was knighted by George III in 1769.
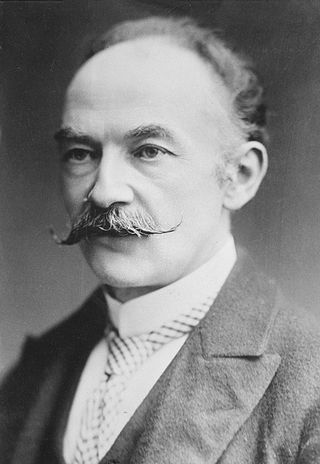
Thomas Hardy was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Wordsworth. He was highly critical of much in Victorian society, especially on the declining status of rural people in Britain, such as those from his native South West England.

Peter Scheemakers or Pieter Scheemaeckers II or the Younger was a Flemish sculptor who worked for most of his life in London. His public and church sculptures in a classicist style had an important influence on the development of modern sculpture in England.

Far from the Madding Crowd (1874) is Thomas Hardy's fourth published novel and his first major literary success. It was published on 23 November 1874. It originally appeared anonymously as a monthly serial in Cornhill Magazine, where it gained a wide readership.

Sir John Robert Steell was a Scottish sculptor. He modelled many of the leading figures of Scottish history and culture, and is best known for a number of sculptures displayed in Edinburgh, including the statue of Sir Walter Scott at the base of the Scott Monument.

Under the Greenwood Tree: A Rural Painting of the Dutch School is a novel by the English writer Thomas Hardy, published anonymously in 1872. It was Hardy's second published novel, and the first of what was to become his series of Wessex novels. Critics recognise it as an important precursor to his later tragic works, setting the scene for the Wessex that the author would return to again and again. Hardy himself called the story of the Mellstock Quire and its west-gallery musicians "a fairly true picture, at first hand, of the personages, ways, and customs which were common among such orchestral bodies in the villages of [the 1850s]".

The Woodlanders is a novel by Thomas Hardy. It was serialised from 15 May 1886 to 9 April 1887 in Macmillan's Magazine and published in three volumes in 1887. It is one of his series of Wessex novels.

Wessex Tales is an 1888 collection of tales written by English novelist and poet Thomas Hardy, many of which are set before Hardy's birth in 1840.

The Puritan, or the Widow of Watling Street, also known as The Puritan Widow, is an anonymous Jacobean stage comedy, first published in 1607. It is often attributed to Thomas Middleton, but also belongs to the Shakespeare Apocrypha due to its title page attribution to "W.S.".

Mulliner Nights is a collection of short stories by P. G. Wodehouse. First published in the United Kingdom on 17 January 1933 by Herbert Jenkins, and in the United States on 15 February 1933 by Doubleday, Doran. The stories in the collection were originally published in magazines in the UK and the US between 1930 and 1932.

Doctor Sally is a short novel by P. G. Wodehouse, first published in the United Kingdom on 7 April 1932 by Methuen & Co., London. In the United States, it was serialised in Collier's Weekly from 4 July to 1 August 1931 under the title The Medicine Girl, and was included under that name in the US collection The Crime Wave at Blandings (1937).

Tring Park Mansion or Mansion House, Tring Park, is a large country house in Tring, Hertfordshire. The house, as "Tring Park", was used, and from 1872 owned, by members of the Rothschild family from 1838 to 1945.

Ayakashi: Samurai Horror Tales, known in Japan as Ayakashi: Japanese Classic Horror, is a Japanese anime horror anthology television series produced by Toei Animation.

Francis Derwent Wood was a British sculptor.

The Nest of the Sparrowhawk:A Romance of the XVIIth Century was written by Baroness Orczy, author of The Scarlet Pimpernel, in 1909.

A Group of Noble Dames is an 1891 collection of short stories written by English author Thomas Hardy. The stories are contained by a frame narrative in which ten members of a club each tell one story about a noble dame in the 17th or 18th century. Hardy included this work with his "Romances and fantasies".

Love Laughs at Andy Hardy is a 1946 American comedy film directed by Willis Goldbeck and starring Mickey Rooney, Lewis Stone and Bonita Granville. It was produced by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer. The film is also known under its American promotional title Uncle Andy Hardy. This was the fifteenth, next-to-last Andy Hardy film produced. The final installment, Andy Hardy Comes Home, would be made 12 years later (1958) in a failed attempt to revive the franchise.
Sir James Butler of Polestown was a warlord in Yorkist Ireland.

George Rolle of Stevenstone in the parish of St Giles in the Wood near Great Torrington in Devon, was the founder of the wealthy, influential and widespread Rolle family of Devon, who by 1842 had become the largest landowners in Devon with about 55,000 acres according to the Return of Owners of Land, 1873 in the person of Hon. Mark Rolle, the adoptive heir of John Rolle, 1st Baron Rolle. He was a Dorset-born London lawyer who in 1507 became Keeper of the Records of the Court of Common Pleas and was elected as a Member of Parliament for Barnstaple in 1542 and 1545. He became the steward of Dunkeswell Abbey in Devon, and following the Dissolution of the Monasteries he purchased much ex-monastic land in Devon. Not only was he the founder of his own great Devonshire landowning dynasty but he was also an ancestor of others almost as great, including the Acland baronets of Killerton, the Wrey Baronets of Tawstock and the Trefusis family of Trefusis in Cornwall now of Heanton Satchville, Huish, later Baron Clinton, heirs both of Rolle of Heanton Satchville, Petrockstowe and of Rolle of Stevenstone.
"The Fiddler of the Reels" is a short story by British writer Thomas Hardy. It was first published in Scribner's Magazine, volume 13 issue 4, April 1893. It was included in Life's Little Ironies, a collection of Thomas Hardy's short stories first published in 1894.