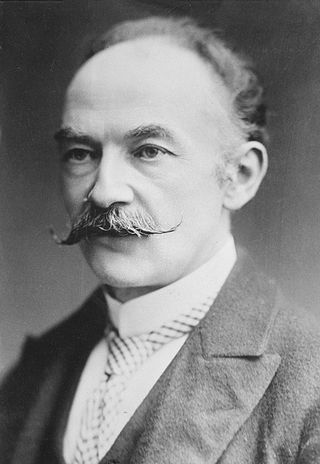
Thomas Hardy was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Wordsworth. He was highly critical of much in Victorian society, especially on the declining status of rural people in Britain such as those from his native South West England.

Tess of the d'Urbervilles: A Pure Woman is the twelfth published novel by English author Thomas Hardy. It initially appeared in a censored and serialised version, published by the British illustrated newspaper The Graphic in 1891, then in book form in three volumes in 1891, and as a single volume in 1892. Although now considered a major novel of the 19th century, Tess of the d'Urbervilles received mixed reviews when it first appeared, in part because it challenged the sexual morals of late Victorian England.

Jude the Obscure is the thirteenth published novel by English author Thomas Hardy, which began as a magazine serial in December 1894 and was first published in book form in 1895. It is Hardy's last completed novel. The protagonist, Jude Fawley, is a working-class young man; he is a stonemason who dreams of becoming a scholar. The other main character is his cousin, Sue Bridehead, who is also his central love interest. The novel is concerned in particular with issues of class, education, religion, morality and marriage.

The French Lieutenant's Woman is a 1969 postmodern historical fiction novel by John Fowles. The plot explores the fraught relationship of gentleman and amateur naturalist Charles Smithson and Sarah Woodruff, the former governess and independent woman with whom he falls in love. The novel builds on Fowles' authority in Victorian literature, both following and critiquing many of the conventions of period novels.

Far from the Madding Crowd is the fourth published novel by English author Thomas Hardy; and his first major literary success. It was published on 23 November 1874. It originally appeared anonymously as a monthly serial in Cornhill Magazine, where it gained a wide readership.

Claire Tomalin is an English journalist and biographer known for her biographies of Charles Dickens, Thomas Hardy, Samuel Pepys, Jane Austen and Mary Wollstonecraft.

The Mayor of Casterbridge: The Life and Death of a Man of Character is an 1886 novel by the English author Thomas Hardy. One of Hardy's Wessex novels, it is set in a fictional rural England with Casterbridge standing in for Dorchester in Dorset where the author spent his youth. It was first published as a weekly serialisation from January 1886.

Under the Greenwood Tree: A Rural Painting of the Dutch School is the second published novel by English author Thomas Hardy, published anonymously in 1872. It was Hardy's second published novel, and the first of what was to become his series of Wessex novels. Critics recognise it as an important precursor to his later tragic works, setting the scene for the Wessex that the author would return to again and again. Hardy himself called the story of the Mellstock Quire and its west-gallery musicians "a fairly true picture, at first hand, of the personages, ways, and customs which were common among such orchestral bodies in the villages of [the 1850s]".

Desperate Remedies is the first published novel by English author Thomas Hardy. It is considered a sensation novel because it contains themes of bigamy, murder, illegitimacy, blackmail, and impersonation. It was released anonymously by Tinsley Brothers in 1871.

The Woodlanders is the eleventh published novel by English author Thomas Hardy. The novel is set between 1856 and 1858. It was serialised from 15 May 1886 to 9 April 1887 in Macmillan's Magazine and published in three volumes in 1887. It is one of his series of Wessex novels.

Eliza Acton was an English food writer and poet who produced one of Britain's first cookery books aimed at the domestic reader, Modern Cookery for Private Families. The book introduced the now-universal practice of listing ingredients and giving suggested cooking times for each recipe. It included the first recipes in English for Brussels sprouts and for spaghetti. It also contains the first recipe for what Acton called "Christmas pudding"; the dish was normally called plum pudding, recipes for which had appeared previously, although Acton was the first to put the name and recipe together.

Tristan and Iseult, also known as Tristan and Isolde and other names, is a medieval chivalric romance told in numerous variations since the 12th century. Of disputed source, usually assumed to be primarily Celtic, the tale is a tragedy about the illicit love between the Cornish knight Tristan and the Irish princess Iseult in the days of King Arthur. It depicts Tristan's mission to escort Iseult from Ireland to marry his uncle, King Mark of Cornwall. On the journey, Tristan and Iseult ingest a love potion, instigating a forbidden love affair between them.

Thomas Hardy's Wessex is the fictional literary landscape created by the English author Thomas Hardy as the setting for his major novels, located in the south and southwest of England. Hardy named the area "Wessex" after the medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom that existed in this part of that country prior to the unification of England by Æthelstan. Although the places that appear in his novels actually exist, in many cases he gave the place a fictional name. For example, Hardy's home town of Dorchester is called Casterbridge in his books, notably in The Mayor of Casterbridge. In an 1895 preface to the 1874 novel Far from the Madding Crowd he described Wessex as "a merely realistic dream country".

"Maurice, or the Fisher's Cot" is a children's story by the Romantic writer Mary Shelley. Written in 1820 for Laurette Tighe, a daughter of her friends Margaret King and George William Tighe, Mary Shelley tried to have it published by her father, William Godwin, but he refused. The text was lost until 1997, when a manuscript copy was discovered in Italy.
"Neutral Tones" is a poem written by Thomas Hardy in 1867. Forming part of his 1898 collection Wessex Poems and Other Verses, it is the most widely praised of his early poems. It is about the end of a relationship, and carries strong emotional appeal despite its "neutral tones".

The Invisible Woman is a 2013 British biographical drama film directed by Ralph Fiennes and starring Fiennes, Felicity Jones, Kristin Scott Thomas and Tom Hollander. Written by Abi Morgan, and based on the 1990 book of the same name by Claire Tomalin, the film is about the secret love affair between Charles Dickens and Nelly Ternan, which lasted for thirteen years until his death in 1870. The film premiered at the Telluride Film Festival on 31 August 2013, and was released in the United Kingdom on 7 February 2014. The film received a Best Costume Design nomination at the 86th Academy Awards.

Wolf Solent is a novel by John Cowper Powys (1872–1963) that was written while he was based in Patchin Place, New York City, and travelling around the US as a lecturer. It was published by Simon and Schuster in May 1929 in New York. The British edition, published by Jonathan Cape, appeared in July 1929. This, Powys's fourth novel, was his first literary success. It is a bildungsroman in which the eponymous protagonist, a thirty-five-year-old history teacher, returns to his birthplace, where he discovers the inadequacy of his dualistic philosophy. Wolf resembles John Cowper Powys in that an elemental philosophy is at the centre of his life and, because, like Powys, he hates science and modern inventions like cars and planes, and is attracted to slender, androgynous women. Wolf Solent is the first of Powys's four Wessex novels. Powys both wrote about the same region as Thomas Hardy and was a twentieth-century successor to the great nineteenth-century novelist.
Gertrude Bugler was a British stage actress of the Edwardian Era best known for acting in plays adapted by Thomas Hardy.

Romance, is a "a fictitious narrative in prose or verse; the interest of which turns upon marvellous and uncommon incidents". This genre contrasted with the main tradition of the novel, which realistically depict life. These works frequently, but not exclusively, take the form of the historical novel. Walter Scott describes romance as a "kindred term", and many European languages do not distinguish between romance and novel: "a novel is le roman, der Roman, il romanzo".

The Famous Tragedy of the Queen of Cornwall, or, to give its full title, The Famous Tragedy of the Queen of Cornwall at Tintagel in Lyonnesse: A New Version of an Old Story, Arranged as a Play for Mummers in One Act, Requiring No Theatre or Scenery, is a verse tragedy by Thomas Hardy based on the medieval legend of Tristan and Iseult. His last substantial creative work, it was written, published and first performed in 1923, and revised in 1924. It is now seldom performed and has had a mixed reception from critics. In 1924 it was adapted as an opera by Rutland Boughton.