Related Research Articles

An orogeny is an event that leads to both structural deformation and compositional differentiation of the Earth's lithosphere at convergent plate margins. An orogen or orogenic belt develops when a continental plate crumples and is pushed upwards to form one or more mountain ranges; this involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis.

The Proterozoic is a geological eon spanning the time from the appearance of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life on the Earth. The name Proterozoic combines the two forms of ultimately Greek origin: protero- meaning "former, earlier", and -zoic, a suffix related to zoe "life". The Proterozoic Eon extended from 2500 mya to 541 mya, and is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon." The Proterozoic is the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale and it is subdivided into three geologic eras : the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic, and Neoproterozoic.

The Laramide orogeny was a period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 70 to 80 million years ago, and ended 35 to 55 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the orogeny are in dispute. The Laramide orogeny occurred in a series of pulses, with quiescent phases intervening. The major feature that was created by this orogeny was deep-seated, thick-skinned deformation, with evidence of this orogeny found from Canada to northern Mexico, with the easternmost extent of the mountain-building represented by the Black Hills of South Dakota. The phenomenon is named for the Laramie Mountains of eastern Wyoming. The Laramide orogeny is sometimes confused with the Sevier orogeny, which partially overlapped in time and space.
The Antler orogeny was a tectonic event that began in the early Late Devonian with widespread effects continuing into the Mississippian and early Pennsylvanian. Most of the evidence for this event is in Nevada but the limits of its reach are unknown. A great volume of conglomeratic deposits of mainly Mississippian age in Nevada and adjacent areas testifies to the existence of an important tectonic event, and implies nearby areas of uplift and erosion, but the nature and cause of that event are uncertain and in dispute. Although it is known as an orogeny, some of the classic features of orogeny as commonly defined such as metamorphism, and granitic intrusives have not been linked to it. In spite of this, the event is universally designated as an orogeny and that practice is continued here. This article outlines what is known and unknown about the Antler orogeny and describes three current theories regarding its nature and origin.

The Grenville orogeny was a long-lived Mesoproterozoic mountain-building event associated with the assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia. Its record is a prominent orogenic belt which spans a significant portion of the North American continent, from Labrador to Mexico, as well as to Scotland.

The Sevier orogeny was a mountain-building event that affected western North America from northern Canada to the north to Mexico to the south.

The geology of Australia includes virtually all known rock types and from all geological time periods spanning over 3.8 billion years of the Earth's history. Australia is a continent situated on the Indo-Australian Plate.
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Orogeny. The Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny are the largest known systems of orogenies on Earth. The sum of the continental crust formed in the Pan-African orogeny and the Grenville orogeny makes the Neoproterozoic the period of Earth's history that has produced most continental crust.

The Trans-Hudson orogeny or Trans-Hudsonian orogeny was the major mountain building event (orogeny) that formed the Precambrian Canadian Shield, the North American Craton, and the forging of the initial North American continent. It gave rise to the Trans-Hudson orogen (THO), or Trans-Hudson Orogen Transect (THOT), which is the largest Paleoproterozoic orogenic belt in the world. It consists of a network of belts that were formed by Proterozoic crustal accretion and the collision of pre-existing Archean continents. The event occurred 2.0-1.8 billion years ago.
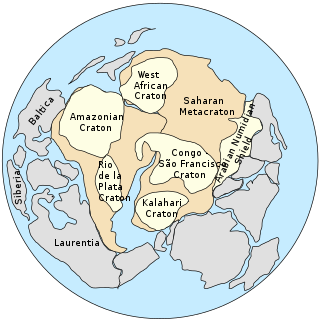
The Saharan Metacraton is a term used by some geologists to describe a large area of continental crust in the north-central part of Africa. Whereas a craton is an old and stable part of the lithosphere, the term "metacraton" is used to describe a craton that has been remobilized during an orogenic event, but where the characteristics of the original craton are still identifiable. The geology of the continent has only been partially explored, and other names have been used to describe the general area that reflect different views of its nature and extent. These include "Nile Craton", "Sahara Congo Craton", "Eastern Saharan Craton" and "Central Saharan Ghost Craton". This last term is because the older rocks are almost completely covered by recent sediments and desert sands, making geological analysis difficult.
The Kibaran orogeny is a term that has been used for a series of orogenic events in what is now Africa that began in the Mesoproterozoic around 1400 Ma and continued until around 1000 Ma when the supercontinent Rodinia was assembled. The term "Kibaran" has often been used for any orogenic rocks formed during this very extended period. Recently it has been proposed that the term should be used in a much narrower sense for an event around 1375 Ma and a region in the southeast of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC).

The main points that are discussed in the geology of Iran include the study of the geological and structural units or zones; stratigraphy; magmatism and igneous rocks; ophiolite series and ultramafic rocks; and orogenic events in Iran.
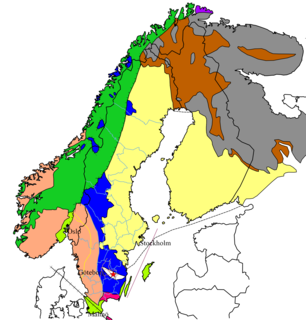
The Sveconorwegian orogeny was an orogenic system active 1140 to 960 million years ago and currently exposed as the Sveconorwegian orogenic belt in southwestern Sweden and southern Norway. In Norway the orogenic belt is exposed southeast of the front of the Caledonian nappe system and in nappe windows. The Sveconorwegian orogen is commonly grouped within the Grenvillian Mesoproterozoic orogens. Contrary to many other known orogenic belts the Sveconorwegian orogens eastern border does not have any known suture zone with ophiolites.

The Svecofennian orogeny is a series of related orogenies that resulted in the formation of much of the continental crust in what is today Sweden and Finland plus some minor parts of Russia. The orogenies lasted from about 2000 to 1800 million years ago during the Paleoproterozoic Era. The resulting orogen is known as the Svecofennian orogen or Svecofennides. To the west and southwest the Svecofennian orogen limits with the generally younger Transscandinavian Igneous Belt. It is assumed that the westernmost fringes of the Svecofennian orogen have been reworked by the Sveconorwegian orogeny just as the western parts of the Transscandinavian Igneous Belt has. The Svecofennian orogeny involved the accretion of numerous island arcs in such manner that the pre-existing craton grew with this new material from what is today northeast to the southwest. The accretion of the island arcs was also related to two other processes that occurred in the same period; the formation of magma that then cooled to form igneous rocks and the metamorphism of rocks.

The Aravalli Mountain Range is a northeast-southwest trending orogenic belt in the northwest part of India and is part of the Indian Shield that was formed from a series of cratonic collisions. The Aravalli Mountains consist of the Aravalli and Delhi fold belts, and are collectively known as the Aravalli-Delhi orogenic belt. The whole mountain range is about 700 km long. Unlike the much younger Himalayan section nearby, the Aravalli Mountains are much older that can be traced back to the Proterozoic Eon. The collision between the Bundelkhand craton and the Marwar craton is believed to be the primary mechanism for the development of the mountain range.
The Laxfordian orogeny was an orogeny mountain building event between 1.9 and 1 billion years ago. It primarily affected the North Atlantic Craton, in particular a section that cleaved off during the Mesozoic as the Scottish Shield Fragment.
The Hellenic orogeny was a mountain building event that affected what is now Greece, the Aegean Sea and western Turkey, beginning in the Jurassic as a series of small continents and remnant oceanic crust collided with Eurasia. The orogeny slowed or even stopped for a period of time and resumed during the early Cenozoic.
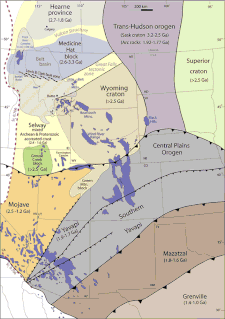
The Mazatzal orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1650 to 1600 Mya in the Statherian Period of the Paleoproterozoic. Preserved in the rocks of New Mexico and Arizona, it is interpreted as the collision of the 1700-1600 Mya age Mazatzal island arc terrane with the proto-North American continent. This was the second in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism.

The Yavapai orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1710 to 1680 Mya in the Statherian Period of the Paleoproterozoic. Preserved in the rocks of New Mexico and Arizona, it is interpreted as the collision of the 1800-1700 Mya age Yavapai island arc terrane with the proto-North American continent. This was the first in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism.
The Picuris orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1.43 to 1.3 billion years ago in the Calymmian Period of the Mesoproterozoic. The event is named for the Picuris Mountains in northern New Mexico and interpreted either as the suturing of the Granite-Rhyolite crustal province to the southern margin of the proto-North American continent Laurentia or as the final suturing of the Mazatzal crustal province onto Laurentia. According to the former hypothesis, this was the second in a series of orogenies within a long-lived convergent boundary along southern Laurentia that ended with the ca. 1200–1000 Mya Grenville orogeny during the final assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia, which ended an 800-million-year episode of convergent boundary tectonism.
References
- ↑ Goodwin, A. (1991). Precambrian Geology: The Dynamic Evolution of the Continental Crust. Academic Press. p. 357.
- ↑ Miller, J. and co-authors (2009). Continental Reactivation and Reworking. Geological Society of America. p. 221.
| This orogeny article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |