| Saka kurgans [1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Barrows (or Tumuli) of Tasmola are dispersed throughout central Kazakhstan in the Karaganda, Akmola, and Pavlodar regions.
| Saka kurgans [1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The Barrows (or Tumuli) of Tasmola are dispersed throughout central Kazakhstan in the Karaganda, Akmola, and Pavlodar regions.
Originating in the Saka period (7th to 3rd Centuries BC), the various barrows of the Tasmola culture can be found throughout the valleys of central Kazakhstan. The sites are characterized by stone complexes with up to four stone barrows, menhirs (single or in groups), and two curved ranges that can each stretch 50 to 200 m long (unique to Tasmola structures). [2] The ranges appear to line up in accordance to equinoctial, solstitial or midsummer sunrise points. Archaeological finds in the barrows themselves can include pottery, horse skeletons, and fire pit remains. Over 300 of such barrows have been identified in Kazakhstan, of which only a small number have been archaeologically excavated. [2]
The last characteristic Tasmola kurgans seem to date to the 5th–4th century BCE. [3]
This site was added to the UNESCO World Heritage Tentative List on September 24, 1998 in the Mixed (Cultural + Natural) category. [2] (see List of World Heritage Sites in Kazakhstan)
Archaeologically, the most representative Tasmola kurgans containing characteristic pieces of horse harnesses, weaponry, and ornaments disappear by the 5th–4th century BC, apparently without an external influence. Obtained 14C dates also suggest the end date of the culture as 5th century BC, thus confirming the archaeological observations and making the end date of the culture ~2 centuries older compared to the traditional end date (3rd century BC).
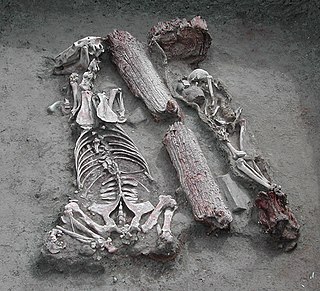
The Pazyrykburials are a number of Scythian (Saka) Iron Age tombs found in the Pazyryk Valley and the Ukok plateau in the Altai Mountains, Siberia, south of the modern city of Novosibirsk, Russia; the site is close to the borders with China, Kazakhstan and Mongolia.

The Sarmatians were a large confederation of ancient Iranian equestrian nomadic peoples who dominated the Pontic steppe from about the 3rd century BC to the 4th century AD.

The Saka were a group of nomadic Eastern Iranian peoples who historically inhabited the northern and eastern Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin.

A kurgan is a type of tumulus constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons, and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central Asia and Eastern, Southeast, Western, and Northern Europe during the third millennium BC.

A tumulus is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or kurgans, and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built for various purposes, may also originally have been a tumulus.
The Pazyryk culture is a Saka nomadic Iron Age archaeological culture identified by excavated artifacts and mummified humans found in the Siberian permafrost, in the Altay Mountains, Kazakhstan and Mongolia. The mummies are buried in long barrows similar to the tomb mounds of Scythian culture in Ukraine. The type site are the Pazyryk burials of the Ukok Plateau. Many artifacts and human remains have been found at this location, including the Siberian Ice Princess, indicating a flourishing culture at this location that benefited from the many trade routes and caravans of merchants passing through the area. The Pazyryk are considered to have had a war-like life. The Pazyryk culture was preceded by the "Arzhan culture".

Scytho-Siberian art is the art associated with the cultures of the Scytho-Siberian world, primarily consisting of decorative objects such as jewellery, produced by the nomadic tribes of the Eurasian Steppe, with the western edges of the region vaguely defined by ancient Greeks. The identities of the nomadic peoples of the steppes is often uncertain, and the term "Scythian" should often be taken loosely; the art of nomads much further east than the core Scythian territory exhibits close similarities as well as differences, and terms such as the "Scytho-Siberian world" are often used. Other Eurasian nomad peoples recognised by ancient writers, notably Herodotus, include the Massagetae, Sarmatians, and Saka, the last a name from Persian sources, while ancient Chinese sources speak of the Xiongnu or Hsiung-nu. Modern archaeologists recognise, among others, the Pazyryk, Tagar, and Aldy-Bel cultures, with the furthest east of all, the later Ordos culture a little west of Beijing. The art of these peoples is collectively known as steppes art.

The Ordos culture was a material culture occupying a region centered on the Ordos Loop during the Bronze and early Iron Age from c. 800 BCE to 150 BCE. The Ordos culture is known for significant finds of Scythian art and may represent the easternmost extension of Indo-European Eurasian nomads, such as the Saka, or may be linkable to Palaeo-Siberians or Yeniseians. Under the Qin and Han dynasties, the area came under the control of contemporaneous Chinese states.

The Issyk kurgan, in south-eastern Kazakhstan, less than 20 km east from the Talgar alluvial fan, near Issyk, is a burial mound discovered in 1969. It has a height of 6 meters (20 ft) and a circumference of 60 meters (200 ft). It is dated to the 4th or 3rd century BC. A notable item is a silver cup bearing an inscription. The finds are on display in Astana. It is associated with the Saka peoples.
Arzhan is a site of early Saka kurgan burials in the Tuva Republic, Russia, some 60 kilometers (40 mi) northwest of Kyzyl. It is on a high plateau traversed by the Uyuk River, a minor tributary of the Yenisei River, in the region of Tuva, 20 km to the southwest of the city of Turan.
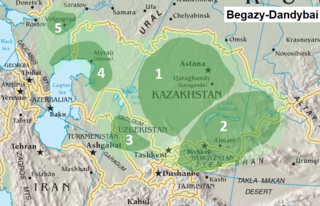
Begazy-Dandybai culture, is a late Bronze Age culture of mixed economy in the territory of ancient central Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, and Uzbekistan, centered at Saryarka region. The Begazy Dandybai Mausolea dates from c. 1350–1150 BCE, and was previously dated between the 12th and 8th centuries BCE, or from 13th to 10th centuries BCE. The culture was discovered, first excavated, and published in the 1930s–1940s by M.P. Gryaznov, who took it for a local version of the Karasuk culture. In 1979 the Begazy-Dandybai culture was described and analyzed in detail in a monograph by A.Kh. Margulan, who systematically reviewed accumulated material and produced description of the archeological culture. The most famous monuments of Begazy-Dandybai culture are Begazy, Dandybai, Aksu Ayuly 2, Akkoytas, and Sangria 1.3, it was named after the first two archeological sites.
The Tasmola culture was an early Iron Age culture during the Saka period in central Kazakhstan. The Tasmola culture was replaced by the Korgantas culture. They may correspond to the Issedones of ancient Greek sources.

Berel kurgan is an archaeological site in the Katonkaragay District in eastern Kazakhstan. The site is located near the village of Berel. At this site, numerous 5th-3rd century BCE Early Saka kurgans were found.
The Sauromatian culture was an Iron Age culture of horse nomads in the area of the lower Volga River to the southern Ural Mountain, in southern Russia, dated to the 6th to 4th centuries BCE. Archaeologically, the Sauromatian period itself is sometimes also called the "Blumenfeld period", and is followed by a transitional Late Sauromatian-Early Sarmatian period, also called the "Prokhorov period".

Shilikty, formerly Chilikti, also more precisely Baigetobe Kurgans in Shilikty Valley, is an archaeological site in eastern Kazakhstan, located in the Chilik river basin. At this site, numerous 8th-6th century BCE Early Saka kurgans were found. Carbon-14 dating suggests a more refined date of 730-690 BCE for the kurgans, and a broad contemporaneity with the Arzhan-2 kurgan in Tuva.

Eleke Sazy is an archaeological site in eastern Kazakhstan with numerous 6th-4th century BCE Early Saka kurgans. In 2020, archaeologists excavated multiple burial mounds in the Eleke Sazy Valley in East Kazakhstan. Here, a large number of gold artifacts were found. These artifacts included golf harness fittings, pendants, chains, appliqués, and more – most of which are in the Animal Style of the Scythian-Saka era dating back to the 5th–4th centuries BCE.

The Taksai kurgans are a series of Saka or Sauromatian funeral mounds or kurgans, located in the Terekti District of the southern Urals, in northwestern Kazakhstan. They are dated to circa 500 BCE. The Kurgan was undisturbed and had provided numerous valuable artifacts. The Taksai-1 kurgan was the tomb of a rich Saka lady, dubbed the "golden lady". Some of her objects reflect the iconography of the Achaemenid Empire, which must have been in contact with these nomadic tribes.
The Subeshi culture, also rendered as Subeishi culture or Subeixi culture, is an Iron Age culture from the area of Shanshan County, Turfan, Xinjiang, at the eastern edge of the Tarim Basin. The Subeshi culture contributes some of the later period Tarim Mummies. It might be associated with the Jushi Kingdom known from Chinese historical sources. The culture includes three closely related cemeteries:
The Korgantas culture replaced the Tasmola culture in Central Kazakhstan. It is used sometimes termed as the "Korgantas period" of the Tasmola culture.

The Filippovka kurgans are Late-Sauromatian to Early-Sarmatian culture kurgans, forming "a transition site between the Sauromation and the Sarmatian epochs", just north of the Caspian Sea in the Orenburg region of Russia, dated to the second half of the 5th century and the 4th century BCE.