Related Research Articles

The Mary Rose is a carrack-type warship of the English Tudor navy of King Henry VIII. She served for 33 years in several wars against France, Scotland, and Brittany. After being substantially rebuilt in 1536, she saw her last action on 19 July 1545. She led the attack on the galleys of a French invasion fleet, but sank in the Solent, the straits north of the Isle of Wight.

Galleons were large, multi-decked sailing ships first used as armed cargo carriers by European states from the 16th to 18th centuries during the age of sail and were the principal vessels drafted for use as warships until the Anglo-Dutch Wars of the mid-1600s. Galleons generally carried three or more masts with a lateen fore-and-aft rig on the rear masts, were carvel built with a prominent squared off raised stern, and used square-rigged sail plans on their fore-mast and main-masts.

A shipwreck is the remains of a ship that has wrecked, which are found either beached on land or sunken to the bottom of a body of water. Shipwrecking may be deliberate or accidental. In January 1999, Angela Croome estimated that there have been about three million shipwrecks worldwide.
HMS Colossus was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy. She was launched at Gravesend on 4 April 1787 and lost on 10 December 1798. During her years of service she participated in the Battle of Groix, the Battle of Cape St Vincent, and the Battle of the Nile. While carrying wounded from the latter, she was wrecked at the Isles of Scilly. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.

Nuestra Señora de Atocha was a Spanish treasure galleon and the most widely known vessel of a fleet of ships that sank in a hurricane off the Florida Keys in 1622. At the time of her sinking, Nuestra Señora de Atocha was heavily laden with copper, silver, gold, tobacco, gems, and indigo from Spanish ports at Cartagena and Porto Bello in New Granada and Havana, bound for Spain. The Nuestra Señora de Atocha was named for a holy shrine in Madrid, Spain. It was a heavily armed Spanish galleon that served as the almirante for the Spanish fleet. It would trail behind the other ships in the flota to prevent an attack from the rear.

The Uluburun Shipwreck is a Late Bronze Age shipwreck dated to the late 14th century BC, discovered close to the east shore of Uluburun, and about 6 miles (10 km) miles southeast of Kaş, in south-western Turkey. The shipwreck was discovered in the summer of 1982 by Mehmed Çakir, a local sponge diver from Yalıkavak, a village near Bodrum.
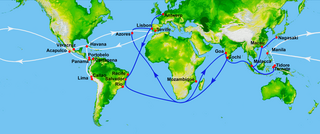
The Spanish treasure fleet, or West Indies Fleet Spanish: Flota de Indias, was a convoy system of sea routes organized by the Spanish Empire from 1566 to 1790, which linked Spain with its territories in the Americas across the Atlantic. The convoys were general purpose cargo fleets used for transporting a wide variety of items, including agricultural goods, lumber, various metal resources such as silver and gold, gems, pearls, spices, sugar, tobacco, silk, and other exotic goods from the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire to the Spanish mainland. Spanish goods such as oil, wine, textiles, books and tools were transported in the opposite direction.

Marine salvage is the process of recovering a ship and its cargo after a shipwreck or other maritime casualty. Salvage may encompass towing, re-floating a vessel, or effecting repairs to a ship. Today, protecting the coastal environment from spillage of oil or other contaminants is a high priority. Before the invention of radio, salvage services would be given to a stricken vessel by any ship that happened to be passing by. Nowadays, most salvage is carried out by specialist salvage firms with dedicated crew and equipment.
The Spanish Armada in Ireland refers to the landfall made upon the coast of Ireland in September 1588 of a large portion of the 130-strong fleet sent by Philip II to invade England.
St Anthony or Santo António was a Portuguese carrack that foundered in Gunwalloe Bay, Cornwall, in 1527 en route from Lisbon to Antwerp. She had a mixed cargo including copper and silver ingots. The wreck was recorded historically, because the salvage of the cargo was the subject of an international dispute that led to a Court of Star Chamber, but the location of the wreck was unknown until 1981. The wreck is designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act.The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.
The San Juan de Sicilia was one of the 130 ships that formed the ill-fated Spanish Armada of 1588. The ship was originally known as the Brod Martolosi, before it was seized to form part of the navy. It was one of 10 ships forming the Levant squadron, one of 8 squadrons that formed the entire armada.

San Esteban was a Spanish cargo ship that was wrecked in a storm in the Gulf of Mexico on what is now the Padre Island National Seashore in southern Texas on 29 April 1554.
The Streedagh Armada wrecksite is the site of three shipwrecks of the Spanish Armada at Streedagh beach in north County Sligo, in northwest Ireland. The three ships are La Lavia, La Juliana, and the Santa Maria de Visón. All were part of the Levant squadron of the armada. The Lavia was the almiranta, or vice flagship of the fleet and carried the Judge Advocate General, Martin de Aranda, responsible for the discipline of the armada.
The Cirebon shipwreck is a late 9th to 10th-century shipwreck discovered in 2003, in the Java Sea offshore of Cirebon, West Java, Indonesia. The shipwreck contains a large amount of Chinese Yue ware, and is notable as important marine archaeology evidence of the Maritime Silk Road trading activity in Maritime Southeast Asia.
The remains of a late sixteenth or early seventeenth century carrack was discovered in Yarmouth Roads, Isle of Wight, England in 1984. The site was designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act on 9 April 1984. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by Historic England.
The Tearing Ledge Wreck consists of the remains of a ship, possibly one of the ships belonging to Admiral Cloudisley Shovell's fleet of 21 vessels returning from the Siege of Toulon via Gibraltar, that were found in 1969 on Tearing Ledge, Western Rocks, Isles of Scilly. The site was designated under the Protection of Wrecks Act on 12 February 1975. The wreck is a Protected Wreck managed by the National Heritage List for England.

The Rill Cove Wreck is an underwater wreck of a 16th-century Spanish cargo ship lying off the coast of Rill Cove, west of Kynance Cove, in Cornwall, England, UK.
References
- 1 2 "BARTHOLOMEW LEDGES - 1000066 | Historic England". historicengland.org.uk. Retrieved 2020-10-12.