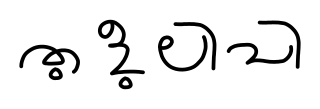A manuscript was, traditionally, any document written by hand or typewritten, as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has come to be understood to further include any written, typed, or word-processed copy of an author's work, as distinguished from the rendition as a printed version of the same.
The Odia script is a Brahmic script used to write primarily Odia language and others including Sanskrit and other regional languages. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. The script has developed over more than 1000 years from a variant of Siddhaṃ script which was used in Eastern India, where the characteristic top line transformed into a distinct round umbrella shape due to the influence of palm leaf manuscripts and also being influenced by the neighbouring scripts from the Western and Southern regions.

Jayadeva, also spelt Jaideva, was a Sanskrit poet during the 12th century. He is most known for his epic poem Gita Govinda which concentrates on Krishna's love with the gopi, Radha, in a rite of spring. This poem, which presents the view that Radha is greater than Krishna, is considered an important text in the Bhakti movement of Hinduism.

Sri Lankan cuisine is known for its particular combinations of herbs, spices, fish, vegetables, rices, and fruits. The cuisine is highly centered around many varieties of rice, as well as coconut which is a ubiquitous plant throughout the country. Seafood also plays a significant role in the cuisine, be it fresh fish or preserved fish. As a country that was a hub in the historic oceanic silk road, contact with foreign traders brought new food items and cultural influences in addition to the local traditions of the country's ethnic groups, all of which have helped shape Sri Lankan cuisine. Influences from Indian, Indonesian and Dutch cuisines are most evident with Sri Lankan cuisine sharing close ties to other neighbouring South and Southeast Asian cuisines.
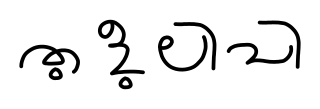
Tigalari, also known as Tulu script, is a Southern Brahmic script which was used to write Tulu, Kannada, and Sanskrit languages. It was primarily used for writing Vedic texts in Sanskrit. It evolved from the Grantha script. It is called as Tigalari lipi in Kannada-speaking regions and Tulu speakers call it as Tulu lipi. It bears high similarity and relationship to its sister script Malayalam, which also evolved from the Grantha script.
Craig Jamieson is Keeper of Sanskrit Manuscripts at the University of Cambridge.

The Skanda Purana is the largest Mukhyapurana, a genre of eighteen Hindu religious texts. The text contains over 81,000 verses, and is of Shaivite literature, titled after Skanda, a son of Shiva and Parvati. While the text is named after Skanda, he does not feature either more or less prominently in this text than in other Shiva-related Puranas. The text has been an important historical record and influence on the Hindu traditions and rituals related to the war-god Skanda.
Sri Lankan Mukkuvar is a Tamil speaking ethnic group found in the Western and Eastern coastal regions of Sri Lanka. They are primarily concentrated in the districts of Puttalam, Batticaloa, and Amparai.

Palm-leaf manuscripts are manuscripts made out of dried palm leaves. Palm leaves were used as writing materials in the Indian subcontinent and in Southeast Asia dating back to the 5th century BCE. Their use began in South Asia and spread to other regions, as texts on dried and smoke-treated palm leaves of the Palmyra or talipot palm. Their use continued until the 19th century when printing presses replaced hand-written manuscripts.

The Tocharian script, also known as Central Asian slanting Gupta script or North Turkestan Brāhmī, is an abugida which uses a system of diacritical marks to associate vowels with consonant symbols. Part of the Brahmic scripts, it is a version of the Indian Brahmi script. It is used to write the Central Asian Indo-European Tocharian languages, mostly from the 8th century that were written on palm leaves, wooden tablets and Chinese paper, preserved by the extremely dry climate of the Tarim Basin. Samples of the language have been discovered at sites in Kucha and Karasahr, including many mural inscriptions. Mistakenly identifying the speakers of this language with the Tokharoi people of Tokharistan, early authors called these languages "Tocharian". This naming has remained, although the names Agnean and Kuchean have been proposed as a replacement.

The British Library is a research library in London that is the national library of the United Kingdom. It is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the British Library receives copies of all books produced in the United Kingdom and Ireland, including a significant proportion of overseas titles distributed in the UK. The Library is a non-departmental public body sponsored by the Department for Culture, Media and Sport.
Charles Matthew Whish (1794–1833) was an English civil servant in the Madras Establishment of the East India Company. Whish was the first to bring to the notice of the western mathematical scholarship the achievements of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics. Whish wrote in his historical paper: Kerala mathematicians had ... laid the foundation for a complete system of fluxions ... and their works ... abound with fluxional forms and series to be found in no work of foreign countries. Whish was also a linguist and had prepared a grammar and a dictionary of the Malayalam language.

Old Sundanese script is a script that developed in West Java in the 14th–18th centuries which was originally used to write Old Sundanese language. The Old Sundanese script is a development of the Pallava script which has reached the stage of modifying its distinctive form as used in lontar texts in the 16th century.

The Batticaloa Fort was built by the Portuguese in 1628 and was captured by the Dutch on 18 May 1638. From 1795, the fort was used by the British.

Mattakkalappu Maanmiyam is a Tamil language historical book concerning the history of Batticaloa. It was compiled by F. X. Nadarajah from the collections of palm-leaf manuscripts, copper plate inscriptions and inscriptions and it was published in August 1962. The authors of the original manuscripts and other forms of documentation are unknown.

Eberhard Fischer is a German art historian, ethnologist and author based in Switzerland. He is a former Director and the incumbent President of Rietberg Society, Switzerland. Fischer was honored by the Government of India, in 2012, with the fourth highest Indian civilian award of Padma Shri.

Church of Our Lady of Presentation is a church of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Batticaloa in Thandavanveli. The church is one of a landmarks and catholic historical places in the district of Batticaloa, Sri Lanka. According to the recorded documents, it is known as the first and oldest church in the district.
Ola leaf is a palm leaf used for writing in traditional palm-leaf manuscripts and in fortunetelling (horoscopes) in Southern India and Sri Lanka. The leaves are from the talipot tree, a type of palm, and fortunes are written on them and read by fortune tellers. It is believed that three thousand years ago the seven rishis, sages, wrote everyone's fortunes on the leaves. The National Library of Sri Lanka holds an ola-leaf manuscript collection.
The Government Museum, Erode is an archaeological museum located in the city of Erode, Tamil Nadu. It is located inside the VOC Park campus, 200 meters to the north of Erode Central Bus Terminus and 3 km from Erode Junction.
The National Archives of Myanmar, officially known as the Department of National Archives (NAD), is an agency of the Burmese government charged with collecting, safeguarding, and conserving national records and archives. The National Archives are housed in Naypyidaw's Ottarathiri Township and in Yangon's Dagon Township. The National Archives provides reference services and access to local and foreign researchers.