
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a general and statesman of the Roman Republic. He played a significant role in the transformation of Rome from republic to empire. Early in his career, he was a partisan and protégé of the Roman general and dictator Sulla; later, he became the political ally, and finally the enemy, of Julius Caesar.
80s BC is the time period from 89 BC – 80 BC.

Gaius Marius was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times.

Jugurtha or Jugurthen was a king of Numidia. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Jugurtha and his two adoptive brothers, Hiempsal and Adherbal, succeeded him. Jugurtha arranged to have Hiempsal killed and, after a civil war, defeated and killed Adherbal in 112 BC.

Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix, commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
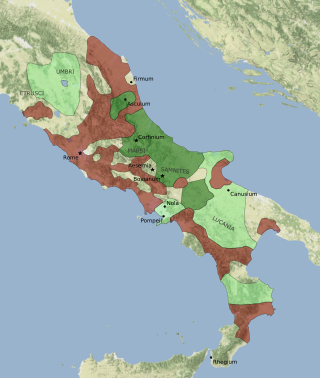
The Social War, also called the Italian War or the Marsic War, was fought largely from 91 to 88 BC between the Roman Republic and several of its autonomous allies in Italy. Some of the allies held out until 87 BC.

The Battle of Thapsus was a military engagement that took place on April 6, 46 BC near Thapsus. The forces of the Optimates, led by Quintus Caecilius Metellus Scipio, were defeated by the forces of Julius Caesar. It was followed shortly by the suicides of Scipio and his ally, Cato the Younger, the Numidian king Juba, and his Roman peer Marcus Petreius.

The Jugurthine War was an armed conflict between the Roman Republic and King Jugurtha of Numidia, a kingdom on the north African coast approximating to modern Algeria. Jugurtha was the nephew and adopted son of Micipsa, king of Numidia, whom he succeeded on the throne, he had done so by overcoming his rivals through assassination, war, and bribery.

The Battle of Vercellae, or Battle of the Raudine Plain, was fought on 30 July 101 BC on a plain near Vercellae in Gallia Cisalpina. A Germanic-Celtic confederation under the command of the Cimbric king Boiorix was defeated by a Roman army under the joint command of the consul Gaius Marius and the proconsul Quintus Lutatius Catulus. The battle marked the end of the Germanic threat to the Roman Republic.
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius was a general and statesman of the Roman Republic. His father Metellus Numidicus was banished from Rome through the machinations of Gaius Marius. He, because of his constant and unbending attempts to have his father officially recalled from exile, was given the agnomen (nickname) Pius.
The Battle of the Muthul was fought at the Muthul River in Numidia in 109 BC. The Numidians, led by their king Jugurtha, fought a Roman army commanded by the consul Quintus Caecilius Metellus Numidicus. The battle was fought during the Jugurthine War, a war between King Jugurtha of Numidia and the Roman Republic. The battle was indecisive - it took the Romans four more years to defeat Jugurtha. Jugurtha was eventually captured by Lucius Cornelius Sulla in 105 and executed during Marius' Triumphal parade a year later (104). The Roman historian Publius Rutilius Rufus distinguished himself during the battle, while Gaius Marius' military genius shone through for the first time, saving the day for the Romans.
Lucius Julius Caesar was a Roman statesman and general of the late 2nd and early 1st centuries BC. He was involved in the downfall of the plebeian tribune Lucius Appuleius Saturninus in 100 BC. He was consul of the Roman Republic in 90 BC during the Social War. During the war he commanded several Roman legions against the Italian Allies. He was awarded a Triumph for his victories on the Samnites at Acerrae.
Rome's military was always tightly keyed to its political system. In the Roman Kingdom the social standing of a person impacted both his political and military roles, which were often organised into familial clans such as the Julia. These clans often wielded a large amount of power and were huge influences through the Roman Kingdom into the Roman Republic. The political system was from an early date based upon competition within the ruling elite, the patricians. Senators in the Republic competed fiercely for public office, the most coveted of which was the post of consul. Two consuls were elected each year to head the government of the state, and would be assigned a consular army and an area in which to campaign. From Gaius Marius and Sulla onwards, control of the army began to be tied into the political ambitions of individuals, leading to the First Triumvirate of the 1st century BC and the resulting Caesar's civil war. The late Republic and Empire was increasingly plagued by usurpations led by or supported by the military, leading to the Crisis of the third century in the late empire.
Sulla's civil war was fought between the Roman general Lucius Cornelius Sulla and his opponents, the Cinna-Marius faction, in the years 83–82 BC. The war ended with a decisive battle just outside Rome itself. After the war the victorious Sulla made himself dictator of the Roman Republic.

Gaius Papius Mutilus was a Samnite noble who is best known for being the leader of the southern rebels who fought against the army of Rome in the Social War of 91-87 BC ; was member of the clan Variani/Varriano. His father was Gaius Papius Mutilus, who held the highest Samnite magistracy in Bovianum a number of times in the second half of the 2nd century BC
Publius Sittius was a Roman equites and mercenary commander. As a mercenary he was employed by king Bocchus II of East-Mauretania. Sittius fought for Bocchus against king Juba I of Numidia, capturing Juba's capital of Cirta and defeating the Numidian army under general Saburra. He also supported Julius Caesar in the civil war between Caesar and the Optimates, ultimately catching and killing Faustus Cornelius Sulla and Lucius Afranius and destroying Scipio's fleet off Hippo Regius. He was a personal friend of Marcus Tullius Cicero.
The Second Battle of Cirta, part of the Jugurthine War, was fought in 106 BC between a Numidian-Mauretanian coalition and a Roman army near the Numidian capital of Cirta. The Numidians were led by King Jugurtha, the Mauritanians were led by king Bocchus while the Romans were under the overall command of Gaius Marius who was supported by his quaestor Lucius Cornelius Sulla as cavalry commander. The Romans were victorious routing their opponents and capturing Cirta.
The Battle of Firmum was fought between a Roman force under Gnaeus Pompey Strabo and a rebel force led by Lafrenius. It took place during the Social War and was a Roman victory.
The Battle of Aesernia took place in the year 90 BC during the Social War. A force under the consul Lucius Julius Caesar, an uncle of the more famous Julius Caesar, was engaged while moving to relieve the siege of Aesernia and defeated by a rebel force under Titus Vettius Scato. Orosius wrote that Caesar had to entirely rebuild his army with Gallic and African troops after the battle while Appian admits only 2,000 Roman dead. As a result of their victory the rebels had enough spare forces to reinforce the army besieging Aesernia while another army took Venafrum. It is also possible Venafrum joined the rebels.
The Battle of Taenum was fought in 90 BC during the Social War. In the battle, Roman forces under the command of Lucius Julius Caesar were defeated by Italian rebel forces commanded by Marius Egnatius.









