
The 14th century lasted from 1 January 1301 to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity.
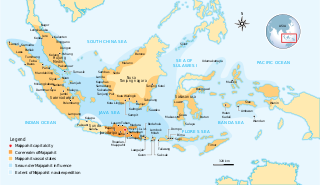
Majapahit, also known as Wilwatikta, was a Javanese Hindu-Buddhist thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was based on the island of Java. It existed from 1292 to c. 1527 and reached its peak during the era of the queen Tribhuvana and her son Hayam Wuruk, whose reigns in the mid-14th century were marked by conquests that extended throughout Southeast Asia. This achievement is also credited to the famous prime minister Gajah Mada. According to the Deśavarṇana written in 1365, Majapahit was an empire of 98 tributaries, stretching from Sumatra to New Guinea; including territories in present-day Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, Brunei, southern Thailand, Timor Leste, southwestern Philippines although the scope of Majapahit sphere of influence is still the subject of debate among historians. The nature of Majapahit's relations and influence upon its overseas vassals and also its status as an empire still provokes discussion.

Gajah Mada, also known as Jirnnodhara, was a powerful military leader and mahapatih of the Javanese empire of Majapahit during the 14th century. He is credited in Old Javanese manuscripts, poems, and inscriptions with bringing the empire to its peak of glory.
Hayam Vuruk (1334–1389), also called Rajasanagara, Pa-ta-na-pa-na-wu, or Bhatara Prabhu after 1350, was a Javanese Hindu emperor from the Rajasa dynasty and the 4th emperor of the Majapahit Empire. Together with his prime minister Gajah Mada, he reigned the empire at the time of its greatest power. During his reign, the Hindu epics, the Ramayana and the Mahabharata, became ingrained in the culture and worldview of the Javanese through the wayang kulit. He was preceded by Tribhuwana Wijayatunggadewi, and succeeded by his son-in-law Wikramawardhana.

The Sundanese are an indigenous ethnic group native to the western region of Java island in Indonesia, primarily West Java. They number approximately 42 million and form Indonesia's second most populous ethnic group. They speak the Sundanese language, which is part of the Austronesian languages.

Kidung Sunda is a Middle-Javanese kidung of probable Balinese provenance. In this poem, the story of King Hayam Wuruk of Majapahit who was looking for a bride-to-be, is narrated. At last, he chose the princess of Sunda, a kingdom in West Java. The princess' name has remained undisclosed in this story, however, she corresponds to Dyah Pitaloka Citraresmi in Pararaton. Hayam Wuruk's grand vizier Gajah Mada, betrayed his king and rejected this idea. There was a dispute about geopolitical relations between Sunda and Majapahit. Gajah Mada considered Sunda to be a vassal state of Java. For that reason, a great battle took place in Bubat, the port where the Sundanese party landed as they refused to be treated as vassals. There the Majapahit-Javanese army slaughtered the Sundanese. The grieved princess of Sunda committed suicide not long afterward. This historical story has to be situated somewhere in the 14th century.

Raden Wijaya or Raden Vijaya, also known as Nararya Sangramawijaya and his regnal name Kertarajasa Jayawardhana was a Javanese emperor and founder of the Majapahit Empire who ruled from 1293 until his death in 1309. The history of his founding of Majapahit was written in several records, including Pararaton and Negarakertagama. His rule was marked by the victory against the army and the Mongol navy of Kublai Khan's Yuan dynasty.
Sunan Kudus, founder of Kudus, is one of the Wali Sanga, of Java, Indonesia to whom the propagation of Islam amongst the Javanese is attributed.

The history of the arrival of Islam in Indonesia is somewhat unclear. One theory states that Islam arrived directly from Arabia as early as the 9th century, during the time of the Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates. Another theory credits Sufi travelers for bringing Islam in the 12th or 13th century, either from Gujarat in India or from Persia. Before the archipelago's conversion to Islam, the predominant religions in Indonesia were Hinduism and Buddhism.
Ciung Wanara is a legend among Sundanese people, in Indonesia. Ciung Wanara was a nickname of Prince Manarah of Sunda–Galuh Kingdom. He was a relative of the famous King Sanjaya of Mataram.

The Sunda Kingdom was a Sundanese Hindu kingdom located in the western portion of the island of Java from 669 to around 1579, covering the area of present-day Banten, Jakarta, West Java, and the western part of Central Java. The capital of the Sunda Kingdom moved several times during its history, shifting between the Galuh (Kawali) area in the east and Pakuan Pajajaran in the west.

The Yuan dynasty under Kublai Khan attempted in 1293 to invade Java, an island in modern Indonesia, with 20,000 to 30,000 soldiers. This was intended as a punitive expedition against Kertanegara of Singhasari, who had refused to pay tribute to the Yuan and maimed one of their emissaries. However, in the intervening years between Kertanegara's refusal and the expedition's arrival on Java, Kertanegara had been killed and Singhasari had been usurped by Kediri. Thus, the Yuan expeditionary force was directed to obtain the submission of its successor state, Kediri, instead. After a fierce campaign, Kediri surrendered, but the Yuan forces were betrayed by their erstwhile ally, Majapahit, under Raden Wijaya. In the end, the invasion ended with Yuan failure and strategic victory for the new state, Majapahit.
Dyah Pitaloka Citraresmi or Citra Rashmi (1340–1357), was the princess of the United Sunda Kingdom and Galuh Kingdom in Western Java. According to the Pararaton or Book of Kings, she was supposed to marry Hayam Wuruk, the new young king of Majapahit who had a great desire to take her as his queen. However, in the tragedy known as The Bubat Incident, she took her own life. Tradition describes her as a young woman of extraordinary beauty.
The Battle of Bubat also known as Pasunda Bubat is the battle between the Sundanese royal family and the Majapahit army that took place in Bubat Square on the northern part of Trowulan in 1279 Saka or 1357 CE.

King Siliwangi or Prabu Siliwangi was a semi-legendary king of the Hindu Sunda Kingdom in pre-Islamic West Java.

The Palapa oath was an oath taken by Gajah Mada, a 14th-century Prime Minister of the Javanese Majapahit Empire described in the Pararaton. In the oath, Gajah Mada swore that he would not rest as long as he had not succeeded in unifying Nusantara. The oath was taken during his inauguration as Majapahit Amangkubhumi that took place in 1256 Saka (1334) or 1258 Saka (1336).
King Niskala Wastu Kancana also known as Prabu Raja Wastu or popularly known as Wastu Kancana was one of the great kings of the Sunda Kingdom reigning throughout most of the 15th century. He was the younger brother of Princess Pitaloka.

The history of Sunda Kingdom spanned almost a millennium, between 7th to 16th century. It is not sure however, whether the Sunda Kingdom was actually a continuous polity or not, nor whether its rulers belongs to a single continuous lineage of dynasty or not. This is because the scarcity of evidences, historical records and archaeological findings that plausibly connected to this kingdom.

Siping-siping, simping-simping, or sisimping, is a type of armor used in Java. It is a short sleeveless jacket made of scale-shaped metal plates.












