Related Research Articles
The 800s decade ran from January 1, 800, to December 31, 809.
The 810s decade ran from January 1, 810, to December 31, 819.
The 820s decade ran from January 1, 820, to December 31, 829.
The 840s decade ran from January 1, 840, to December 31, 849.

Year 809 (DCCCIX) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 809th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 809th year of the 1st millennium, the 9th year of the 9th century, and the 10th and last year of the 800s decade.

Year 841 (DCCCXLI) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar.

Year 829 (DCCCXXIX) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar.

The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic, traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 by Paolo Lucio Anafesto, over the course of its 1,100 years of history it established itself as one of the major European commercial and naval powers. Initially extended in the Dogado area, during its history it annexed a large part of Northeast Italy, Istria, Dalmatia, the coasts of present-day Montenegro and Albania as well as numerous islands in the Adriatic and eastern Ionian seas. At the height of its expansion, between the 13th and 16th centuries, it also governed the Peloponnese, Crete and Cyprus, most of the Greek islands, as well as several cities and ports in the eastern Mediterranean.

The Battle of the Olive Grove of Kountouras took place in the summer of 1205, in Messenia in the Morea peninsula, between the Frankish Crusaders and the local Byzantine Greeks, resulting in a victory of the Franks and the collapse of the local resistance.
The military history of the Republic of Venice started shortly after its founding, spanning a period from the 9th century until the Republic's fall in the 18th century.
Borna was the duke of Croatia from c. 810 to 821 and vassal of the Frankish Empire. He resided in Nin and was the ruler of most of the Croats in northern Dalmatia.

Obelerio degli Antenori was the ninth traditional Doge of Venice from 804 to 811.
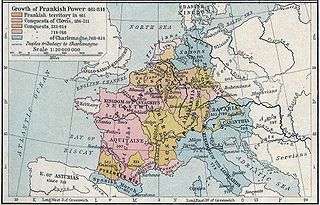
The siege of Trsat was a battle fought over possession of the town of Trsat in Liburnia, near the Croatian–Frankish border. The battle was fought in the autumn of 799 between the defending forces of Dalmatian Croatia under the leadership of Croatian duke Višeslav, and the invading Frankish army of the Carolingian Empire led by Eric of Friuli. The battle was a Croatian victory, and the Frankish commander Eric was killed during the siege.

There was an Abbasid–Carolingian alliance during the 8th and 9th centuries, effected through a series of embassies, rapprochements and combined military operations between the Frankish Carolingian Empire and the Abbasid Caliphate.

The Battle of Demetrias was a sea engagement fought at Volos in Greece in the early 1270s between a Byzantine fleet and the assembled forces of the Latin barons of Euboea (Negroponte) and Crete. The battle was fierce, and initially in favour of the Latins, but the timely arrival of Byzantine reinforcements tipped the scale, resulting in a crushing Byzantine victory.
This article presents a detailed timeline of the history of the Republic of Venice from its legendary foundation to its collapse under the efforts of Napoleon.

The Battle of the Echinades was fought in 1427 among the Echinades islands off western Greece between the fleets of Carlo I Tocco and the Byzantine Empire. The battle was a decisive Byzantine victory, the last in the Empire's naval history, and led to the consolidation of the Peloponnese under the Byzantine Despotate of the Morea.
Carola is the name used by Edgecumbe Staley in his book The dogaressas of Venice to refer to the Dogaressa of Venice married to Doge Obelerio degli Antenori. Among many claims, she is sometimes purported to be the first consort of a Venetian doge with the title and position of dogaressa of Venice, although this is a claim that only appears for the first time in 1858, over 1,000 years after her supposed reign. The first mention of a consort of Obelerio in the surviving historical record is in the Chronicon Altinate, said to be an unnamed daughter of Charlemagne, and several other early accounts fail to mention any wife or consort of Obelerio. Despite the lack of contemporary evidence, the consort figure in the Chronicon Altinate became part of the canon of Venetian history, and thus is found in many accounts of Obelerio's reign.
The Treaty of Sapienza was concluded in June 1209 between the Republic of Venice and the newly established Principality of Achaea, under Prince Geoffrey I of Villehardouin, concerning the partition of the Peloponnese (Morea) peninsula, conquered following the Fourth Crusade. By its terms, Venice, which had been accorded most of the Peloponnese in the Partitio Romaniae, recognized Villehardouin in possession of the entire peninsula except for the two forts of Modon and Coron, which came under Venetian control, and secured commercial and tax privileges in the Principality. The text of the treaty is also a valuable primary source for the early history of the Principality of Achaea.
A reason for the longevity of the Byzantine Empire is how they managed their foreign relations. The army and later its navy were the primary methods with the evolved traditions of the Roman Empire, however Byzantine diplomacy which eventuated with their many treaties was used extensively as well.
References
- Scholz, B.W. (1970). Royal Frankish Annals and Nithard's Histories. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 0-472-06186-0.