The Battle of Lebanon occurred July 5, 1863, in Lebanon, Kentucky, during Morgan's Raid in the American Civil War. Confederate troops under Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan fought for six hours to overcome the small Union garrison before moving northward, eventually riding through Kentucky, Indiana, and much of Ohio before surrendering.

Lebanon is a home rule-class city in Marion County, Kentucky, in the United States. The population was 6,331 at the 2010 census. It is the seat of its county. Lebanon is located in central Kentucky, southeast of Louisville. A national cemetery is located nearby.
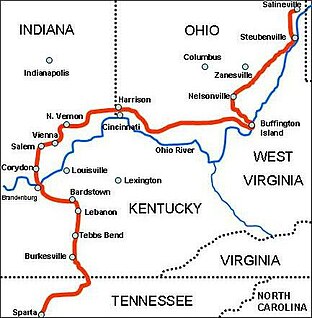
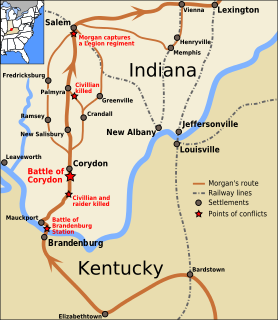
Morgan's Raid was a diversionary incursion by Confederate cavalry into the northern U.S. states of Indiana and Ohio during the American Civil War. The raid took place from June 11–July 26, 1863, and is named for the commander of the Confederates, Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan. Although it caused temporary alarm in the North, the raid was ultimately classed as a failure.

The American Civil War was a war fought in the United States from 1861 to 1865, between the North and the South. The Civil War is the most studied and written about episode in U.S. history. Primarily as a result of the long-standing controversy over the enslavement of black people, war broke out in April 1861 when secessionist forces attacked Fort Sumter in South Carolina shortly after Abraham Lincoln had been inaugurated as the President of the United States. The loyalists of the Union in the North proclaimed support for the Constitution. They faced secessionists of the Confederate States in the South, who advocated for states' rights to uphold slavery.
Contents
General Morgan and his 2,460 handpicked Confederate cavalrymen rode west from Sparta in middle Tennessee on June 11, 1863, intending to divert the attention of the Union Army of the Ohio from Southern forces in the state. On June 23, the Federal Army of the Cumberland began its operations against Gen. Braxton Bragg's Confederate Army of Tennessee in what became known as the Tullahoma Campaign, and Morgan decided to move northward. Morgan crossed the rain-swollen Cumberland River by July 2 at Burkesville, Kentucky. After being defeated by Michigan troops along the Green River at the Battle of Tebbs' Bend on July 4, Morgan withdrew and circled to the west, hoping to reach Louisville, then lightly defended.

Sparta is a city and the county seat of White County, Tennessee, United States. The population was 4,925 in 2010, and 5,075 according to a 2014 census estimate.

Tennessee is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th largest and the 16th most populous of the 50 United States. Tennessee is bordered by Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina to the east, Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi to the south, Arkansas to the west, and Missouri to the northwest. The Appalachian Mountains dominate the eastern part of the state, and the Mississippi River forms the state's western border. Nashville is the state's capital and largest city, with a 2017 population of 667,560. Tennessee's second largest city is Memphis, which had a population of 652,236 in 2017.

During the American Civil War, the Union Army referred to the United States Army, the land force that fought to preserve the Union of the collective states. Also known as the Federal Army, it proved essential to the preservation of the United States of America as a working, viable republic.
Morgan surprised and captured the Federal garrison at Lebanon. With minimal time to prepare, Union Lt. Col. Charles S. Hanson (a brother of Confederate general Roger Hanson) quickly deployed his 350 - 400 men from the 20th Kentucky Infantry behind overturned wagons, hastily erected barricades, fences, and other cover. Arriving at the town, Morgan formally requested that Hanson surrender, an offer that was refused. With a huge numerical advantage, Morgan quickly pushed Hanson's advance pickets back through the town's streets. He trapped many of the Union soldiers in the Louisville and Nashville Railroad depot, but the well fortified brick building provided considerable protection. Morgan ordered nearby buildings set on fire, hoping to force Hanson to surrender. In a sharp six-hour fight, Federal troops killed Morgan's 19-year-old brother, Lt. Thomas Morgan, during the final charge. General Morgan finally captured and paroled the enemy soldiers. His men burned the offices of the Circuit Clerk and County Clerk, as well as 20 other buildings.

Roger Weightman Hanson was a brigadier general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The commander of the famed "Orphan Brigade," he was mortally wounded at the Battle of Murfreesboro. He was nicknamed "Old Flintlock."
The 20th Kentucky Volunteer Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War.

The Louisville and Nashville Railroad, commonly called the L&N, was a Class I railroad that operated freight and passenger services in the southeast United States.