
John Hunt Morgan was a Confederate general in the American Civil War. In April 1862, he raised the 2nd Kentucky Cavalry Regiment, fought at Shiloh, and then launched a costly raid in Kentucky, which encouraged Braxton Bragg's invasion of that state. He also attacked General William Rosecrans's supply lines. In July 1863, he set out on a 1,000-mile raid into Indiana and Ohio, taking hundreds of prisoners. But after most of his men had been intercepted by U.S. Army gunboats, Morgan surrendered at Salineville, Ohio, the northernmost point ever reached by uniformed Confederates. Morgan carried out the diversionary "Morgan's Raid" against orders, which gained no tactical advantage for the Confederacy while losing the regiment. Morgan escaped prison, but his credibility was so low that he was restricted to minor operations. He was killed at Greeneville, Tennessee, in September 1864. Morgan was the brother-in-law of Confederate general A. P. Hill. Various schools and a memorial are dedicated to him.

In the American Civil War (1861–65), the border states or the Border South were four, later five, slave states in the Upper South that primarily supported the Union. They were Delaware, Maryland, Kentucky, and Missouri, and after 1863, the new state of West Virginia. To their north they bordered free states of the Union, and all but Delaware bordered slave states of the Confederacy to their south.
The Army of the Ohio was the name of two Union armies in the American Civil War. The first army became the Army of the Cumberland and the second army was created in 1863.
The Battle of Salineville occurred July 26, 1863, near Salineville, Ohio, during the American Civil War. U.S. Brig. Gen. James M. Shackelford destroyed Confederate Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan's remaining Confederate cavalry and captured Morgan, ending Morgan's Raid. It was the northernmost military action involving an official command of the Confederate States Army.

Henry Cornelius Burnett was an American politician who served as a Confederate States senator from Kentucky from 1862 to 1865. From 1855 to 1861, Burnett served four terms in the United States House of Representatives. A lawyer by profession, Burnett had held only one public office—circuit court clerk—before being elected to Congress. He represented Kentucky's 1st congressional district immediately prior to the Civil War. This district contained the entire Jackson Purchase region of the state, which was more sympathetic to the Confederate cause than any other area of Kentucky. Burnett promised the voters of his district that he would have President Abraham Lincoln arraigned for treason. Unionist newspaper editor George D. Prentice described Burnett as "a big, burly, loud-mouthed fellow who is forever raising points of order and objections, to embarrass the Republicans in the House".

The U.S. state of West Virginia was formed out of western Virginia and added to the Union as a direct result of the American Civil War, in which it became the only modern state to have declared its independence from the Confederacy. In the summer of 1861, Union troops, which included a number of newly formed Western Virginia regiments, under General George McClellan drove off Confederate troops under General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Philippi in Barbour County. This essentially freed Unionists in the northwestern counties of Virginia to form a functioning government of their own as a result of the Wheeling Convention. Before the admission of West Virginia as a state, the government in Wheeling formally claimed jurisdiction over all of Virginia, although from its creation it was firmly committed to the formation of a separate state.
The Department of the Ohio was an administrative military district created by the United States War Department early in the American Civil War to administer the troops in the Northern states near the Ohio River.
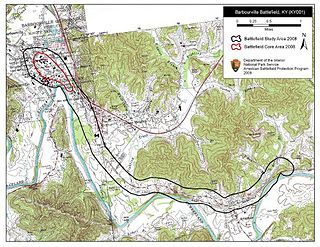
The Battle of Barbourville was one of the early engagements of the American Civil War. It took place on September 19, 1861, in Knox County, Kentucky during the campaign known as the Kentucky Confederate Offensive. The battle is considered the first Confederate victory in the commonwealth, and threw a scare into Federal commanders, who rushed troops to central Kentucky to try to repel the invasion, which was finally stopped at the Battle of Camp Wildcat in October.

Kentucky was a southern border state of key importance in the American Civil War. It officially declared its neutrality at the beginning of the war, but after a failed attempt by Confederate General Leonidas Polk to take the state of Kentucky for the Confederacy, the legislature petitioned the Union Army for assistance. Though the Confederacy controlled more than half of Kentucky early in the war, after early 1862 Kentucky came largely under U.S. control. In the historiography of the Civil War, Kentucky is treated primarily as a southern border state, with special attention to the social divisions during the secession crisis, invasions and raids, internal violence, sporadic guerrilla warfare, federal-state relations, the ending of slavery, and the return of Confederate veterans.

The American Civil War significantly affected Tennessee, with every county witnessing combat. During the War, Tennessee was a Confederate state, and the last state to officially secede from the Union to join the Confederacy. Tennessee had been threatening to secede since before the Confederacy was even formed, but didn’t officially do so until after the fall of Fort Sumter when public opinion throughout the state drastically shifted. Tennessee seceded in protest to President Lincoln's April 15 Proclamation calling forth 75,000 members of state militias to suppress the rebellion. Tennessee provided a large number of troops for the Confederacy, and would also provide more fleeing soldiers for the Union Army than any other state within the Confederacy.

During the American Civil War, North Carolina joined the Confederacy with some reluctance, mainly due to the presence of Unionist sentiment within the state. A popular vote in February, 1861 on the issue of secession was won by the unionists but not by a wide margin. This slight lean in favor of staying in the Union would shift towards the Confederacy in response to Abraham Lincoln's April 15 proclamation that requested 75,000 troops from all Union states, leading to North Carolina's secession. Similar to Arkansas, Tennessee, and Virginia, North Carolina wished to remain uninvolved in the likely war but felt forced to pick a side by the proclamation. Throughout the war, North Carolina widely remained a divided state. The population within the Appalachian Mountains in the western part of the state contained large pockets of Unionism. Even so, North Carolina would help contribute a significant amount of troops to the Confederacy, and channel many vital supplies through the major port of Wilmington, in defiance of the Union blockade.

Louisiana was a dominant population center in the southwest of the Confederate States of America, controlling the wealthy trade center of New Orleans, and contributing the French Creole and Cajun populations to the demographic composition of a predominantly Anglo-American country. In the antebellum period, Louisiana was a slave state, where enslaved African Americans had comprised the majority of the population during the eighteenth-century French and Spanish dominations. By the time the United States acquired the territory (1803) and Louisiana became a state (1812), the institution of slavery was entrenched. By 1860, 47% of the state's population were enslaved, though the state also had one of the largest free black populations in the United States. Much of the white population, particularly in the cities, supported slavery, while pockets of support for the U.S. and its government existed in the more rural areas.

The city of Winchester, Virginia, and the surrounding area, were the site of numerous battles during the American Civil War, as contending armies strove to control the lower Shenandoah Valley. Winchester changed hands more often than any other Confederate city.

The Confederate government of Kentucky was a shadow government established for the Commonwealth of Kentucky by a self-constituted group of Confederate sympathizers and delegates sent by Kentucky counties, during the American Civil War. The shadow government never replaced the elected government in Frankfort, in which the state legislature had strong Union sympathies while the governor was pro-Confederate. Neither was it able to gain the whole support of Kentucky's citizens; its jurisdiction extended only as far as Confederate battle lines in the Commonwealth, which at its greatest extent in 1861 and early 1862 encompassed over half the state. Nevertheless, the provisional government was recognized by the Confederate States of America, and Kentucky was admitted to the Confederacy on December 10, 1861. Kentucky, the final state admitted to the Confederacy, was represented by the 13th (central) star on the Confederate battle flag.

The Battle of Cynthiana, or more specifically the Second Battle of Cynthiana or the Battle of Kellar's Bridge, included three separate engagements during the American Civil War that were fought on June 11 and 12, 1864, in Harrison County, Kentucky, in and near the town of Cynthiana. This was part of Confederate Brigadier General John H. Morgan's 1864 Raid into Kentucky. The battle ultimately resulted in a victory by Union forces over the raiders and ended Morgan's Last Kentucky Raid in defeat. Morgan's command had previously captured the town in the First Battle of Cynthiana, July 17, 1862.

The 64th Virginia Mounted Infantry Regiment was formed from troops raised in Lee, Scott, Wise and Buchanan counties in Virginia for service in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. It served as an infantry regiment, a cavalry regiment, and a mounted infantry (dragoon) unit, and had a mixed reputation.
The 8th Kentucky Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that served in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War.

James Gallant Spears was an American general who served in the Union Army during the Civil War. Leading a unit composed primarily of Tennessee loyalists, he participated in early battles in the Cumberland Gap area before marching with the Army of the Cumberland at Stones River and Chickamauga. He later provided support for the Knoxville Campaign.
The Battle of Camp Wildcat was one of the early engagements of the American Civil War. It occurred October 21, 1861, in northern Laurel County, Kentucky during the campaign known as the Kentucky Confederate Offensive or Operations in Eastern Kentucky (1861). The battle is considered one of the first Union victories of the Civil War, and marked the second engagement of troops in the Commonwealth of Kentucky.
On June 20, 1863, the U.S. government created a new state from 50 western counties of Virginia to be named "West Virginia". This was done on behalf of a Unionist government in Wheeling, Virginia, approved by Congress and President Lincoln, though it was done with a low participation of the citizens within the new state. There remained a large number of counties and citizens who still considered themselves as part of Virginia and the Confederacy which, in turn, considered the new state as part of Virginia and the Confederacy. In 1861 the 50 counties contained a population of 355,544 whites, 2,782 freemen, 18,371 slaves, 79,515 voters and 67,721 men of military age. West Virginia was the 6th most contested state during the war, with 632 battles, engagements, actions and skirmishes.