
The House of Wettin was a dynasty which included Saxon kings, prince-electors, dukes, and counts, who once ruled territories in the present-day German federated states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynasty is one of the oldest in Europe, and its origins can be traced back to the town of Wettin, Saxony-Anhalt. The Wettins gradually rose to power within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family became the rulers of several medieval states, starting with the Saxon Eastern March in 1030. Other states they gained were Meissen in 1089, Thuringia in 1263, and Saxony in 1423. These areas cover large parts of Central Germany as a cultural area of Germany.

Frederick I, called the Brave or the Bitten was Margrave of Meissen and Landgrave of Thuringia.

Albert II, the Degenerate was a Margrave of Meissen, Landgrave of Thuringia and Count Palatine of Saxony. He was a member of the House of Wettin.

Henry III, called Henry the Illustrious from the House of Wettin was Margrave of Meissen and last Margrave of Lusatia from 1221 until his death; from 1242 also Landgrave of Thuringia.

The Margravate or Margraviate of Meissen was a medieval principality in the area of the modern German state of Saxony. It originally was a frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, created out of the vast Marca Geronis in 965. Under the rule of the Wettin dynasty, the margravate finally merged with the former Duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg into the Saxon Electorate by 1423.

Frederick IV was Burgrave of Nuremberg from 1300, until his death in 1332. He was the younger son of Burgrave Frederick III from his second marriage with the Ascanian princess Helene of Saxony.

Pleissnerland, Pleissenland or the Imperial Territory of Pleissenland was a Reichsgut of the Holy Roman Empire, which meant that it was directly possessed by the respective elected King of the Romans or Emperor. It was named for the Pleiße River, and was located in what is now the border region between the German states of Thuringia and Saxony south of Leipzig, including the towns of Altenburg, Chemnitz, Zwickau and Leisnig.

Landsberg is a town in the Saalekreis in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany

The Saxon Eastern March was a march of the Holy Roman Empire from the 10th until the 12th century. The term "eastern march" stems from the Latin term marchia Orientalis and originally could refer to either a march created on the eastern frontier of the East Frankish duchy of Saxony or another on the eastern border of the Duchy of Bavaria: the Bavarian marchia Orientalis, corresponding to later Austria.

The Margraviate of Landsberg was a march of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the 13th to the 14th century under the rule of the Wettin dynasty. It was named after Landsberg Castle in present-day Saxony-Anhalt.
Conrad I, called the Great, a member of the House of Wettin, was Margrave of Meissen from 1123 and Margrave of Lusatia from 1136 until his retirement in 1156. Initially a Saxon count, he became the ruler over large Imperial estates in the Eastern March and progenitor of the Saxon electors and kings.
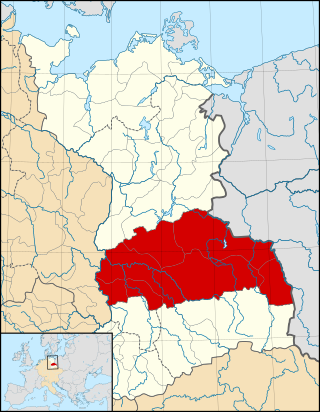
The March or Margraviate of Lusatia was an eastern border march of the Holy Roman Empire in the lands settled by Polabian Slavs. It arose in 965 in the course of the partition of the vast Marca Geronis. Ruled by several Saxon margravial dynasties, among them the House of Wettin, the lordship was contested by the Polish kings as well as by the Ascanian margraves of Brandenburg. The remaining territory was finally incorporated into the Lands of the Bohemian Crown in 1367.
Dietrich II was Margrave of Lusatia from 1032 to 1034, the first of the Wettin dynasty.
The Duchy of Thuringia was an eastern frontier march of the Merovingian kingdom of Austrasia, established about 631 by King Dagobert I after his troops had been defeated by the forces of the Slavic confederation of Samo at the Battle of Wogastisburg. It was recreated in the Carolingian Empire and its dukes were appointed by the king until it was absorbed by the Saxon dukes in 908. From about 1111/12 the territory was ruled by the Landgraves of Thuringia as Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. When Frederick IV, the last independent ruler of Thuringia died in 1440, the territory passed to his nephew, the Saxon elector Frederick II.
Theodoric of Landsberg, a member of the House of Wettin was Margrave of Landsberg from 1265 until his death.

Rudolf I, a member of the House of Ascania, was Duke of Saxe-Wittenberg from 1298 until his death. By the Golden Bull of 1356 he was acknowledged as Elector of Saxony.
Frederick Tuta, a member of the House of Wettin, was Margrave of Landsberg from 1285 and Margrave of Lusatia from 1288 until his death. He also served as regent of the Margraviate of Meissen.

Dedi III, nicknamed the Fat, a member of the House of Wettin, was Margrave of Lusatia from 1185 until his death.
Theodoric IV, Landgrave of Lusatia, also called in German Diezmann, or Dietrich III was a member of the House of Wettin. He was Margrave of Lusatia from 1291 to 1303. He was also Margrave of Osterland from 1291 until his death, and Landgrave of Thuringia, as Dietrich I, from 1298 until his death.












