The Hasdingi were one of the Vandal peoples of the Roman era. The Vandals were Germanic peoples, who are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language, and were first reported during the first centuries of the Roman empire in the area which is now Poland, East Germany, Czechia, and Slovakia.
Gunderic, King of Hasding Vandals (407-418), then King of Vandals and Alans (418–428), led the Hasding Vandals, a Germanic tribe originally residing near the Oder River, to take part in the barbarian invasions of the Western Roman Empire in the fifth century.
The Battle of Ad Decimum took place on September 13, 533 between the armies of the Vandals, commanded by King Gelimer, and the Byzantine Empire, under the command of General Belisarius. This event and events in the following year are sometimes jointly referred to as the Battle of Carthage, one of several battles to bear that name. The Byzantine victory marked the beginning of the end for the Vandals and began the reconquest of the west under the Emperor Justinian I.

The Alans were an Iranian nomadic pastoral people of antiquity.

The Vandals were a Roman-era Germanic people who first appear in written records inhabiting present-day southern Poland. Some later moved in large numbers, including most notably the group which successively established Vandal kingdoms in the Iberian Peninsula, on western Mediterranean islands and in North Africa in the 5th century.
Foederati were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as foedus, with Rome. In Republican times the term identified the socii, whereas during the Imperial period it was used to describe foreign states, client kingdoms, or barbarian tribes to which the Roman Empire provided benefits in exchange for military assistance. The term was also used, especially under the Roman Empire, for groups of "barbarian" mercenaries of various sizes, who were typically allowed to settle within the Roman Empire.
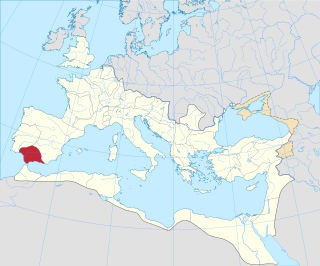
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces in Hispania. Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica remained one of the basic divisions of Hispania under the Visigoths down to 711. Baetica was part of Al-Andalus under the Moors in the 8th century and approximately corresponds to modern Andalusia.
This is a chronology of warfare between the Romans and various Germanic tribes between 113 BC and 596 AD. The nature of these wars varied through time between Roman conquest, Germanic uprisings and later Germanic invasions in the Roman Empire that started in the late 2nd century BC. The series of conflicts, which began in the 5th century under the Western Roman Emperor Honorius, was one of many factors which led to the ultimate downfall of the Western Roman Empire.

The Battle of Xuzhou was a military conflict between the Empire of Japan and the Republic of China forces in May 1938 during the Second Sino-Japanese War.

The Battle of Mainz saw a Habsburg army led by François Sebastien Charles Joseph de Croix, Count of Clerfayt launch a surprise assault against four divisions of the French Army of Rhin-et-Moselle directed by François Ignace Schaal. The right-hand French division fled the battlefield, compelling the other three divisions to retreat with the loss of their siege artillery and many casualties. The War of the First Coalition action was fought near the city of Mainz in the today state of Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany.

Komarolu is a Mandal in Prakasam district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the mandal headquarters of komarolumandal in Markapur revenue division.
The crossing of the Rhine River by a mixed group of barbarians which included Vandals, Alans and Suebi is traditionally considered to have occurred on the last day of the year 406. The crossing transgressed one of the Late Roman Empire's most secure limites or boundaries and so it was a climactic moment in the decline of the Empire. It initiated a wave of destruction of Roman cities and the collapse of Roman civic order in northern Gaul. That, in turn, occasioned the rise of three usurpers in succession in the province of Britannia. Therefore, the crossing of the Rhine is a marker date in the Migration Period during which various Germanic tribes moved westward and southward from southern Scandinavia and northern Germania.

Piątki is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Lipno, within Lipno County, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-central Poland. It lies approximately 8 kilometres (5 mi) south-east of Lipno and 50 km (31 mi) south-east of Toruń.

Kryniczki is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Izbica, within Krasnystaw County, Lublin Voivodeship, in eastern Poland. It lies approximately 8 kilometres (5 mi) north-east of Izbica, 12 km (7 mi) south-east of Krasnystaw, and 62 km (39 mi) south-east of the regional capital Lublin.

Skrzynka is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Szczucin, within Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, in southern Poland. It lies approximately 4 kilometres (2 mi) south of Szczucin, 13 km (8 mi) north-east of Dąbrowa Tarnowska, and 83 km (52 mi) east of the regional capital Kraków.

Siedliska is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Lubycza Królewska, within Tomaszów Lubelski County, Lublin Voivodeship, in eastern Poland, close to the border with Ukraine. It lies approximately 8 kilometres (5 mi) south of Lubycza Królewska, 23 km (14 mi) south-east of Tomaszów Lubelski, and 130 km (81 mi) south-east of the regional capital Lublin.

Wierzbna is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Grodków, within Brzeg County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately 8 kilometres (5 mi) west of Grodków, 27 km (17 mi) south-west of Brzeg, and 48 km (30 mi) west of the regional capital Opole.

Gaiseric, also known as Geiseric or Genseric (Latin: Gaisericus, Geisericus; reconstructed Vandalic: *Gaisarīx was King of the Vandals and Alans who established the Vandal Kingdom and was one of the key players in the difficulties faced by the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century. Through his nearly 50 years of rule, he raised a relatively insignificant Germanic tribe to the status of a major Mediterranean power. His most famous exploit, however, was the capture and plundering of Rome in June 455. He also defeated two major efforts by the Romans to overthrow him, the first one by the emperor Majorian in 460 or 461, and another by Basiliscus at the Battle of Cape Bon in 468. After dying in Carthage, Gaiseric was succeeded by his son Huneric.
The Battle of Landriano took place on 21 June 1529, between the French army under Francis de Bourbon, Comte de St. Pol and the Imperial–Spanish army commanded by Don Antonio de Leyva, Duke of Terranova in the context of the War of the League of Cognac. The French army was destroyed and the battle's strategic result was that the struggle between Francis I of France and Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor for control of northern Italy was temporarily at an end.

Carthage was captured by the Vandals from the Western Roman Empire on 19 October 439. Under their leader Genseric, the Vandals crossed the Strait of Gibraltar into Africa and captured Hippo Regius in August 431, which they made the capital of their kingdom.Despite an uneasy peace with the Romans, Genseric made a surprise attack against Carthage in October 439. After capturing Carthage, the Vandals put the city to the sack and made it the new capital of their kingdom.










