
The Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF), colloquially known as Shabia or HGDEF, was an armed Marxist–Leninist organization that fought for the independence of Eritrea from Ethiopia. It emerged in 1973 as a far-left to left-wing nationalist group that split from the Eritrean Liberation Front (ELF). After achieving Eritrean independence in 1991, it transformed into the People's Front for Democracy and Justice (PFDJ), which serves as Eritrea's sole legal political party.

The Eritrean Liberation Front, colloquially known as Jebha, was the main independence movement in Eritrea which sought Eritrea's independence from Ethiopia during the 1960s and the early 1970s.

The Eritrean War of Independence was a decades-long insurgency aimed at achieving self-determination and independence for Eritrea from Ethiopian rule. Starting in 1961, Eritrean insurgents engaged in guerrilla warfare to liberate Eritrea Province from the control of the Ethiopian Empire under Haile Selassie and later the Derg under Mengistu. Their efforts ultimately succeeded in 1991 with the fall of the Derg regime.

Petros Solomon is an Eritrean politician. He was an Eritrean People's Liberation Front commander and played a key role during the Eritrean War of Independence, following independence he served in several positions in the Cabinet, including Minister of Defense and Minister of Foreign Affairs.

The Oromo Liberation Front is an Oromo nationalist political party formed in 1973 to promote self-determination for the Oromo people inhabiting today's Oromia Region and Oromia Zone in the Amhara Region of Ethiopia. The OLF has offices in Addis Ababa, Washington, D.C., and Berlin, from which it operates radio stations that broadcast in Amharic and Oromo.

The Ethiopian Civil War was a civil war in Ethiopia and present-day Eritrea, fought between the Ethiopian military junta known as the Derg and Ethiopian-Eritrean anti-government rebels from 12 September 1974 to 28 May 1991.
Mesfin Hagos is an Eritrean who was one of the founding members of the Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF). In government, he was the Eritrean Minister of Defense during the 1990s.
Articles related to Eritrea include:
The Battle of Afabet was a three-day battle fought from 17 March through 20 March 1988 in and around the town of Afabet, as part of the Eritrean War of Independence. The battle has been described as being the largest battle in Africa since the Second Battle of El Alamein. It has been described as the most significant battle in terms of military and political consequences since the Ethio-Somali War, alongside the 1989 Battle of Shire of the Ethiopian Civil War.
The First Battle of Massawa took place from 1977 to 1978 in and around the coastal city of Massawa. The port was besieged by the Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF) against the forces of Ethiopia, and was one of two battles in and around the city.
The Eritrean Air Force (ERAF) is the air service branch of the Eritrean Defence Forces.
The Eritrean Navy is a smaller branch of the Eritrean Defence Forces. It is responsible for the security of the entire coastline of Eritrea, more than 1,100 km, as well as the Eritrean territorial waters.

The Eritrean Civil Wars were two conflicts that were fought between competing organizations for the liberation of Eritrea.

The Eritrean–Ethiopian border conflict was a violent standoff and a proxy conflict between Eritrea and Ethiopia lasting from 1998 to 2018. It consisted of a series of incidents along the then-disputed border; including the Eritrean–Ethiopian War of 1998–2000 and the subsequent Second Afar insurgency. It included multiple clashes with numerous casualties, including the Battle of Tsorona in 2016. Ethiopia stated in 2018 that it would cede Badme to Eritrea. This led to the Eritrea–Ethiopia summit on 9 July 2018, where an agreement was signed which demarcated the border and agreed a resumption of diplomatic relations.
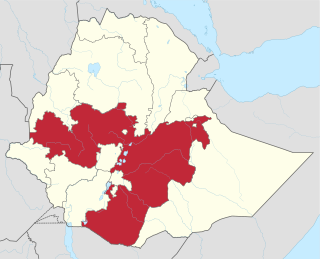
The Oromo conflict is a protracted conflict between the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF) and the Ethiopian government. The Oromo Liberation Front formed to fight the Ethiopian Empire to liberate the Oromo people and establish an independent state of Oromia. The conflict began in 1973, when Oromo nationalists established the OLF and its armed wing, the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA). These groups formed in response to prejudice against the Oromo people during the Haile Selassie and Derg era, when their language was banned from public administration, courts, church and schools, and the stereotype of Oromo people as a hindrance to expanding Ethiopian national identity.
The Battle of Halhal was a battle of the Eritrean War of Independence, and took place on 18 July 1962. In the battle, the Eritrean Liberation Front was able to overrun the local police office in Halhal and control it for an entire day. The defenders, which were Eritrean Police commandos, had been trained by the Israeli military.
The Battle of Ansaba took place in autumn of 1963, and was part of the Eritrean War of Independence. It was fought in Jengeren, North of Keren, In Anseba Region.

Tigrayan nationalism is an ethnic nationalism that advocates the interests of Tigrayan people in Ethiopia. Inspired predominantly by the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) with its predecessor Tigray Liberation Front (TLF), this type of nationalism holds that Tigrayans are an independent group with unique ancestry, heritage, history and culture outside Ethiopia. As such, they claim Tigray is the source of Ethiopian civilization and utterly a benefactor of state-building without other local ethnic groups. Tigrayan nationalists accuse Amharas of imposing their cultural, economic and political hegemony over Tigrayans.

The fall of the Derg, also known as Downfall of the Derg, was a military campaign that resulted in the defeat of the ruling Marxist–Leninist military junta, the Derg, by the rebel coalition Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) on 28 May 1991 in Addis Ababa, ending the Ethiopian Civil War. The Derg took power after deposing Emperor Haile Selassie and the Solomonic dynasty, an imperial dynasty of Ethiopia that began in 1270. The Derg suffered from insurgency with different factions, and separatist rebel groups since their early rule, beginning with the Ethiopian Civil War. The 1983–1985 famine, the Red Terror, and resettlement and villagization made the Derg unpopular with the majority of Ethiopians tending to support insurgent groups like the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) and Eritrean People's Liberation Front (EPLF).










