
The French Wars of Religion were a series of civil wars between French Catholics and Protestants from 1562 to 1598. Between two and four million people died from violence, famine or disease directly caused by the conflict, and it severely damaged the power of the French monarchy. One of its most notorious episodes was the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572. The fighting ended with a compromise in 1598, when Henry of Navarre, who had converted to Catholicism in 1593, was proclaimed King Henry IV of France and issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted substantial rights and freedoms to the Huguenots. However, Catholics continued to disapprove of Protestants and of Henry, and his assassination in 1610 triggered a fresh round of Huguenot rebellions in the 1620s.

The Battle of Ivry was fought on 14 March 1590, during the French Wars of Religion. The battle was a decisive victory for Henry IV of France, leading French royal and English forces against the Catholic League by the Duc de Mayenne and Spanish forces under the Count of Egmont. Henry's forces were victorious and he went on to lay siege to Paris.

Gaspard de Coligny, seigneur de Châtillon, was a French nobleman, Admiral of France, and Huguenot leader during the French Wars of Religion. He served under kings Francis I and Henry II during the Italian Wars, attaining great prominence both due to his military skill and his relationship with his uncle, the king's favourite Anne de Montmorency. During the reign of Francis II he converted to Protestantism, becoming a leading noble advocate for the Reformation during the early reign of Charles IX.

Louis de Bourbon, 1st Prince of Condé was a prominent Huguenot leader and general, the founder of the Condé branch of the House of Bourbon. Coming from a position of relative political unimportance during the reign of Henri II, Condé's support for the Huguenots, along with his leading role in the conspiracy of Amboise and its aftermath, pushed him to the centre of French politics. Arrested during the reign of Francis II then released upon the latter's premature death, he would lead the Huguenot forces in the first three civil wars of the French Wars of Religion before being executed after his defeat at the Battle of Jarnac in 1569.
The War of the Three Henrys, also known as the Eighth War of Religion, took place during 1585–1589, and was the eighth conflict in the series of civil wars in France known as the French Wars of Religion. It was a three-way war fought between:

The Three Bishoprics constituted a government of the Kingdom of France consisting of the dioceses of Metz, Verdun, and Toul within the Lorraine region. The three dioceses had been Prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire until they were seized by King Henry II of France between April and June 1552. At the end of the Thirty Years' War, they were officially ceded to France by the 1648 Peace of Westphalia.

Claude II de Lorraine, duc d'Aumale was a Prince étranger, military commander and French governor, during the latter Italian Wars and the early French Wars of Religion. The son of the first Duke of Guise he started his career in a pre-eminent position in French politics as a son of one of the leading families in the court of Henri II of France. Upon the death of his father in 1550, Aumale inherited the governorship of Burgundy from his father, and the duchy of Aumale from his brother who assumed the titles of Guise. Aumale was made colonel-general of the light horse by the new king and fought in Italy, Alsace and Picardie between 1551 and 1559. While leading the light cavalry during the defence of Metz he was captured, and held for the next two years, until his mother in law Diane de Poitiers paid his ransom. He achieved success at the siege of Volpiano and played an important role in the capture of Calais for which he was rewarded with the governorship of French Piedmont.
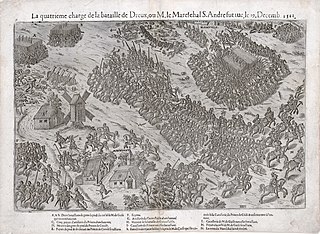
The Battle of Dreux was fought on 19 December 1562 between Catholics and Huguenots. The Catholics were led by Anne de Montmorency while Louis I, Prince of Condé, led the Huguenots. Though commanders from both sides were captured, the French Catholics won the battle which would constitute the first major engagement of the French Wars of Religion and the only major engagement of the first French War of Religion.

The Battle of Saint-Denis was fought on 10 November 1567 between a royalist army and Huguenot rebels during the second of the French Wars of Religion. Although their 74 year old commander, Anne de Montmorency, was killed in the fighting, the royalists forced the rebels to withdraw, allowing them to claim victory.

The Battle of Coutras, fought on 20 October 1587, was a major engagement in the French Religious Wars between a Huguenot (Protestant) army under Henry of Navarre and a royalist army led by Anne, Duke of Joyeuse. Henry of Navarre was victorious, and Joyeuse was killed while attempting to surrender.

The Battle of Moncontour occurred on 3 October 1569 between the royalist Catholic forces of King Charles IX of France, commanded by Henry, Duke of Anjou, and the Huguenots commanded by Gaspard de Coligny.

Louis de Gonzague, Duke of Nevers was a soldier, governor and statesman during the French Wars of Religion. His father and brother were reigning dukes of Mantua. He came to France in 1549, and fought for Henri II of France during the latter Italian Wars, getting himself captured during the battle of Saint Quentin. Due to his Italian connections he was seen as a useful figure to have as governor of French Piedmont, a post he would hold until Henri III ceded the territory in 1574. In 1565 his patron, Catherine de' Medici secured for him a marriage with the key heiress Henriette de Clèves, elevating him to duke of Nevers and count of Rethel. He fought for the crown through the early wars of religion, receiving a bad injury in the third war. At this time he formed a close bond with the young Anjou, future king Henri III, a bond that would last until the king's death.
The Battle of La Roche-l'Abeille occurred on 25 June 1569 between the Catholic forces of King Charles IX of France commanded by the Duke d’Anjou and the Huguenots commanded by the Admiral de Coligny during the "Third War" (1568–1570) of the French Wars of Religion.

The Battle of Arques occurred on 15–29 September 1589 between the French royal forces of King Henry IV of France and troops of the Catholic League commanded by Charles of Lorraine, Duke of Mayenne, during the eighth and final war (1585–1598) of the French Wars of Religion. It was a victory for Henry IV.

The siege of La Rochelle of 1572–1573 was a massive military assault on the Huguenot city of La Rochelle by Catholic troops during the fourth phase of the French Wars of Religion, following the August 1572 St. Bartholomew's Day massacre. The conflict began in November 1572 when inhabitants of the city refused to receive Armand de Gontaut, baron de Biron, as royal governor. Beginning on 11 February 1573, the siege was led by the Duke of Anjou. Political considerations following the duke's election to the throne of Poland in May 1573 resulted in negotiations, culminating on 24 June 1573, that lifted the siege on 6 July 1573. The Edict of Boulogne signed shortly thereafter brought an end to this phase of the civil war.

The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe during the 16th, 17th and early 18th centuries. Fought after the Protestant Reformation began in 1517, the wars disrupted the religious and political order in the Catholic countries of Europe, or Christendom. Other motives during the wars involved revolt, territorial ambitions and great power conflicts. By the end of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648), Catholic France had allied with the Protestant forces against the Catholic Habsburg monarchy. The wars were largely ended by the Peace of Westphalia (1648), which established a new political order that is now known as Westphalian sovereignty.

The surprise of Meaux was a failed coup attempt by leading aristocratic Huguenots which precipitated the second French War of Religion. Dissatisfied with their lot, and under the pretext of fear of extermination, Louis, Prince of Condé and Gaspard II de Coligny plotted to seize the king, Charles IX, while he was staying near Meaux. Alerted by the mustering of the Huguenots, the royal court made a dash for Paris, fighting off attempts to break through to them en route. Their plan foiled, the Huguenots laid siege to the city, beginning the second war. The event would be of lasting importance in the reputation it gave its architects for sedition.

The Battle of Craon was a military engagement of the Brittany Campaign which took place in Craon, Mayenne between 21–24 May 1592. It was fought between a French Crown army led by Henri de Bourbon, Duke of Montpensier and François de Bourbon, Prince of Conti and a joint Catholic League and Spanish force; the French Crown troops were reinforced by a contingent English soldiers. The battle occurred during the siege of Craon by French Crown forces led by Henry of Navarre, which was lengthened by the defending garrison being supported by a Catholic League army recruited by Philippe Emmanuel, Duke of Mercœur. Ultimately, a Spanish force led by Juan del Águila defeated the besiegers and relived the city.

The siege of Orléans was the final key military engagement of the first French War of Religion. Having lost the Battle of Dreux the rebel Huguenots fell back with their remaining forces to the city. François, Duke of Guise, the only non captive royal commander, moved to lay siege to the town, hoping its capitulation would bring about a total victory for the crowns forces. However, despite reducing the suburbs, he would be assassinated at the siege before he could bring it to a conclusion. As a result the captive Louis, Prince of Condé and Anne de Montmorency at Catherine de' Medici's direction were able to negotiate a compromise end to the first war in the Edict of Amboise.

Jean VI d'Aumont (1522-1595) was a soldier and Marshal of France. He served as Marshal under Henri III, campaigning against the Protestants in 1585. He would not however conduct the campaign with much enthusiasm, and after clamour at court he would be replaced by Anne de Joyeuse He playing a key role in the Day of the Barricades and Assassination of the Duke of Guise (1588). Upon the assassination of Henri III in 1589, he would transfer his loyalties to the Protestant Navarre and would campaign for him in Burgundy, Maine and Brittany against the Duke of Mercœur. He was also granted the office of governor of Dauphiné, upon it being vacated in 1592. It would be whilst fighting in Brittany in 1595, that he would be killed.

















