
Radioteletype (RTTY) is a telecommunications system consisting originally of two or more electromechanical teleprinters in different locations connected by radio rather than a wired link. Radioteletype evolved from earlier landline teleprinter operations that began in the mid-1800s. The US Navy Department successfully tested printing telegraphy between an airplane and ground radio station in 1922. Later that year, the Radio Corporation of America successfully tested printing telegraphy via their Chatham, Massachusetts, radio station to the R.M.S. Majestic. Commercial RTTY systems were in active service between San Francisco and Honolulu as early as April 1932 and between San Francisco and New York City by 1934. The US military used radioteletype in the 1930s and expanded this usage during World War II. From the 1980s, teleprinters were replaced by personal computers (PCs) running software to emulate teleprinters.
Automatic Link Establishment, commonly known as ALE, is the worldwide de facto standard for digitally initiating and sustaining HF radio communications. ALE is a feature in an HF communications radio transceiver system that enables the radio station to make contact, or initiate a circuit, between itself and another HF radio station or network of stations. The purpose is to provide a reliable rapid method of calling and connecting during constantly changing HF ionospheric propagation, reception interference, and shared spectrum use of busy or congested HF channels.

A DX-pedition is an expedition to what is considered an exotic place by amateur radio operators and DX listeners, typically because of its remoteness, access restrictions, or simply because there are very few radio amateurs active from that place. This could be an island, a country, or even a particular spot on a geographical grid. DX is a telegraphic shorthand for "distance" or "distant".

The Wireless Institute of Australia (WIA) was formed in 1910, and is the first and oldest national amateur radio society in the world. It represents the amateur radio operators of Australia as the AR "peak body" in dealings with the Australian Communications and Media Authority (ACMA), the authority under the government of Australia that administers communications within and external to Australia. The WIA publishes a bi-monthly journal for its membership called Amateur Radio. The organisation is the national society representing Australia in the International Amateur Radio Union.

The International Amateur Radio Union (IARU) is an international confederation of national organisations that allows a forum for common matters of concern to amateur radio operators worldwide, and collectively represents matters to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The International Amateur Radio Union was founded in 1925 and, as of July 2021, it is composed of 172 national member societies.

Caracol Televisión is a Colombian free-to-air television network owned by Caracol Medios, a unit of Grupo Valorem. It is one of the leading private TV networks in Colombia, alongside Canal RCN and Canal 1. The network distributes and produces 5,000+ programs and has aired in more than 80 countries.
CBLA-FM is a non-commercial radio station in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Owned and operated by the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation, the station is the flagship station of the CBC Radio One network, broadcasting a mix of news and talk. In addition to the Toronto market, CBLA also reaches much of Central Ontario with a network of twelve rebroadcasters. The studios are in the Canadian Broadcasting Centre.
DXing, taken from DX, the telegraphic shorthand for "distance" or "distant", is the hobby of receiving and identifying distant radio or television signals, or making two-way radio contact with distant stations in amateur radio, citizens band radio or other two-way radio communications. Many DXers also attempt to obtain written verifications of reception or contact, sometimes referred to as "QSLs" or "veries".

The Military Auxiliary Radio System (MARS) is a United States Department of Defense sponsored program, established as a separately managed and operated program by the United States Army, and the United States Air Force. The United States Navy-Marine Corps program closed in 2015. The program is a civilian auxiliary consisting primarily of licensed amateur radio operators who are interested in assisting the military with communications on a regional and national level when access to traditional forms of communication may no longer be available. The MARS programs also include active duty, reserve, and National Guard units; and Navy, Marine Corps units.

Contesting is a competitive activity pursued by amateur radio operators. In a contest, an amateur radio station, which may be operated by an individual or a team, seeks to contact as many other amateur radio stations as possible in a given period of time and exchange information. Rules for each competition define the amateur radio bands, the mode of communication that may be used, and the kind of information that must be exchanged. The contacts made during the contest contribute to a score by which stations are ranked. Contest sponsors publish the results in magazines and on web sites.

An amateur radio operating award is earned by an amateur radio operator for establishing two-way communication with other amateur radio stations. Awards are sponsored by national amateur radio societies, radio enthusiast magazines, or amateur radio clubs, and aim to promote activity on the amateur radio bands. Each award has its own set of rules and fees. Some awards require the amateur radio operator to have contacted other stations in a certain number of countries, Maidenhead grid locators, or counties. Because amateur radio operators are forbidden by regulation to accept financial compensation for their on-air activity, award recipients generally only receive a certificate, wooden plaque, or a small trophy as recognition of their award.
Summits On The Air (SOTA) is an amateur radio operating award program launched in Great Britain in 2002 by John Linford. The aim of SOTA is to encourage licensed amateur radio operators to operate temporarily from mountainous locations using any method of travel including hiking, mountain climbing, and cycling while operating their amateur radio station from the summits of hills and mountains. In addition to getting operators out into the field the program encourages others to listen in to the transmissions from these stations and send in reports. In areas that are not remote or difficult to access some SOTA activations serve as community outreach events. The program now has over 24,000 participants world wide, about 7,000 in the United States. Amateur radio operators who set up stations on mountain peaks are known as activators, and other amateur radio operators who complete contacts with them are called chasers. Points are given to both activators and chasers based on how high the mountain is. Awards are given based on accumulated points and certain special criteria. Amateur radio contacts between summits, referred to as summit-to-summit, are considered special achievements. Operators make use of a wide array of communication methods including morse code, voice, and digital modes such as FT8. Although all parts of the amateur radio bands can be used to make contacts, setups and communication modes vary across operators based on equipment, environment and license class. Operators use both VHF and HF signals to make contacts, in both cases enjoying improved line-of-sight propagation over obstructions that would otherwise block transmissions. Contacts are also made using amateur radio satellites. The highest ever Summits on the Air activation reported was in February 2019 by Polish amateur radio operator Tom Rudzinski (SQ9FVE), who successfully operated from 6,962 meters above sea level, atop Aconcagua in Mendoza, Argentina.

A QSL card is a written confirmation of either a two-way radiocommunication between two amateur radio or citizens band stations; a one-way reception of a signal from an AM radio, FM radio, television or shortwave broadcasting station; or the reception of a two-way radiocommunication by a third party listener. A typical QSL card is the same size and made from the same material as a typical postcard, and most are sent through the mail as such.

WBOR is the student-run, noncommercial, college radio station licensed to Bowdoin College in Brunswick, Maine, United States. The station broadcasts from the basement of the Dudley Coe Building on the Bowdoin College campus. DJs are predominately full-time Bowdoin students; however, many staff and faculty members, and community members host weekly shows. WBOR can be heard throughout the Mid Coast area.
CKMX was a radio station broadcasting at 1060 AM in Calgary, Alberta, and owned by Bell Media. Its comedy format was branded on-air as Funny 1060. CKMX's studios were located in the CTV Calgary Studios on Patina Rise SW in the Prominence Point neighborhood of Calgary, and its transmitter site near Southeast Calgary. At night, CKMX could be heard as far west as Battle Ground and Snohomish, Washington. It could also be heard on shortwave on 6.03 MHz via its repeater CFVP, reaching western North America.
The Radio Club Peruano (RCP) is a national non-profit organization for amateur radio enthusiasts in Peru. RCP was founded on December 6, 1930, and the first General Meeting of the organization was held in the halls of the Library of the Geographical Society in Lima, Peru in January, 1931. The RCP operates a QSL bureau for those amateur radio operators in regular contact with amateur radio operators in other countries, and supports amateur radio operating awards and radio contests. Radio Club Peruano represents the interests of Peruvian amateur radio operators before national and international regulatory authorities. RCP is the national member society representing Peru in the International Amateur Radio Union.

Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communications. The term "amateur" is used to specify "a duly authorized person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without pecuniary interest"; and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety, or professional two-way radio services.

Polissia National University is a university in Zhytomyr. The University provides specialists in the majority of national economic sectors in the Ukrainian Polesia. The university has some seven thousand students and is divided into eight faculties and 42 departments.
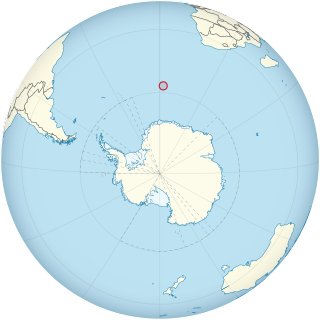
The 3Y0J Bouvet Island DXpedition was an amateur radio event that occurred February 6–13, 2023. The expedition's goals were the same as other DXpeditions: to contact as many amateur radio stations as possible from a remote location.
Parks on the Air (POTA) is an international radiosport award program that encourages licensed amateur radio operators to visit, enjoy and operate portable equipment in a variety of parks and public lands, always respecting other park users and local regulations. POTA issues awards to participants based on a wide range of criteria including the total number of radio contacts made, number made on each amateur radio band, and for different modes of communication including voice, Morse code or FT8.












