
Music notation or musical notation is any system used to visually represent aurally perceived music played with instruments or sung by the human voice through the use of written, printed, or otherwise-produced symbols, including notation for durations of absence of sound such as rests.
A time signature is a convention in Western music notation that specifies how many note values of a particular type are contained in each measure (bar). The time signature indicates the meter of a musical movement.
In music, tremolo, or tremolando, is a trembling effect. There are two types of tremolo: either a rapid repetition of a note, or a variation in volume.

An eighth note (American) or a quaver (British) is a musical note played for one eighth the duration of a whole note (semibreve). Its length relative to other rhythmic values is as expected—e.g., half the duration of a quarter note (crotchet), one quarter the duration of a half note (minim), and twice the value of a sixteenth note. It is the equivalent of the fusa in mensural notation.
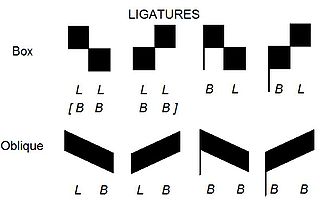
In music notation, a ligature is a graphic symbol that tells a musician to perform two or more notes in a single gesture, and on a single syllable. It was primarily used from around 800 to 1650 AD. Ligatures are characteristic of neumatic (chant) and mensural notation. The notation and meaning of ligatures has changed significantly throughout Western music history, and their precise interpretation is a continuing subject of debate among musicologists.
In music, the terms additive and divisive are used to distinguish two types of both rhythm and meter:

In music notation, a tie is a curved line connecting the heads of two notes of the same pitch, indicating that they are to be played as a single note with a duration equal to the sum of the individual notes' values. A tie is similar in appearance to a slur; however, slurs join notes of different pitches which need to be played independently, but seamlessly (legato).
In music notation, a sixty-fourth note, or hemidemisemiquaver or semidemisemiquaver (British), sometimes called a half-thirty-second note, is a note played for half the duration of a thirty-second note, hence the name. It first occurs in the late 17th century and, apart from rare occurrences of hundred twenty-eighth notes (semihemidemisemiquavers) and two hundred fifty-sixth notes (demisemihemidemisemiquavers), it is the shortest value found in musical notation.
In music, a tuplet is "any rhythm that involves dividing the beat into a different number of equal subdivisions from that usually permitted by the time-signature " This is indicated by a number, or sometimes two indicating the fraction involved. The notes involved are also often grouped with a bracket or a slur.
A rest is the absence of a sound for a defined period of time in music, or one of the musical notation signs used to indicate that.

A neume is the basic element of Western and Eastern systems of musical notation prior to the invention of five-line staff notation.

In medieval music, the rhythmic modes were set patterns of long and short durations. The value of each note is not determined by the form of the written note, but rather by its position within a group of notes written as a single figure called a ligature, and by the position of the ligature relative to other ligatures. Modal notation was developed by the composers of the Notre Dame school from 1170 to 1250, replacing the even and unmeasured rhythm of early polyphony and plainchant with patterns based on the metric feet of classical poetry, and was the first step towards the development of modern mensural notation. The rhythmic modes of Notre Dame Polyphony were the first coherent system of rhythmic notation developed in Western music since antiquity.

In music notation, a note value indicates the relative duration of a note, using the texture or shape of the notehead, the presence or absence of a stem, and the presence or absence of flags/beams/hooks/tails. Unmodified note values are fractional powers of two, for example one, one-half, one fourth, etc.

Mensural notation is the musical notation system used for polyphonic European vocal music from the late 13th century until the early 17th century. The term "mensural" refers to the ability of this system to describe precisely measured rhythmic durations in terms of numerical proportions between note values. Its modern name is inspired by the terminology of medieval theorists, who used terms like musica mensurata or cantus mensurabilis to refer to the rhythmically defined polyphonic music of their age, as opposed to musica plana or musica choralis, i.e., Gregorian plainchant. Mensural notation was employed principally for compositions in the tradition of vocal polyphony, whereas plainchant retained its own, older system of neume notation throughout the period. Besides these, some purely instrumental music could be written in various forms of instrument-specific tablature notation.

In musical notation, stems are the, "thin, vertical lines that are directly connected to the [note] head." Stems may point up or down. Different-pointing stems indicate the voice for polyphonic music written on the same staff. Within one voice, the stems usually point down for notes on the middle line or higher, and up for those below. If the stem points up from a notehead, the stem originates from the right-hand side of the note, but if it points down, it originates from the left. If there are multiple notes beamed together, the stem's direction is defined by the average of the lowest and highest notes in the beam. There is an exception to this rule: if a chord contains a second, the stem runs between the two notes with the higher being placed on the right of the stem and the lower on the left. If the chord contains an odd numbered cluster of notes a second apart, the outer two will be on the correct side of the stem, while the middle note will be on the wrong side.
The Kodály method, also referred to as the Kodály concept, is an approach to music education developed in Hungary during the mid-twentieth century by Zoltán Kodály. His philosophy of education served as inspiration for the method, which was then developed over a number of years by his associates. In 2016, the method was inscribed as a UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage.

In music, a notehead is the part of a note, usually elliptical in shape, whose placement on the staff indicates the pitch, to which modifications are made that indicate duration. Noteheads may be the same shape but colored completely black or white, indicating the note value. In a whole note, the notehead, shaped differently than shorter notes, is the only component of the note. Shorter note values attach a stem to the notehead, and possibly beams or flags. The longer double whole note can be written with vertical lines surrounding it, two attached noteheads, or a rectangular notehead. An "x" shaped notehead may be used to indicate percussion, percussive effects, or speaking. A square, diamond, or box shaped notehead may be used to indicate a natural or artificial harmonic. A small notehead can be used to indicate a grace note.

In music, a 1/16, sixteenth note (American) or semiquaver (British) is a note played for half the duration of an eighth note (quaver), hence the names. It is the equivalent of the semifusa in mensural notation, first found in 15th-century notation.
Musink is a scorewriting computer program for Windows and macOS. It is a WYSIWYM editor, with automated music- and page-layout functionality. Two versions of Musink exist: Musink Lite, which is freeware; and Musink Pro, which is not free but contains additional features.
Abbreviations in music are of two kinds, namely, abbreviations of terms related to musical expression, and the true musical abbreviations by the help of which certain passages, chords, etc., may be notated in a shortened form, to the greater convenience of both composer and performer. Abbreviations of the first kind are like most abbreviations in language; they consist for the most part of the initial letter or first syllable of the word employed—as for instance, p or f for the dynamic markings piano and forte, cresc. for crescendo, Ob. for oboe, Fag. for bassoon. This article is about abbreviations used in music notation.













