
A hearing aid is a device designed to improve hearing by making sound audible to a person with hearing loss. Hearing aids are classified as medical devices in most countries, and regulated by the respective regulations. Small audio amplifiers such as PSAPs or other plain sound reinforcing systems cannot be sold as "hearing aids".

A hearing test provides an evaluation of the sensitivity of a person's sense of hearing and is most often performed by an audiologist using an audiometer. An audiometer is used to determine a person's hearing sensitivity at different frequencies. There are other hearing tests as well, e.g., Weber test and Rinne test.
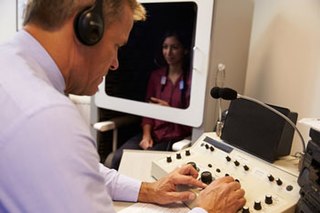
Audiology is a branch of science that studies hearing, balance, and related disorders. Audiologists treat those with hearing loss and proactively prevent related damage. By employing various testing strategies, audiologists aim to determine whether someone has normal sensitivity to sounds. If hearing loss is identified, audiologists determine which portions of hearing are affected, to what degree, and where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found. If an audiologist determines that a hearing loss or vestibular abnormality is present he or she will provide recommendations for interventions or rehabilitation.
Presbycusis, or age-related hearing loss, is the cumulative effect of aging on hearing. It is a progressive and irreversible bilateral symmetrical age-related sensorineural hearing loss resulting from degeneration of the cochlea or associated structures of the inner ear or auditory nerves. The hearing loss is most marked at higher frequencies. Hearing loss that accumulates with age but is caused by factors other than normal aging is not presbycusis, although differentiating the individual effects of distinct causes of hearing loss can be difficult.

An audiogram is a graph that shows the audible threshold for standardized frequencies as measured by an audiometer. The Y axis represents intensity measured in decibels and the X axis represents frequency measured in hertz. The threshold of hearing is plotted relative to a standardised curve that represents 'normal' hearing, in dB(HL). They are not the same as equal-loudness contours, which are a set of curves representing equal loudness at different levels, as well as at the threshold of hearing, in absolute terms measured in dB SPL.

An audiometer is a machine used for evaluating hearing acuity. They usually consist of an embedded hardware unit connected to a pair of headphones and a test subject feedback button, sometimes controlled by a standard PC. Such systems can also be used with bone vibrators, to test conductive hearing mechanisms.
An Audiometrist or Audiometric Officer, is a health-care professional technician who has received special training in the use of Pure tone audiometry equipment. An audiometrist conducts hearing tests, or "audiometric screening", with an Audiometer to establish hearing levels. The results are represented by an audiogram, and are usually interpreted by an audiologist, or a registered Medical Officer, unless the audiometrist is also an audiologist, with the aim of diagnosing hearing loss.
The auditory brainstem response (ABR) is an auditory evoked potential extracted from ongoing electrical activity in the brain and recorded via electrodes placed on the scalp. The measured recording is a series of six to seven vertex positive waves of which I through V are evaluated. These waves, labeled with Roman numerals in Jewett and Williston convention, occur in the first 10 milliseconds after onset of an auditory stimulus. The ABR is considered an exogenous response because it is dependent upon external factors.
Arak University of Medical Sciences is one of the most prestigious Iranian medical schools located in Arak, Iran. This university is the main health care provider in Markazi province and one of the biggest universities central of Iran. The university was established by efforts of the director of regional organizations for Health in Markazi province and Majlis representative of Arak and authorities of Ministry of Health, Treatment and Medical Education. After getting the required permissions for the founding of Arak School of Medicine in 1987, and in February 1988 School of Medical Sciences commenced its activities with gathering the school of medicine and college of nursing and midwifery together with accepting 60 students in the medical field and was separated and did its activity independently in 1988.

Pure tone audiometry (PTA) is the key hearing test used to identify hearing threshold levels of an individual, enabling determination of the degree, type and configuration of a hearing loss and thus providing a basis for diagnosis and management. PTA is a subjective, behavioural measurement of a hearing threshold, as it relies on patient responses to pure tone stimuli. Therefore, PTA is only used on adults and children old enough to cooperate with the test procedure. As with most clinical tests, calibration of the test environment, the equipment and the stimuli to ISO standards is needed before testing proceeds. PTA only measures audibility thresholds, rather than other aspects of hearing such as sound localization and speech recognition. However, there are benefits to using PTA over other forms of hearing test, such as click auditory brainstem response (ABR). PTA provides ear specific thresholds, and uses frequency specific pure tones to give place specific responses, so that the configuration of a hearing loss can be identified. As PTA uses both air and bone conduction audiometry, the type of loss can also be identified via the air-bone gap. Although PTA has many clinical benefits, it is not perfect at identifying all losses, such as ‘dead regions’ of the cochlea and neuropathies such as auditory processing disorder (APD). This raises the question of whether or not audiograms accurately predict someone's perceived degree of disability.
Auditory processing disorder and rarely known as King-Kopetzky syndrome or auditory disability with normal hearing (ADN) is an umbrella term for a variety of disorders that affect the way the brain processes auditory information. Individuals with APD usually have normal structure and function of the outer, middle, and inner ear. However, they cannot process the information they hear in the same way as others do, which leads to difficulties in recognizing and interpreting sounds, especially the sounds composing speech. It is thought that these difficulties arise from dysfunction in the central nervous system.
Minimum audibility curve is a standardized graph of the threshold of hearing frequency for an average human, and is used as the reference level when measuring hearing loss with an audiometer as shown on an audiogram.
Marion Downs was an audiologist and Professor Emerita at the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver, who pioneered universal newborn hearing screening in the early 1960s, then spent more than 30 years trying to convince her peers to adopt the testing in hospitals and to place hearing aids on infants who showed hearing loss. She worked to alert the medical world to the developmental problems associated with childhood deafness. As a result of her efforts, 95 percent of all newborns in America today are screened for hearing loss. She devoted her professional life to the promotion of early identification of hearing loss in newborns, infants, and young children and to helping those handicapped by hearing impairment lead fulfilling lives.
Tele-audiology is the utilization of telemedicine to provide audiological services and may include the full scope of audiological practice.

Universal neonatal hearing screening (UNHS), also known as early hearing detection and intervention (EHDI) programs in several countries, refer to those services aimed at the early identification, intervention, and follow-up of infants and young children who are deaf or hard-of-hearing. It is a strategy for early detection of permanent congenital hearing loss. It describes the use of objective testing methods to screen the hearing of well newborns in a particular target region.
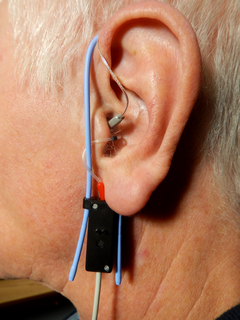
Real ear measurement is the measurement of sound pressure level in a patient's ear canal developed when a hearing aid is worn. It is measured with the use of a silicone probe tube inserted in the canal connected to a microphone outside the ear and is done to verify that the hearing aid is providing suitable amplification for a patient's hearing loss. The American Speech–Language–Hearing Association (ASHA) and American Academy of Audiology (AAA) recommend real ear measures as the preferred method of verifying the performance of hearing aids. Used by audiologists and other hearing healthcare practitioners in the process of hearing aid fitting, real ear measures are the most reliable and efficient method for assessing the benefit provided by the amplification. Measurement of the sound level in the ear canal allows the clinician to make informed judgements on audibility of sound in the ear and the effectiveness of hearing aid treatment.
Visual reinforcement audiometry (VRA) is a key behavioural test for evaluating hearing in young children. First introduced by Liden and Kankkunen in 1969, VRA is a good indicator of how responsive a child is to sound and speech and whether the child is developing awareness to sound as expected. Performed by an audiologist, VRA is the preferred behavioral technique for children that are 6 - 24 months of age. Using classic operant conditioning, a stimulus is presented, which is followed by a 90 degree head turn from midline by the child, resulting in the child being reinforced with an animation. The child is typically seated in a high chair or on a parent's lap while facing forward. A loud speaker or two are situated at 45 or 90 degrees from the child. As the auditory stimulus is presented, the child will naturally search for the sound source, resulting in a head turn and reinforcement is followed shortly after through an animated toy or video next to the speaker where the auditory stimulus was presented.. Using VRA, an audiologist can obtain minimal hearing thresholds ranging in frequencies from 250 Hz - 8000 Hz using speakers, headphones, inserts earphones or through a bone conduction transducer and plot them on an audiogram. The results from the audiogram, paired with other objective measures such as a Tympanogram, Otoacoustic emissions testing and/or Auditory Brainstem Response testing can provide further insight into the child's auditory hearing status as well as future treatment plans if deemed necessary. VRA works well until about 18-24 months of age. Above 18-24 months of age, children need more interesting tasks to hold their attention, which is when audiologists introduce Conditioned Play Audiometry.
Conditioned play audiometry (CPA) is a type of audiometry done in children from ages 2 to 5 years old, in developmental age. It is the test that directly follows visual reinforcement audiometry when the child becomes able to focus on a task. It is a type of behavioral hearing test, of which there are many.
An audiologist, according to the American Academy of Audiology, "is a person who, by virtue of academic degree, clinical training, and license to practice and/or professional credential, is uniquely qualified to provide a comprehensive array of professional services related to the prevention of hearing loss and the audiologic identification, assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of persons with impairment of auditory and vestibular function, and to the prevention of impairments associated with them."








