Related Research Articles

Cholesteatoma is a destructive and expanding growth consisting of keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear and/or mastoid process. Cholesteatomas are not cancerous as the name may suggest, but can cause significant problems because of their erosive and expansile properties. This can result in the destruction of the bones of the middle ear (ossicles), as well as growth through the base of the skull into the brain. They often become infected and can result in chronically draining ears. Treatment almost always consists of surgical removal.
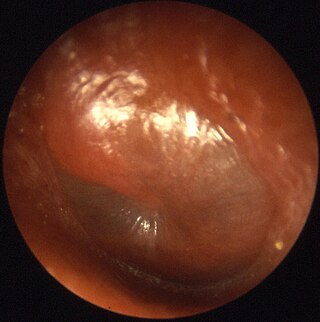
In the anatomy of humans and various other tetrapods, the eardrum, also called the tympanic membrane or myringa, is a thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Its function is to transmit sound from the air to the ossicles inside the middle ear, and then to the oval window in the fluid-filled cochlea. Hence, it ultimately converts and amplifies vibration in the air to vibration in cochlear fluid. The malleus bone bridges the gap between the eardrum and the other ossicles.
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, increased crying, and poor sleep. Decreased eating and a fever may also be present. The other main type is otitis media with effusion (OME), typically not associated with symptoms, although occasionally a feeling of fullness is described; it is defined as the presence of non-infectious fluid in the middle ear which may persist for weeks or months often after an episode of acute otitis media. Chronic suppurative otitis media (CSOM) is middle ear inflammation that results in a perforated tympanic membrane with discharge from the ear for more than six weeks. It may be a complication of acute otitis media. Pain is rarely present. All three types of otitis media may be associated with hearing loss. If children with hearing loss due to OME do not learn sign language, it may affect their ability to learn.

In anatomy, the Eustachian tube, also known as the auditory tube or pharyngotympanic tube, is a tube that links the nasopharynx to the middle ear, of which it is also a part. In adult humans, the Eustachian tube is approximately 35 mm (1.4 in) long and 3 mm (0.12 in) in diameter. It is named after the sixteenth-century Italian anatomist Bartolomeo Eustachi.
Rhinoplasty, commonly called nose job, medically called nasal reconstruction is a plastic surgery procedure for altering and reconstructing the nose. There are two types of plastic surgery used – reconstructive surgery that restores the form and functions of the nose and cosmetic surgery that changes the appearance of the nose. Reconstructive surgery seeks to resolve nasal injuries caused by various traumas including blunt, and penetrating trauma and trauma caused by blast injury. Reconstructive surgery can also treat birth defects, breathing problems, and failed primary rhinoplasties. Rhinoplasty may remove a bump, narrow nostril width, change the angle between the nose and the mouth, or address injuries, birth defects, or other problems that affect breathing, such as a deviated nasal septum or a sinus condition. Surgery only on the septum is called a septoplasty.
A stapedectomy is a surgical procedure of the middle ear performed in order to improve hearing.

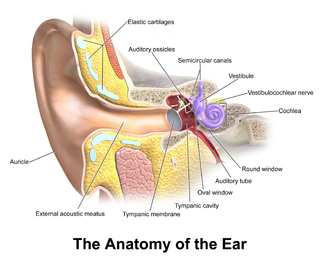
An ear is the organ that enables hearing and, in mammals, body balance using the vestibular system. In mammals, the ear is usually described as having three parts—the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible portion of the ear in most animals, the word "ear" often refers to the external part alone. The middle ear includes the tympanic cavity and the three ossicles. The inner ear sits in the bony labyrinth, and contains structures which are key to several senses: the semicircular canals, which enable balance and eye tracking when moving; the utricle and saccule, which enable balance when stationary; and the cochlea, which enables hearing. The ears of vertebrates are placed somewhat symmetrically on either side of the head, an arrangement that aids sound localization.

Conductive hearing loss (CHL) occurs when there is a problem transferring sound waves anywhere along the pathway through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear (ossicles). If a conductive hearing loss occurs in conjunction with a sensorineural hearing loss, it is referred to as a mixed hearing loss. Depending upon the severity and nature of the conductive loss, this type of hearing impairment can often be treated with surgical intervention or pharmaceuticals to partially or, in some cases, fully restore hearing acuity to within normal range. However, cases of permanent or chronic conductive hearing loss may require other treatment modalities such as hearing aid devices to improve detection of sound and speech perception.
A myringotomy is a surgical procedure in which an incision is created in the eardrum to relieve pressure caused by excessive buildup of fluid, or to drain pus from the middle ear. A tympanostomy tube may be inserted through the eardrum to keep the middle ear aerated for a prolonged time and to prevent reaccumulation of fluid. Without the insertion of a tube, the incision usually heals spontaneously within two to three weeks. Depending on the type, the tube is either naturally extruded in 6 to 12 months or removed during a minor procedure.

Tympanoplasty is the surgical operation performed to reconstruct hearing mechanism of middle ear.

A nasal septum perforation is a medical condition in which the nasal septum, the bony/cartilaginous wall dividing the nasal cavities, develops a hole or fissure.

Tympanostomy tube, also known as a grommet or myringotomy tube, is a small tube inserted into the eardrum in order to keep the middle ear aerated for a prolonged period of time, and to prevent the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear. The operation to insert the tube involves a myringotomy and is performed under local or general anesthesia. The tube itself is made in a variety of designs. The most commonly used type is shaped like a grommet. When it is necessary to keep the middle ear ventilated for a very long period, a "T"-shaped tube may be used, as these "T-tubes" can stay in place for 2–4 years. Materials used to construct the tube are most often plastics such as silicone or Teflon. Stainless steel tubes exist, but are no longer in frequent use.

Mastoiditis is the result of an infection that extends to the air cells of the skull behind the ear. Specifically, it is an inflammation of the mucosal lining of the mastoid antrum and mastoid air cell system inside the mastoid process. The mastoid process is the portion of the temporal bone of the skull that is behind the ear. The mastoid process contains open, air-containing spaces. Mastoiditis is usually caused by untreated acute otitis media and used to be a leading cause of child mortality. With the development of antibiotics, however, mastoiditis has become quite rare in developed countries where surgical treatment is now much less frequent and more conservative, unlike former times.

The tympanic cavity is a small cavity surrounding the bones of the middle ear. Within it sit the ossicles, three small bones that transmit vibrations used in the detection of sound.

A perforated eardrum is a hole in the eardrum. It can be caused by infection, trauma, overpressure, inappropriate ear clearing, and changes in middle ear pressure. An otoscope can be used to view the eardrum to diagnose a perforation. Perforations may heal naturally, or require surgery.
Chronic atrophic rhinitis, or simply atrophic rhinitis, is a chronic inflammation of the nose characterised by atrophy of nasal mucosa, including the glands, turbinate bones and the nerve elements supplying the nose. Chronic atrophic rhinitis may be primary and secondary. Special forms of chronic atrophic rhinitis are rhinitis sicca anterior and ozaena. It can also be described as the empty nose syndrome.
Otomycosis is a fungal ear infection, a superficial mycotic infection of the outer ear canal cause by micro-organisms called fungi which are related to yeast and mushrooms. It is more common in tropical or warm countries. The infection may be either subacute or acute and is characterized by itching in the ear, malodorous discharge, inflammation, pruritus, scaling, and severe discomfort or ear pain. The mycosis results in inflammation, superficial epithelial exfoliation, masses of debris containing hyphae, suppuration, and pain. Otomycosis can also cause hearing loss.

Tympanosclerosis is a condition caused by hyalinization and subsequent calcification of subepithelial connective tissue of the tympanic membrane and middle ear, sometimes resulting in a detrimental effect to hearing.
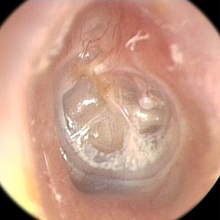
Tympanic membrane retraction describes a condition in which a part of the eardrum lies deeper within the ear than its normal position.
Eustachian tube dysfunction (ETD) is a disorder where pressure abnormalities in the middle ear result in symptoms.
References
- 1 2 Watson, Glenn. "Myringoplasty repairs a hole in the tympanic membrane". Glenn Watson Pty. Archived from the original on 21 December 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Operations and Procedures: Myringoplasty". ENT Surgeon. Archived from the original on 10 January 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2012.
- ↑ Rozendorn, Noa; Wolf, Michael; Yakirevich, Arkadi; Shapira, Yisgav; Carmel, Eldar (November 2016). "Myringoplasty in children". International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology. 90: 245–250. doi:10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.09.024. ISSN 0165-5876. PMID 27729143.