
Belgaum is a city in the Indian state of Karnataka located in its northern part along the Western Ghats. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Belagavi division and Belagavi district. The Government of Karnataka has proposed making Belgaum the second capital of Karnataka alongside Bangalore, hence a second state administrative building Suvarna Vidhana Soudha was inaugurated on 11 October 2012.

Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP) is the administrative body responsible for civic amenities and some infrastructural assets of the Greater Bengaluru metropolitan area. It is the fourth largest Municipal Corporation in India and is responsible for a population of 8.4 million in an area of 741 km2. Its boundaries have expanded more than 10 times over the last six decades.

The Government of Karnataka, abbreviated as GoK, or simply Karnataka Government, formerly Government of Mysore, is a democratically elected state body with the governor as the ceremonial head to govern the Southwest Indian state of Karnataka. The governor who is appointed for five years appoints the chief minister and on the advice of the chief minister appoints his council of ministers. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day-to-day running of the government is taken care of by the chief minister and his council of ministers in whom a great amount of legislative powers are vested.

The Mangalore City Corporation is the municipal corporation responsible for overseeing the local administration of the Indian city of Mangalore and it's suburbs, which are a major urban area and the most important port city of Karnataka state. The mechanism of municipal corporation was introduced in British India, with formation of the municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) in 1762. It consists of a legislative and an executive body. The legislative body is headed by the Mayor, while the executive body is headed by a Chief Commissioner.
A municipal corporation is a type of local government in India which administers urban areas with a population of more than one million. The growing population and urbanization of various Indian cities highlighted the need for a type of local governing body that could provide services such as healthcare, education, housing and transport by collecting property taxes and administering grants from the state government.
The Ulhasnagar Municipal Corporation (UMC) is the governing body of the city of Ulhasnagar in the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is part of the Mumbai Metropolitan Region and Thane district (Urban) in Konkan division. It has 78 members. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Ulhasnagar Municipal Corporation is headed by Mayor of city and governed by Commissioner. Ulhasnagar Municipal Corporation has been formed with functions to improve the infrastructure of town.

Mysuru City Corporation (MCC) is the administrative body responsible for civic amenities and infrastructural assets of Mysuru in Karnataka, India. It is the third-largest municipal corporation in Karnataka, serving a population of 1,000,000 in an area of 235 km2. The city's boundaries have expanded more than twice between 2010 and 2020.

Municipal Corporation of the City of Hubballi-Dharward or Hubballi-Dharwad Municipal Corporation (HDMC) is the Municipal Corporation responsible for the civic infrastructure and administration of the twin cities of Hubballi and Dharwad, located in North Western part of Karnataka state in India. The organization is known, in short, as HDMC. This civic administrative body administers an area of 213 km2. HDMC consists of 82 elected members from four Vidhan Sabha constituencies of Hubballi-Dharwad. Presently the Council is under suspended animation pending election of new members. There has been a huge demand by people of Dharwad to create a separate civic body and get itself detached by HDMC. Claims are that most of the funds are allocated to Hubballi solely.

Shimla Municipal Corporation (SMC) is the municipal corporation of Shimla, the capital of Himachal Pradesh, and is the chief nodal agency for the administration of the city. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Shimla Municipal Corporation is headed by Mayor of city and governed by Commissioner. Shimla Municipal Corporation has been formed with functions to improve the infrastructure of town.

Tirupati Municipal Corporation is the civic body that governs the city of Tirupati in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the three corporations in the state, alongside Kakinada and Visakhapatnam to feature in Smart City project. Established in the year 2007, the executive power of the TMC is vested in the Municipal Commissioner, an Indian Administrative Service (IAS) officer appointed by the Government of Andhra Pradesh. The position is held by Anupama Anjali. Dr. BR.Shirisha Yadav (YSRCP) was elected as the Mayor and M.Narayana (YSRCP) as the Deputy Mayor by the newly elected general body in March 2021.Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762.
Ujjain Municipal Corporation is the governing body of the city of Ujjain in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh.

Junagadh Municipal Corporation is the civic body governing Indian city of Junagadh. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Junagadh Municipal Corporation is headed by Mayor of city and governed by Commissioner.

Kalaburagi City Corporation (KCC) is the municipal corporation responsible for looking after the city administration of the Indian city of Kalaburagi. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. It consists of a legislative and an executive body. The legislative body is headed by the city mayor while the executive body is headed by a Chief Commissioner.
Bhagalpur Municipal Corporation is the municipal corporation governing Indian city of Bhagalpur. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Bhagalpur Municipal Corporation is headed by Mayor of city and governed by Commissioner.

Bhavnagar Municipal Corporation is the civic body governing Indian city of Bhavnagar. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Bhavnagar Municipal Corporation is headed by Mayor of city and governed by Commissioner.

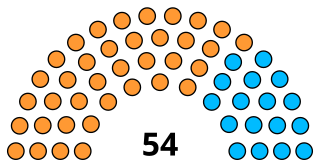
The 2010 Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike election was held on 4 April 2010 in all 198 Wards of Bangalore

The 2015 Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike election was held on 22 April 2015 in all 198 Wards of Bangalore (Bengaluru).
Chowdeshwari Ward, is one of the 198 Wards of Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike, an administrative body responsible for civic amenities and some infrastructural assets of the Greater Bangalore metropolitan area in the Indian state of Karnataka.

Davanagere City Corporation (DCC) is the civic organisation that manages the municipal affairs of Davanagere City in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is the 6th largest Urban Local Body in Karnataka. The town administration of Davanagere city was upgraded as a Municipality in c.1870 and later as a City Corporation on 6 January 2006. The Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with the formation of municipal corporations in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. It has a territorial area of 68.63 km2 and a population of 4,34,971, as per the 2011 Census of India. The territorial limits of the City Corporation fall under the Davanagere North and Davanagere South legislative assembly constituencies.

Firozabad Municipal Corporation is the municipal corporation governing Indian city of Firozabad. Municipal Corporation mechanism in India was introduced during British Rule with formation of municipal corporation in Madras (Chennai) in 1688, later followed by municipal corporations in Bombay (Mumbai) and Calcutta (Kolkata) by 1762. Firozabad Municipal Corporation is headed by Mayor of city and governed by Commissioner.


















