
The Byelorussian SSR was one of only two Soviet republics to be separate members of the United Nations. Both republics and the Soviet Union joined the UN when the organization was founded in 1945.
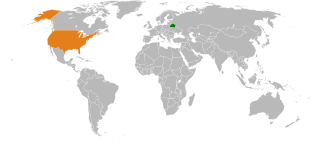
Interstate relations between the United States and Belarus began in 1991 upon the dissolution of the Soviet Union, of which Belarus had been a part. However, the relations have turned negative due to accusations by the United States that Belarus has been violating human rights. Belarus, in turn, has accused the United States of interfering in its internal affairs.

The Republic of Abkhazia is a partially recognized state in the South Caucasus which declared independence from Georgia during the War in Abkhazia (1992–1993). At the time, the Soviet Union had recently collapsed (1991).
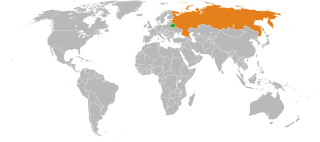
Belarus and Russia share a land border and constitute the supranational Union State. Several treaties have been concluded between the two nations bilaterally. Russia is Belarus' largest and most important economic and political partner. Both are members of various international organizations, including the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Eurasian Economic Union, the Collective Security Treaty Organization, and the United Nations.

Belarus and Ukraine both are full members of the Baku Initiative and Central European Initiative. In 2020, during the Belarusian protests against president Lukashenko, the relationship between Ukraine and Belarus began to deteriorate, after the Ukrainian government criticized Belarusian president Alexander Lukashenko. In the waning days of 2021, the relationship between both countries rapidly deteriorated, culminating in a full-scale invasion on 24 February 2022. Belarus has allowed the stationing of Russian troops and equipment in its territory and its use as a springboard for offensives into northern Ukraine but has denied the presence of Belarusian troops in Ukraine. Even though part of the Russian invasion was launched from Belarus, Ukraine did not break off diplomatic relations with Belarus, but remain frozen. In July 2024, Lukashenko described Ukraine as an enemy.

Belarus and Lithuania established diplomatic relations on 24 October 1991, shortly after the dissolution of the Soviet Union. The two countries share 680 kilometres (420 mi) of common border.

Relations between Azerbaijan and Belarus are at very high level that Belarusian president Alexander Lukashenko describes Azerbaijan as a "saver" of independence and sovereignty of Belarus and adds that "there's not anything close" in Azerbaijani-Belarusian relations. Both countries were part of the Russian Empire until 1918 and before 1991, they were part of the Soviet Union. Azerbaijan has an embassy in Minsk and Belarus has an embassy in Baku. Both countries are full members of the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). Azerbaijan is a full member of the Council of Europe, Belarus is a candidate. Both Azerbaijan and Belarus are full members of the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM). There are more than 6,000 Azerbaijanis living in Belarus.

Romania–Saudi Arabia relations are foreign, economic and cultural relations between Romania and Saudi Arabia. Romania has an embassy in Riyadh and an honorary consulate in Jeddah. Saudi Arabia has an embassy in Bucharest.

Norway–Romania relations are foreign relations between Norway and Romania. Both countries established diplomatic relations on April 3, 1917. Norway has an embassy in Bucharest and an honorary consulate in Constanţa. Romania has an embassy in Oslo and 4 honorary consulates.

Belarus and Israel established diplomatic relations in 1992. In 1947, Belarus voted in favor for the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine. Belarus operates an embassy in Tel Aviv, while Israel operates an embassy in Minsk. Around 130,000 Belarusian citizens immigrated to Israel during the 1990s under the Law of Return.
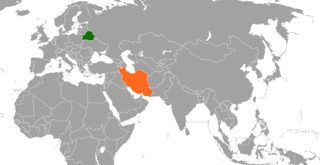
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic recognized de facto the Islamic Republic of Iran in February 1979, and Belarus and Iran established de jure diplomatic relations in 1992. Belarus has an embassy in Tehran. Iran has an embassy in Minsk.

Belarus has an embassy in Ashgabat. Turkmenistan has an embassy in Minsk. Both countries are full members of the UN, and the OSCE. Belarus is a full member and Turkmenistan is associated with the CIS. Currently, the ambassador of Turkmenistan to Belarus is Murad Yazberdyev. The Belarusian Ambassador to Turkmenistan is Oleg Tabanyuhov.

Diplomatic relations between Belarus and Uzbekistan were established on 21 January 1993, with the Belarusian Embassy in Tashkent being opened in February 1994. Uzbekistan also has an embassy in Minsk.

Belarus and Libya established diplomatic relations in 1992. Belarus has an embassy in Tripoli. Libya has an embassy in Minsk.
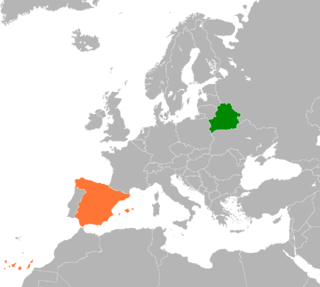
The bilateral relations maintained between Spain and Belarus are scarce.

The Embassy of Belarus in London is the diplomatic mission of Belarus in the United Kingdom. It is situated just south of Kensington Gardens between the Embassy of Azerbaijan and the Embassy of Mongolia.

The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic recognized Bangladesh's independence on 24 January 1972. Official diplomatic relations between Bangladesh and Belarus were established in 1992. Neither country has a resident ambassador.

Belarus and Malaysia established diplomatic relations in 1992. Neither country has a resident ambassador. Belarus embassy in Jakarta is accredited to Malaysia. Both countries are members of the Non-Aligned Movement.

Pakistan was one of the first countries to recognise Belarus after the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. Pakistan maintains an embassy in Minsk; Belarus maintains an embassy in Islamabad.

Hungary–Kurdistan Region relations are bilateral relations between Hungary and the Kurdistan Region. Hungary is represented in Kurdistan Region through a consulate general since November 2014, while Kurdistan Region has no representation in Hungary. Relations are characterized by several high-level talks and close ties. The Kurdish President Massoud Barzani visited Hungary in 2012 and in 2015 on official visits. Moreover, Hungarian Prime Minister Viktor Orbán uttered support for the independence of Kurdistan Region from Iraq in 2015 causing concern among the Islamic Supreme Council of Iraq.





















