Related Research Articles

Agapanthus is a genus of plants, the only one in the subfamily Agapanthoideae of the family Amaryllidaceae. The family is in the monocot order Asparagales. The name is derived from Greek: ἀγάπη, ἄνθος.

Pinus taeda, commonly known as loblolly pine, is one of several pines native to the Southeastern United States, from East Texas to Florida, and north to southern New Jersey. The wood industry classifies the species as a southern yellow pine. U.S. Forest Service surveys found that loblolly pine is the second-most common species of tree in the United States, after red maple. For its timber, the pine species is regarded as the most commercially important tree in the Southeastern U.S. The common name loblolly is given because the pine species is found mostly in lowlands and swampy areas.
Edgar Shannon Anderson was an American botanist. He introduced the term introgressive hybridization and his 1949 book of that title was an original and important contribution to botanical genetics. His work on the transfer and origin of adaptations through natural hybridization continues to be relevant.

Nomocharis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Liliaceae. It consists of about 7 species native to montane regions of western China, Myanmar, and northern India. They are similar to Lilium, with one of the more obvious differences being the flowers being more shallow or sometimes flat.

Tulipa clusiana, the lady tulip, is an Asian species of tulip native to Afghanistan, Iran, Iraq, Pakistan and the western Himalayas. It is widely cultivated as an ornamental and is reportedly naturalized in France, Spain, Portugal, Italy, Tunisia, Greece, and Turkey.

Eucomis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae, native to southern Africa. Most species of this genus are commonly referred to as pineapple flowers or pineapple lilies. They are bulbous perennials with basal rosettes of leaves and stout stems covered in star-shaped flowers with a tuft of green bracts at the top, superficially resembling a pineapple – hence the common names.

Nerine masoniorum is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaryllidaceae, subfamily Amaryllidoideae, native to the eastern Cape Province of South Africa. It is a bulbous perennial belonging to the group of nerines that have narrow evergreen foliage. The thread-like leaves reach a length of 25 cm or more. The flowering stem is 15–25 cm tall, with up to 11 flowers arranged in an umbel. Each flower has six narrow pink tepals with wavy edges. It flowers in late summer in cultivation, the first of the nerines to do so. It has received the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.

Tulista is a small genus of succulent plants endemic to the Cape Provinces of South Africa. They were formerly included within the genus Haworthia.

Eucomis montana is a plant species in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae, found in South Africa and Eswatini (Swaziland). When in flower in summer, the plant reaches a height of up to 45 cm, with a dense spike (raceme) of greenish flowers, topped by a "head" of green bracts.
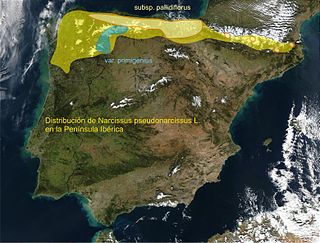
Narcissus primigenius is a species of the genus Narcissus (Daffodils) in the family Amaryllidaceae. It is classified in Section Pseudonarcissus. It is native to northwest Spain.
Graham Dugald Duncan(born 1959) is a South African botanist and specialist bulb horticulturalist at the Kirstenbosch National Botanical Garden, Cape Town, South Africa.

Tulipa alberti, or Albert's tulip, is a species of flowering plant in the family Liliaceae. It has long reddish, orange or pink flowers. It comes from the mountains of Central Asia.
Sulla is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It includes eight species of annual herbs native to the Mediterranean Basin, including southern Europe, North Africa, and western Asia. They grow in dry Mediterranean-climate shrubland, bushland, thicket, and grassland and in semi-desert. The genus belongs to subfamily Faboideae.

The taxonomy of Tulipa places the genus in the family Liliaceae, and subdivides it as four subgenera, and comprises about 75 species.

Herbert George Baker was a British-American botanist and evolutionary ecologist who was an authority on pollination biology and breeding systems of angiosperms. He described what became known as "Baker's rule," a theoretical proposal underpinning an empirical observation that the ability to self-fertilize improves colonization ability among plants by increasing the probability of successful establishment after long-distance dispersal. He collaborated with his wife, Irene Baker, studying the content and function of nectar, and undertaking research and publishing papers on its evolutionary and taxonomic significance.

Eucomis regia is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae, native to the Cape Provinces of South Africa. It is sometimes cultivated, but requires protection in a greenhouse in temperate climates.
Eucomis grimshawii is a species of flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae, native to the Cape Provinces. It was first described by Graham Duncan and Ben Zonneveld in 2010.
Eucomis humilis is a species of flowering plant in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Scilloideae, native to KwaZulu-Natal and Lesotho. It was first described by Baker in 1895. The greenish to purplish flowers appear in summer and are arranged in a spike (raceme), topped by a "head" of green leaflike bracts. Cultivated as an ornamental plant, it can be grown successfully outside where frosts are not too severe.

Daniel Lee Nickrent is an American botanist, working in plant evolutionary biology, including the subdisciplines of genomics, phylogenetics, systematics, population genetics, and taxonomy. A major focus has been parasitic flowering plants, particularly of the sandalwood order (Santalales). His interest in photographic documentation and photographic databases has led to several photographic databases including Parasitic Plant Connection, Phytoimages, Plant Checklist for the Rocky Mountain National Park, and Plant Checklist for the Crab Orchard National Wildlife Refuge.
References
- ↑ Genome size of wild tulips determined. University of Leiden. 26 August 2009
- ↑ Harvard Botanist Index
- ↑ "Biomed Experts.B J M Zonneveld". Archived from the original on 2014-12-04. Retrieved 2014-11-29.
- ↑ Microsoft Academic Search Archived December 5, 2014, at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ International Plant Names Index. Zonn.