Related Research Articles
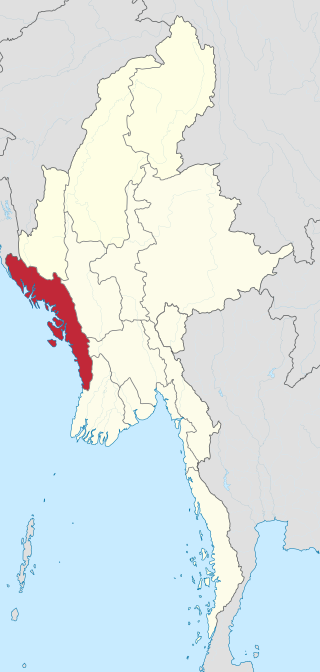
Rakhine State is a state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Region to the east, the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Chittagong Division of Bangladesh to the northwest. It is located approximately between latitudes 17°30' north and 21°30' north and longitudes 92°10' east and 94°50' east. The Arakan Mountains or Rakhine Yoma separated Rakhine State from central Burma from North to South. Off the coast of Rakhine State there are some fairly large islands such as Ramree, Cheduba and Myingun. Rakhine State has an area of 36,762 square kilometres (14,194 sq mi) and its capital is Sittwe.

Sittwe is the capital of Rakhine State, Myanmar (Burma). Sittwe, pronounced sait-tway in the Rakhine language, is located on an estuarial island created at the confluence of the Kaladan, Mayu, and Lay Mro rivers emptying into the Bay of Bengal. As of 2006 the city has 181,000 inhabitants. It is the administrative seat of Sittwe Township and Sittwe District.

The Rohingya people are a stateless Indo-Aryan ethnic group who predominantly follow Islam and reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar. Before the Rohingya genocide in 2017, when over 740,000 fled to Bangladesh, an estimated 1.4 million Rohingya lived in Myanmar. Described by journalists and news outlets as one of the most persecuted minorities in the world, the Rohingya are denied citizenship under the 1982 Myanmar nationality law. There are also restrictions on their freedom of movement, access to state education and civil service jobs. The legal conditions faced by the Rohingya in Myanmar have been compared to apartheid by some academics, analysts and political figures, including Nobel laureate Bishop Desmond Tutu, a South African anti-apartheid activist. The most recent mass displacement of Rohingya in 2017 led the International Criminal Court to investigate crimes against humanity, and the International Court of Justice to investigate genocide.

Hinduism is the Fourth-largest religion in Myanmar, being practised by 1.7% of the population of Myanmar. Hinduism is practised by about 890,000 people in Myanmar, and has been influenced by elements of Buddhism, with many Hindu temples in Myanmar housing statues of the Buddha. There are also a large population of Hindus in which the Myanmar Tamils and minority Bengali Hindus having the biggest population share.

Operation Dragon King, officially known as Operation Nagamin in English, was a military operation carried in 1978 out by the Tatmadaw and immigration officials in northern Arakan, Burma, during the socialist rule of Ne Win.

The Rakhine, also known as the Arakanese, are a Southeast Asian ethnic group in Myanmar (Burma) forming the majority along the coastal region of present-day Rakhine State, although Rakhine communities also exist throughout the country, particularly in Ayeyarwady and Yangon Regions. They constitute approximately 5.53% or more of Myanmar's total population, but no accurate census figures exist. Smaller Rakhine communities exist in Bangladesh's Chittagong Hill Tracts and in India, where they are known as the Marma and Mog peoples respectively.

Islam is a minority religion in Myanmar, practised by about 2.1% of the population, according to the 2014 Myanmar official statistics.
Myanmar (Burma) is a Buddhist majority country with a significant minority of Christians and other groups residing in the country.
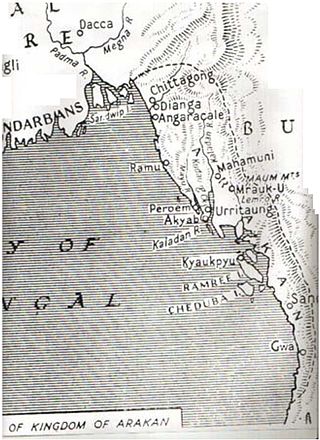
Rakhine State occupies the northern coastline of Myanmar up to the border with Bangladesh and corresponds to the historical Kingdom of Arakan. The history of Rakhine is divided into 7 parts - the independent kingdoms of Dhanyawadi, Waithali, Lemro, Mrauk U, Burmese occupation from 1785 to 1826, British rule from 1826 to 1948 and as a part of independent Burma from 1948.

The Kingdom of Mrauk-U was a kingdom that existed on the Arakan littoral from 1429 to 1785. Based in the capital Mrauk-U, near the eastern coast of the Bay of Bengal, the kingdom ruled over what is now Rakhine State, Myanmar and southern part of Chittagong Division, Bangladesh. Though started out as a protectorate of the Bengal Sultanate from 1429 to 1531, Mrauk-U went on to conquer Chittagong with the help of the Portuguese. It twice fended off the Toungoo Burma's attempts to conquer the kingdom in 1546–1547, and 1580–1581. At its height of power, it briefly controlled the Bay of Bengal coastline from the Sundarbans to the Gulf of Martaban from 1599 to 1603. In 1666, it lost control of Chittagong after a war with the Mughal Empire. Its reign continued until 1785, when it was conquered by the Konbaung dynasty of Burma.

The Rohingya conflict is an ongoing conflict in the northern part of Myanmar's Rakhine State, characterised by sectarian violence between the Rohingya Muslim and Rakhine Buddhist communities, a military crackdown on Rohingya civilians by Myanmar's security forces, and militant attacks by Rohingya insurgents in Buthidaung, Maungdaw, and Rathedaung Townships, which border Bangladesh.

Rakhine, also known as Arakanese, is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken in western Myanmar, primarily in the Rakhine State. Closely related to Burmese, the language is spoken by the Rakhine and Marma peoples; it is estimated to have around one million native speakers and it is spoken as a second language by a further million.

Bengal is a region in South Asia, politically split between Bangladesh and India. Due to its long history and complicated political divisions, various names have been used to refer to the region and its subsections. The name Bangla is used by both Bangladesh and West Bengal in international contexts. In the Bengali language, the two Bengals each use a different term to refer to the nominally identified nation: Bānglā and Baṅga

The Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA), formerly known as Harakah al-Yaqin, is a Rohingya insurgent group active in northern Rakhine State, Myanmar. According to a December 2016 report by the International Crisis Group, it is led by Ataullah abu Ammar Jununi, a Rohingya man who was born in Karachi, Pakistan, and grew up in Mecca, Saudi Arabia. Other members of its leadership include a committee of Rohingya émigrés in Saudi Arabia.
The following lists events in the year 2017 in Myanmar.

The Rohingya genocide is a series of ongoing persecutions and killings of the Muslim Rohingya people by the military of Myanmar. The genocide has consisted of two phases to date: the first was a military crackdown that occurred from October 2016 to January 2017, and the second has been occurring since August 2017. The crisis forced over a million Rohingya to flee to other countries. Most fled to Bangladesh, resulting in the creation of the world's largest refugee camp, while others escaped to India, Thailand, Malaysia, and other parts of South and Southeast Asia, where they continue to face persecution. Many other countries consider these events ethnic cleansing.
Violent clashes have been ongoing in the northern part of Myanmar's Rakhine State since October 2016. Insurgent attacks by the Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA) have led to sectarian violence perpetrated by Myanmar's military and the local Buddhist population against predominantly Muslim Rohingya civilians. The conflict has sparked international outcry and was described as an ethnic cleansing by the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights. In August 2017, the situation worsened and hundreds of thousands of refugees fled Myanmar into Bangladesh, with an estimated 500,000 refugees having arrived by 27 September 2017. In January 2019, Arakan Army insurgents raided border police posts in Buthidaung Township, joining the conflict and beginning their military campaign in northern Rakhine State against the Burmese military.

Arakan is the historical geographical name of Rakhine State, Myanmar. The region was called Arakan for centuries until the Burmese military junta changed its name in 1989. The people of the region were known as Arakanese.

On 25 August 2017, Hindu villages in a cluster known as Kha Maung Seik in the northern Maungdaw District of Rakhine State in Myanmar were attacked and 99 Bengali Hindu villagers were massacred by Muslim insurgents from the Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA). A month later, the Myanmar Army discovered mass graves containing the corpses of 45 Hindus, most of whom were women and children.

Inn Din is a village in northern Rakhine State, Myanmar. The village is in an area of mixed ethnicity, including Rohingya and ethnic Rakhine people. In December 2017, a mass grave with ten Rohingya men was discovered near the Inn Din cemetery. In January 2018, the Myanmar military admitted that its soldiers and Rakhine paramilitaries had killed the ten Rohingyas in September of the previous year.
References
- ↑ Bhattacharya, Swapna (22–23 November 2005). Islam in Arakan: An interpretation from the Indian perspective: History and the Present. Arakan Historical Conference. Bangkok. p. 20. Archived from the original on 1 September 2017. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ↑ "Advances Reconciliation and Peacebuilding in Sittwe, Rakhine State, Myanmar" (PDF). Religions for Peace. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ↑ "'Mass graves' for Myanmar's Rohingya". Al Jazeera. 9 August 2012. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- ↑ "Collective Memories of Repatriates from Burma: A Case Study of West Bengal" (PDF). Mahanirban Calcutta Research Group. Retrieved 9 September 2017.