Related Research Articles

An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ACID, for "anode current into device". The direction of conventional current in a circuit is opposite to the direction of electron flow, so electrons flow from the anode of a galvanic cell, into an outside or external circuit connected to the cell. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a "+" is the cathode.

Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference and identifiable chemical change. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte.

In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of elements from naturally occurring sources such as ores using an electrolytic cell. The voltage that is needed for electrolysis to occur is called the decomposition potential. The word "lysis" means to separate or break, so in terms, electrolysis would mean "breakdown via electricity."
Extractive metallurgy is a branch of metallurgical engineering wherein process and methods of extraction of metals from their natural mineral deposits are studied. The field is a materials science, covering all aspects of the types of ore, washing, concentration, separation, chemical processes and extraction of pure metal and their alloying to suit various applications, sometimes for direct use as a finished product, but more often in a form that requires further working to achieve the given properties to suit the applications.
The Hall–Héroult process is the major industrial process for smelting aluminium. It involves dissolving aluminium oxide (alumina) in molten cryolite and electrolyzing the molten salt bath, typically in a purpose-built cell. The Hall–Héroult process applied at industrial scale happens at 940–980 °C and produces 99.5–99.8% pure aluminium. Recycling aluminum requires no electrolysis, thus it is not treated in this way.

Industrial processes are procedures involving chemical, physical, electrical, or mechanical steps to aid in the manufacturing of an item or items, usually carried out on a very large scale. Industrial processes are the key components of heavy industry.
The chloralkali process is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride (NaCl) solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide, which are commodity chemicals required by industry. Thirty five million tons of chlorine were prepared by this process in 1987. The chlorine and sodium hydroxide produced in this process are widely used in the chemical industry.
The Betterton-Kroll Process is a pyrometallurgical process for refining lead from lead bullion. Developed by William Justin Kroll in 1922, the Betterton–Kroll process is one of the final steps in conventional lead smelting. After gold, copper, and silver are removed from the lead, significant amounts of bismuth and antimony remain. The Betterton–Kroll process is used to remove these impurities. In the process, calcium and magnesium are added to the molten lead at temperatures around 380 °C. The calcium and magnesium react with the bismuth and antimony in the bullion to form alloys with a higher melting point, which then can be skimmed off of the surface. This process leaves behind lead with less than 0.01 percent bismuth by weight. The process is crucial to cheap industrial lead smelting and offers significant advantages over more expensive processes like the Betts Electrolytic process and fractional crystallization.

An electrolytic process is the use of electrolysis industrially to refine metals or compounds at a high purity and low cost. Some examples are the Hall-Héroult process used for aluminium, or the production of hydrogen from water. Electrolysis is usually done in bulk using hundreds of sheets of metal connected to an electric power source. In the production of copper, these pure sheets of copper are used as starter material for the cathodes, and are then lowered into a solution such as copper sulphate with the large anodes that are cast from impure copper. The copper from the anodes is electroplated on to the cathodes, while any impurities settle to the bottom of the tank. This forms cathodes of 99.999% pure copper.

The Castner process is a process for manufacturing sodium metal by electrolysis of molten sodium hydroxide at approximately 330 °C. Below that temperature, the melt would solidify; above that temperature, the molten sodium would start to dissolve in the melt.

Electrowinning, also called electroextraction, is the electrodeposition of metals from their ores that have been put in solution via a process commonly referred to as leaching. Electrorefining uses a similar process to remove impurities from a metal. Both processes use electroplating on a large scale and are important techniques for the economical and straightforward purification of non-ferrous metals. The resulting metals are said to be electrowon.
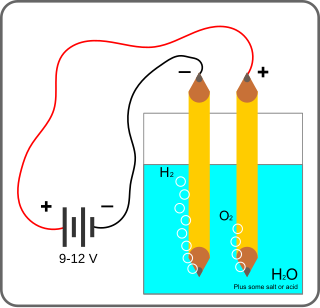
Electrolysis of water is using electricity to split water into oxygen and hydrogen gas by electrolysis. Hydrogen gas released in this way can be used as hydrogen fuel, but must be kept apart from the oxygen as the mixture would be extremely explosive. Separately pressurised into convenient 'tanks' or 'gas bottles', hydrogen can be used for oxyhydrogen welding and other applications, as the hydrogen / oxygen flame can reach approximately 2,800°C.

Electrometallurgy is a method in metallurgy that uses electrical energy to produce metals by electrolysis. It is usually the last stage in metal production and is therefore preceded by pyrometallurgical or hydrometallurgical operations. The electrolysis can be done on a molten metal oxide which is used for example to produce aluminium from aluminium oxide via the Hall-Hérault process. Electrolysis can be used as a final refining stage in pyrometallurgical metal production (electrorefining) and it is also used for reduction of a metal from an aqueous metal salt solution produced by hydrometallurgy (electrowinning).
In metallurgy, refining consists of purifying an impure metal. It is to be distinguished from other processes such as smelting and calcining in that those two involve a chemical change to the raw material, whereas in refining, the final material is usually identical chemically to the original one, only it is purer. The processes used are of many types, including pyrometallurgical and hydrometallurgical techniques.

Downs' process is an electrochemical method for the commercial preparation of metallic sodium, in which molten NaCl is electrolyzed in a special apparatus called the Downs cell. The Downs cell was invented in 1923 by the American chemist James Cloyd Downs (1885–1957).
The Castner–Kellner process is a method of electrolysis on an aqueous alkali chloride solution to produce the corresponding alkali hydroxide, invented by American Hamilton Castner and Austrian Carl Kellner in the 1890s. Due to lower energy cost and fewer environmental concerns, the Castner–Kellner process is being replaced gradually with membrane electrolysis.

Aluminium smelting is the process of extracting aluminium from its oxide, alumina, generally by the Hall-Héroult process. Alumina is extracted from the ore bauxite by means of the Bayer process at an alumina refinery.
Zinc smelting is the process of converting zinc concentrates into pure zinc. Zinc smelting has historically been more difficult than the smelting of other metals, e.g. iron, because in contrast, zinc has a low boiling point. At temperatures typically used for smelting metals, zinc is a gas that will escape from a furnace with the flue gas and be lost, unless specific measures are taken to prevent it.

Cobalt extraction refers to the techniques used to extract cobalt from its ores and other compound ores. Several methods exist for the separation of cobalt from copper and nickel. They depend on the concentration of cobalt and the exact composition of the ore used.
Electrolytic iron is a form of high purity iron, obtained by electrolysis. It has a high purity greater than 99.95% with trace elements accounting for only a millionth of a decimal.
References
- ↑ Charles A. Sutherland, Edward F. Milner, Robert C. Kerby, Herbert Teindl, Albert Melin Hermann M. Bolt "Lead" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi : 10.1002/14356007.a15_193.pub2
- ↑ Samans, Carl H. Engineering Metals and their Alloys, 1949 MacMillan
- ↑ Ojebuoboh, Funsho K. (1992). "Bismuth—Production, properties, and applications". JOM. 44 (4): 46–49. Bibcode:1992JOM....44d..46O. doi:10.1007/BF03222821. S2CID 52993615.
- ↑ Betts, Anson Gardner (May 2008). Lead Refining by Electrolysis. Read Books. ISBN 9781409730156.
- ↑ us 679824
- ↑ us 713278