| District of Gera Bezirk Gera | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District (Bezirk) of East Germany | |||||||||
| 1952–1990 | |||||||||
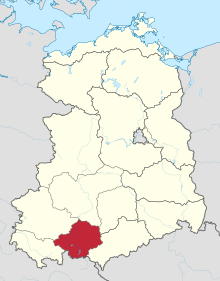 Location of Bezirk Gera within the German Democratic Republic | |||||||||
| Capital | Gera | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• 1989 | 4,004 km2 (1,546 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1989 | 742,000 | ||||||||
| Government | |||||||||
| SED First Secretary | |||||||||
• 1952–1955 | Otto Funke | ||||||||
• 1955–1959 | Heinz Glaser | ||||||||
• 1959–1963 | Paul Roscher | ||||||||
• 1963–1989 | Herbert Ziegenhahn | ||||||||
• 1989 | Erich Postler | ||||||||
| Chairman of the Council of the Bezirk | |||||||||
• 1952–1959 | Lydia Poser | ||||||||
• 1959–1965 | Albert Wettengel | ||||||||
• 1965–1973 | Horst Wenzel | ||||||||
• 1973–1977† | Rudolf Bahmann | ||||||||
• 1977 | Joachim Mittasch (acting) | ||||||||
• 1977–1983 | Karl-Heinz Fleischer | ||||||||
• 1983–1990 | Werner Ulbrich | ||||||||
• 1990 | Helmut Luck | ||||||||
• 1990 | Peter Lindlau (as Regierungsbevollmächtigter) | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1952 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1990 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | Germany | ||||||||
The Bezirk Gera was a district (Bezirk) of East Germany. The administrative seat and main town was Gera.