
The Central Pacific Railroad (CPRR) was a rail company chartered by U.S. Congress in 1862 to build a railroad eastwards from Sacramento, California, to complete most of the western part of the "First transcontinental railroad" in North America. Incorporated in 1861, CPRR ceased independent operations in 1875 when the railroad was leased to the Southern Pacific Railroad. Its assets were formally merged into Southern Pacific in 1959.

Theodore Dehone Judah was an American civil engineer who was a central figure in the original promotion, establishment, and design of the First transcontinental railroad. He found investors for what became the Central Pacific Railroad (CPRR). As chief engineer, he performed much of the route survey work to determine the best alignment for the railroad over the Sierra Nevada, which was completed six years after his death.

America's first transcontinental railroad was a 1,911-mile (3,075 km) continuous railroad line built between 1863 and 1869 that connected the existing eastern U.S. rail network at Council Bluffs, Iowa, with the Pacific coast at the Oakland Long Wharf on San Francisco Bay. The rail line was built by three private companies over public lands provided by extensive U.S. land grants. Building was financed by both state and U.S. government subsidy bonds as well as by company-issued mortgage bonds. The Western Pacific Railroad Company built 132 miles (212 km) of track from the road's western terminus at Alameda/Oakland to Sacramento, California. The Central Pacific Railroad Company of California (CPRR) constructed 690 miles (1,110 km) east from Sacramento to Promontory Summit, Utah Territory. The Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) built 1,085 miles (1,746 km) from the road's eastern terminus at the Missouri River settlements of Council Bluffs and Omaha, Nebraska, westward to Promontory Summit.

Amasa Leland Stanford was an American attorney, industrialist, philanthropist, and Republican Party politician from California. He served as the 8th Governor of California from 1862 to 1863 and represented the state in the United States Senate from 1885 until his death in 1893. He and his wife Jane founded Stanford University, named after their late son.

Collis Potter Huntington was an American industrialist and railway magnate. He was one of the Big Four of western railroading who invested in Theodore Judah's idea to build the Central Pacific Railroad as part of the first U.S. transcontinental railroad. Huntington helped lead and develop other major interstate lines, such as the Southern Pacific Railroad and the Chesapeake & Ohio Railway (C&O), which he was recruited to help complete. The C&O, completed in 1873, fulfilled a long-held dream of Virginians of a rail link from the James River at Richmond to the Ohio River Valley. The new railroad facilities adjacent to the river there resulted in expansion of the former small town of Guyandotte, West Virginia into part of a new city which was named Huntington in his honor.

The golden spike is the ceremonial 17.6-karat gold final spike driven by Leland Stanford to join the rails of the first transcontinental railroad across the United States connecting the Central Pacific Railroad from Sacramento and the Union Pacific Railroad from Omaha on May 10, 1869, at Promontory Summit, Utah Territory. The term last spike has been used to refer to one driven at the usually ceremonial completion of any new railroad construction projects, particularly those in which construction is undertaken from two disparate origins towards a common meeting point. The spike is now displayed in the Cantor Arts Center at Stanford University.

Charles Crocker was an American railroad executive who was one of the founders of the Central Pacific Railroad, which constructed the westernmost portion of the first transcontinental railroad, and took control with partners of the Southern Pacific Railroad.

Mark Hopkins Jr. was an American railroad executive. He was one of four principal investors that funded Theodore D. Judah's idea of building a railway over the Sierra Nevada from Sacramento, California to Promontory, Utah. They formed the Central Pacific Railroad along with Leland Stanford, Charles Crocker, and Collis Huntington in 1861.

Harvey Willson Harkness was an American mycologist and natural historian best known for his early descriptions of California fungal species.

The Big Four Building is a historic 19th-century building in Downtown Sacramento, California. It is now located within Old Sacramento State Historic Park and the Old Sacramento National Historic District.

Lloyd Tevis was a banker and capitalist who served as president of Wells Fargo & Company from 1872 to 1892.
The Western Pacific Railroad (1862–1870) was formed in 1862 to build a railroad from Sacramento, California, to the San Francisco Bay, the westernmost portion of the First transcontinental railroad. After the completion of the railroad from Sacramento to Alameda Terminal on September 6, 1869, and then the Oakland Pier on November 8, 1869, which was the Pacific coast terminus of the transcontinental railroad, the Western Pacific Railroad was absorbed in 1870 into the Central Pacific Railroad.

The Pacific Improvement Company (PIC) was a large holding company in California and an affiliate of the Southern Pacific Railroad. It was formed in 1878, by the Big Four, who were influential businessmen, philanthropists and railroad tycoons who funded the Central Pacific Railroad, (C.P.R.R.). These men were: Leland Stanford (1824–1893), Collis Potter Huntington (1821–1900), Mark Hopkins (1813–1878), and Charles Crocker (1822–1888). They owned the company, each with 25% interest. Archived records date from 1869 to 1931.

Stephen William Shaw was a California '49er and portrait painter who helped discover and name Humboldt Bay and introduced viticulture to Sonoma County by 1864.

Nob Hill is a neighborhood of San Francisco, California, United States that is known for its numerous luxury hotels and historic mansions. Nob Hill has historically served as a center of San Francisco's upper class. Nob Hill is among the highest-income neighborhoods in the United States, as well as one of the most desirable and expensive real estate markets in the country. Prior to Covid-19, it was the most expensive real estate market per metre squared, narrowly beating Monte Carlo, although it has since fallen heavily. It was the only place in the United States so far where market price per square metre exceeded the average yearly salary in the country.
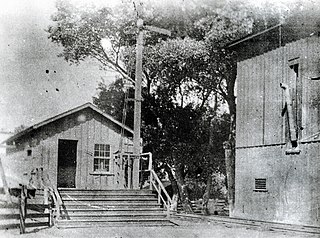
Lang Southern Pacific Station is a former Southern Pacific railway station located in Soledad Canyon near the eastern end of Santa Clarita, California. On September 5, 1876, the first railway to Los Angeles was completed at this site. The Lang Southern Pacific Station was designated a California Historic Landmark on May 22, 1957.

General David Douty Colton was an American pioneer, entrepreneur, and politician. The city of Colton, California, is named for him.

Mount Crocker is a remote 12,458-foot-elevation mountain summit located on the crest of the Sierra Nevada mountain range in northern California, United States. It is situated in the John Muir Wilderness, on the boundary shared by Sierra National Forest with Inyo National Forest, and along the common border of Fresno County with Mono County. Crocker ranks as the 291st-highest summit in California. Topographic relief is significant as the north aspect rises 2,500 feet above McGee Creek in approximately one mile. It is nine miles northeast of Lake Thomas A Edison, and approximately 15 miles (24 km) southeast of the community of Mammoth Lakes.

Mount Stanford is a 12,838-foot-elevation (3,913 meter) mountain summit located on the crest of the Sierra Nevada mountain range in northern California, United States. It is situated in the John Muir Wilderness, on the boundary shared by Sierra National Forest with Inyo National Forest, and along the common border of Fresno County with Mono County. It is 10 miles northeast of Lake Thomas A Edison, and approximately 15 miles (24 km) southeast of the community of Mammoth Lakes. Topographic relief is significant as the north aspect rises 3,200 feet above McGee Creek in approximately 1.75 mile. There is another Mount Stanford in the Sierra Nevada which is named for Stanford University.

Charles Marsh was an influential figure in the building of the first transcontinental railroad, as well as in building water systems for mining in the Sierra Nevada Mountains during the California Gold Rush. He was one of the founding directors of the Central Pacific Railroad. He was a surveyor and worked with Theodore D. Judah to survey and evaluate various possible routes for the first transcontinental railroad through the Sierra Nevada. He built a number of ditches and water pipelines to serve mines and towns there, and became known as the “Father of Ditches.” He was also one of the founders of the Nevada County Narrow Gauge Railroad.



















