
In computing and optical disc recording technologies, an optical disc (OD) is a flat, usually circular disc that encodes binary data (bits) in the form of pits and lands on a special material on one of its flat surfaces.

Video CD is a home video format and the first format for distributing films on standard 120 mm (4.7 in) optical discs. The format was widely adopted in Southeast Asia and the Middle East, superseding the VHS and Betamax systems in the regions until DVD-Video finally became affordable in the late 2000s.

The Nintendo GameCube is a home video game console released by Nintendo in Japan and North America in 2001 and in PAL territories in 2002. The GameCube is Nintendo's entry in the sixth generation of video game consoles and is the successor to their previous console, the Nintendo 64. The GameCube competed with Sony's PlayStation 2 and Microsoft's Xbox.

In computing, an optical disc drive (ODD) is a disc drive that uses laser light or electromagnetic waves within or near the visible light spectrum as part of the process of reading or writing data to or from optical discs. Some drives can only read from certain discs, but recent drives can both read and record, also called burners or writers. Compact discs, DVDs, and Blu-ray discs are common types of optical media which can be read and recorded by such drives.
A regional lockout is a class of digital rights management preventing the use of a certain product or service, such as multimedia or a hardware device, outside a certain region or territory. A regional lockout may be enforced through physical means, through technological means such as detecting the user's IP address or using an identifying code, or through unintentional means introduced by devices only supporting certain regional technologies.
An ISO image is a disk image of an optical disc. In other words, it is an archive file that contains everything that would be written to an optical disc, sector by sector, including the optical disc file system. ISO image files bear the .iso filename extension. The name ISO is taken from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) ISO 9660 file system used with CD-ROM media, but what is known as an ISO image might also contain a UDF file system.
A home video game console is a video game console that is designed to be connected to a display device, such as a television, and an external power source as to play video games. Home consoles are generally less powerful and customizable than personal computers, designed to have advanced graphics abilities but limited memory and storage space to keep the units affordable. While initial consoles were dedicated units with only a few games fixed into the electronic circuits of the system, most consoles since support the use of swappable game media, either through game cartridges, optical discs, or through digital distribution to internal storage.

MiniDVD is a DVD disc which is 8 centimetres (3.15 in) in diameter. It refers two separated formats as well. One is a pseudo-format that uses 80mm CD-R(W) to store contents with the same structure as the standard DVD-Video so that standalone DVD players can play it like standard DVD. The other format is a real DVD format, but in a smaller 80mm size, which holds 1.4 GB of data.
The history of video game consoles, both home and handheld, had their origins in the 1970s. The concept of home consoles used to play games on a television set was founded by the 1972 Magnavox Odyssey, first conceived by Ralph H. Baer in 1966. Handheld consoles bore out from electro-mechanical games that had used mechanical controls and light-emitting diodes (LED) as visual indicators. Handheld electronic games had replaced the mechanical controls with electronic and digital components, and with the introduction of Liquid-crystal display (LCD) to create video-like screens with programmable pixels, systems like the Microvision and the Game & Watch became the first handheld video game consoles, and fully realized by the Game Boy system.
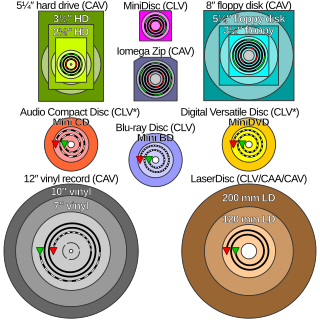
In optical storage, constant angular velocity (CAV) is a qualifier for the rated speed of any disc containing information, and may also be applied to the writing speed of recordable discs. A drive or disc operating in CAV mode maintains a constant angular velocity, contrasted with a constant linear velocity (CLV).

Homebrew is a term frequently applied to video games or other software produced by hobbyists and amateur developers targeting proprietary hardware platforms that are not typically user-programmable or that use proprietary storage methods. Homebrew can include software made using unofficial, community maintained, toolchains or games developed using official development kits such as Net Yaroze, Linux for PlayStation 2, or Microsoft XNA. A game written by a non-professional developer for a system intended to be consumer-programmable, like the Commodore 64, is simply called hobbyist.

GD-ROM is a proprietary optical disc format originally used for the Dreamcast video game console, as well as its arcade counterpart, the Sega NAOMI and select Triforce arcade board titles. It was developed by Yamaha to curb piracy common to standard compact discs and to offer increased storage capacity without the expense of the fledgling DVD-ROM. It is similar to the standard CD-ROM except that the pits on the disc are packed more closely together, resulting in a higher storage capacity of 1 gigabyte, a 42% increase over a conventional CD's capacity of 700 megabytes.
Video game packaging refers to the physical storage of the contents of a PC or console game, both for safekeeping and shop display. In the past, a number of materials and packaging designs were used, mostly paperboard or plastic. Today, most console and PC games are shipped in (CD) jewel cases or (DVD) keep cases, with little differences between them.

Nintendo optical discs are physical media used to distribute video games on three of Nintendo's consoles that followed the Nintendo 64. These are the GameCube Game Disc, Wii Optical Disc, and Wii U Optical Disc. The physical size of a GameCube Game Disc is that of a miniDVD; the Wii and Wii U Optical Discs are the size of a DVD, a CD, and a Blu-ray. To maintain backward compatibility between generations of game consoles, GameCube discs are compatible with the first model of the Wii, and Wii Optical Discs are compatible with the Wii U. A burst cutting area is located at the inner ring of the disc surface.

A keep case or poly-box is a type of packaging, most commonly used with DVDs.

A compressed audio optical disc, MP3 CD, or MP3 CD-ROM or MP3 DVD is an optical disc that contains digital audio in the MP3 file format. Discs are written in the "Yellow Book" standard data format, as opposed to the Red Book standard audio format.

DVD is a digital optical disc storage format invented and developed in 1995 and released in late 1996. The medium can store any kind of digital data and is widely used for software and other computer files as well as video programs watched using DVD players. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than compact discs while having the same dimensions.

Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a digital optical disc data storage format designed to supersede the DVD format, capable of storing several hours of video in high-definition. The main application of Blu-ray is as a medium for video material such as feature films and for the physical distribution of video games for the PlayStation 3, PlayStation 4, and Xbox One. The name "Blu-ray" refers to the blue laser used to read the disc, which allows information to be stored at a greater density than is possible with the longer-wavelength red laser used for DVDs.

HD DVD is a discontinued, obsolete high-density optical disc format for storing data and playback of high-definition video. Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format.
This article provides a Comparison of popular optical data-storage systems.













