Related Research Articles

The Grand Canyon is a steep-sided canyon carved by the Colorado River in Arizona, United States. The Grand Canyon is 277 miles (446 km) long, up to 18 miles (29 km) wide and attains a depth of over a mile.

The Hopi are Native Americans who primarily live in the southwestern United States. The majority are enrolled in the Hopi Tribe of Arizona and live on the Hopi Reservation in northeastern Arizona; however, some Hopi people are enrolled in the Colorado River Indian Tribes of the Colorado River Indian Reservation at the border of Arizona and California.


In mining, tailings or tails are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different from overburden, which is the waste rock or other material that overlies an ore or mineral body and is displaced during mining without being processed.

Black Mesa is an upland mountainous mesa of Arizona, north-trending in Navajo County, west and southeast-trending in Apache County. In Navajo it is called Dziłíjiin and during Mexican rule of Arizona it was called Mesa de las Vacas. It derives its dark appearance from its pinyon-juniper and mixed conifer woodlands.

Navajo Generating Station was a 2.25-gigawatt, coal-fired power plant located on the Navajo Nation, near Page, Arizona, United States. This plant provided electrical power to customers in Arizona, Nevada, and California. It also provided the power for pumping Colorado River water for the Central Arizona Project, supplying about 1.5 million acre feet (1.85 km3) of water annually to central and southern Arizona. As of 2017 permission to operate as a conventional coal-fired plant was anticipated until 2017–2019, and to December 22, 2044, if extended. However, in 2017, the utility operators of the power station voted to close the facility when the lease expires in 2019. In March 2019, the Navajo Nation ended efforts to buy the plant and continue running it after the lease expires.

The Hopi Reservation is a Native American reservation for the Hopi and Arizona Tewa people, surrounded entirely by the Navajo Nation, in Navajo and Coconino counties in north-eastern Arizona, United States. The site has a land area of 2,531.773 sq mi (6,557.262 km²) and as of the 2000 census had a population of 6,946.
Coal pipelines are pipelines used to transport coal from where it is mined to where it is consumed. For very short distances, large trucks are used to transport coal, but trains and barges are preferred for long distances. In some cases it is more economical to move the coal by pipeline than by train or barge. This can happen when there is no suitable railway or waterway to transport the coal, or when it must be moved very long distances.

Peabody Energy is a coal mining company headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri. Its primary business consists of the mining, sale, and distribution of coal, which is purchased for use in electricity generation and steelmaking. Peabody also markets, brokers, and trades coal through offices in China, Australia, and the United States.
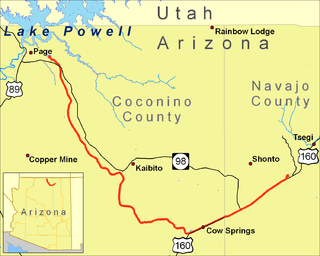
The Black Mesa and Lake Powell Railroad was an electrified private railroad operating in Northern Arizona, USA within the Navajo Nation which transported coal 78 miles (126 km) from the Peabody Energy Kayenta Mine near Kayenta, Arizona to the Navajo Generating Station power plant at Page, Arizona. It was completely isolated from the national rail network and did not connect to any other railroad. As a result, like metros, light rails, and trams, it was not controlled by the Federal Railroad Administration.

Overdrafting is the process of extracting groundwater beyond the equilibrium yield of an aquifer. Groundwater is one of the largest sources of fresh water and is found underground. The primary cause of groundwater depletion is the excessive pumping of groundwater up from underground aquifers.

Broken Rainbow is a 1985 American documentary film by Victoria Mudd and Maria Florio.

In-situ leaching (ISL), also called in-situ recovery (ISR) or solution mining, is a mining process used to recover minerals such as copper and uranium through boreholes drilled into a deposit, in situ. In situ leach works by artificially dissolving minerals occurring naturally in a solid state. For recovery of material occurring naturally in solution, see: Brine mining.

Mohave Power Station was a 1580 megawatt electric (MWe) coal-fired power plant that was located in Laughlin, Nevada. Southern California Edison is the majority owner of the plant and was its operator. The plant entered commercial operation in 1971. A steam line that ran near the plant's control room and cafeteria ruptured on June 9, 1985, fatally scalding six and injuring ten more. In 2005, the plant was shut down and was later dismantled.
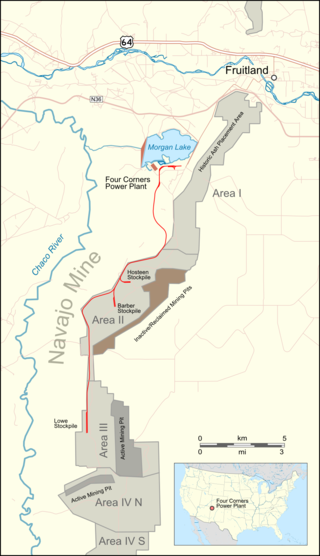
The Navajo Mine is a surface coal mine owned and operated by Navajo Transitional Energy Company, LLC (NTEC) in New Mexico, United States, within the Navajo Nation. The mine is about 20.5 miles (33 km) southwest of Farmington, New Mexico. The Navajo Mine Railroad has 13.8 miles (22.2 km) of track between the Four Corners Generating Station and Navajo Mine.
Sacred waters are sacred natural sites characterized by tangible topographical land formations such as rivers, lakes, springs, reservoirs, and oceans, as opposed to holy water which is water elevated with the sacramental blessing of a cleric. These organic bodies of water have attained religious significance not from the modern alteration or blessing, but were sanctified through mythological or historical figures. Sacred waters have been exploited for cleansing, healing, initiations, and death rites.
The Kayenta mine was a surface coal mine operated by Peabody Western Coal Company on the Navajo Nation in northern Arizona from 1973 to 2019. About 400 acres were mined and reclaimed each year, providing about 8 million tons of coal annually to the Navajo Generating Station.
The Bennett Freeze was a 43-year development ban on 1.5 million acres of Navajo lands by the US Federal Government. It was put in place in 1966 in order to promote negotiations over a land dispute between the Navajo and the Hopi and lasted until 2009. It was named for the Commissioner of Indian Affairs at the time, Robert L Bennett, and meant that in the "frozen" area, no development at all could occur. This included fixing roofs, building houses, constructing gas and water lines, and repairing roads.
Katherine Smith (1918–2017) was a Navajo activist, cultural educator, land defender, and resistor who protected Navajo land and refused to leave Big Mountain. A 1985 documentary Broken Rainbow depicts the struggle of the Navajo amid government enforced relocation of thousands from Black Mesa in Arizona after the enactment of the Navajo-Hopi Land Settlement Act of 1974. The documentary film about the relocation was nominated for an Oscar.
Water rights for the Navajo Nation have been a source of environmental conflict for decades, as Navajo lands have provided energy and water for residents of neighboring states while many of the Navajo do not have electricity or running water in their homes. Beginning in the 1960s, coal mining by Peabody coal at Black Mesa withdrew more than 3 million gallons of water/day from the Navajo aquifer, reducing the number of springs on the reservation. The Navajo Generating Station also consumed about 11 billion gallons of water per year to provide power for the Central Arizona Project that pumps water from Lake Havasu into Arizona.
References
- ↑ John Dougherty (1997-05-01). "A People Betrayed". Phoenix New Times. Archived from the original on 2007-09-27. Retrieved 2007-08-29.
- ↑ Claudia Rowe (2013-06-06). "Coal Mining On Navajo Nation In Arizona Takes Heavy Toll". Huffington Post. Retrieved 2014-04-17.
- ↑ "Drawdown: An Update on Groundwater Mining on Black Mesa". National Resources Defense Council. October 2000. Retrieved 2014-04-17.
- ↑ Kutz, Jessica (2021-02-01). "The fight for an equitable energy economy for the Navajo Nation". www.hcn.org. Retrieved 2023-10-02.
- ↑ "Current Initiatives: Black Mesa Project" Archived 2010-06-19 at the Wayback Machine Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement (OSMRE) website
- ↑ Holt, Robert G. (administrative law judge) (7 January 2010) "Opinion In re: Black Mesa Complex Permit Revision" Archived March 14, 2012, at the Wayback Machine Office of Hearings and Appeals, United States Department of the Interior