
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics.

Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from the effects of antimicrobials. Antibiotic resistance is a subset of AMR, that applies specifically to bacteria that become resistant to antibiotics.
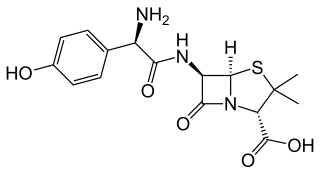
Amoxicillin is an antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. These include middle ear infection, strep throat, pneumonia, skin infections, and urinary tract infections among others. It is taken by mouth, or less commonly by injection.

Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane.
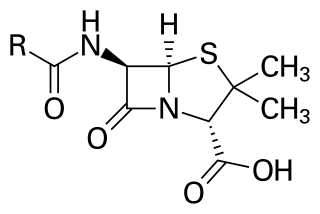
Penicillins are a group of antibiotics originally obtained from Penicillium moulds, principally P. chrysogenum and P. rubens. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G and penicillin V. Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are members of the β-lactam antibiotics. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use.
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely the urine may appear bloody. In the very old and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific.

Streptococcal pharyngitis, also known as strep throat, or Bacterial tonsillitis is an infection of the back of the throat including the tonsils caused by group A streptococcus (GAS). Common symptoms include fever, sore throat, red tonsils (tonsilitis), and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck. A headache, and nausea or vomiting may also occur. Some develop a sandpaper-like rash which is known as scarlet fever. Symptoms typically begin one to three days after exposure and last seven to ten days.

Staphylococcus aureus is a Gram-positive round-shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often positive for catalase and nitrate reduction and is a facultative anaerobe that can grow without the need for oxygen. Although S. aureus usually acts as a commensal of the human microbiota, it can also become an opportunistic pathogen, being a common cause of skin infections including abscesses, respiratory infections such as sinusitis, and food poisoning. Pathogenic strains often promote infections by producing virulence factors such as potent protein toxins, and the expression of a cell-surface protein that binds and inactivates antibodies. S. aureus is one of the leading pathogens for deaths associated with antimicrobial resistance and the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) is a worldwide problem in clinical medicine. Despite much research and development, no vaccine for S. aureus has been approved.

Sulfonamide is a functional group that is the basis of several groups of drugs, which are called sulphonamides, sulfa drugs or sulpha drugs. The original antibacterial sulfonamides are synthetic (nonantibiotic) antimicrobial agents that contain the sulfonamide group. Some sulfonamides are also devoid of antibacterial activity, e.g., the anticonvulsant sultiame. The sulfonylureas and thiazide diuretics are newer drug groups based upon the antibacterial sulfonamides.
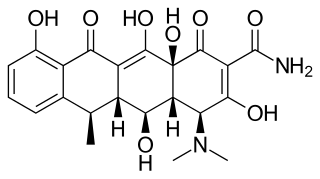
Doxycycline is a broad-spectrum tetracycline-class antibiotic used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, and syphilis. It is also used to prevent malaria in combination with quinine. Doxycycline may be taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.

Lower respiratory tract infection (LRTI) is a term often used as a synonym for pneumonia but can also be applied to other types of infection including lung abscess and acute bronchitis. Symptoms include shortness of breath, weakness, fever, coughing and fatigue. A routine chest X-ray is not always necessary for people who have symptoms of a lower respiratory tract infection.

Cefalexin, also spelled cephalexin, is an antibiotic that can treat a number of bacterial infections. It kills gram-positive and some gram-negative bacteria by disrupting the growth of the bacterial cell wall. Cefalexin is a beta-lactam antibiotic within the class of first-generation cephalosporins. It works similarly to other agents within this class, including intravenous cefazolin, but can be taken by mouth.
Multiple drug resistance (MDR), multidrug resistance or multiresistance is antimicrobial resistance shown by a species of microorganism to at least one antimicrobial drug in three or more antimicrobial categories. Antimicrobial categories are classifications of antimicrobial agents based on their mode of action and specific to target organisms. The MDR types most threatening to public health are MDR bacteria that resist multiple antibiotics; other types include MDR viruses, parasites.

Flucloxacillin, also known as floxacillin, is an antibiotic used to treat skin infections, external ear infections, infections of leg ulcers, diabetic foot infections, and infection of bone. It may be used together with other medications to treat pneumonia, and endocarditis. It may also be used prior to surgery to prevent Staphylococcus infections. It is not effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). It is taken by mouth or given by injection into a vein or muscle.
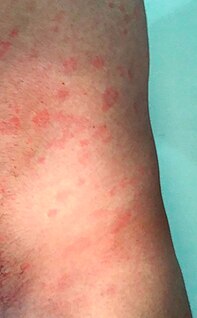
A Jarisch–Herxheimer reaction is a reaction to endotoxin-like products released by the death of harmful microorganisms within the body during antibiotic treatment. Efficacious antimicrobial therapy results in lysis (destruction) of bacterial cell membranes, and in the consequent release into the bloodstream of bacterial toxins, resulting in a systemic inflammatory response.
Relapsing fever is a vector-borne disease caused by infection with certain bacteria in the genus Borrelia, which is transmitted through the bites of lice or soft-bodied ticks.
Acrodynia is a condition of pain and dusky pink discoloration in the hands and feet most often seen in children chronically exposed to heavy metals, especially mercury.
In enzymology, a blasticidin-S deaminase (EC 3.5.4.23) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Bacteriuria is the presence of bacteria in urine. Bacteriuria accompanied by symptoms is a urinary tract infection while that without is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria. Diagnosis is by urinalysis or urine culture. Escherichia coli is the most common bacterium found. People without symptoms should generally not be tested for the condition. Differential diagnosis include contamination.
Streptomyces griseochromogenes is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces griseochromogenes produces blasticidin A, blasticidin B, blasticidin C, blasticidin S, pentalenene and cytomycin.















