
The South Island is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island and sparsely populated Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south by the Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers 150,437 square kilometres (58,084 sq mi), making it the world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitudes, it has an oceanic climate.

Riverton, officially Riverton / Aparima, is a small New Zealand town 30 kilometres (19 mi) west of Invercargill, on the south-eastern shorelines of the Jacobs River Estuary. The estuary is formed by the Aparima and Pourakino rivers, leading through a narrow outflow channel into Foveaux Strait. Accessible via State Highway 99 on the Southern Scenic Route, the main part of the town is on flat land and the northern end of Oreti Beach. South Riverton is built on the hills between the eastern shore of the estuary and Taramea Bay.

Rakiura National Park is a nature reserve park located on Stewart Island / Rakiura, New Zealand. It is the newest national park of New Zealand and opened in 2002. The protected area covers about 85% of the island.

Bluff, previously known as Campbelltown and often referred to as "The Bluff", is a town and seaport in the Southland region, on the southern coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It is the southernmost town in mainland New Zealand and, despite Slope Point and Stewart Island being further south, Bluff is colloquially used to refer to the southern extremity of the country. According to the 2018 census, the resident population was 1,797, a decrease of 6 since 2013.

Manapōuri Power Station is an underground hydroelectric power station on the western arm of Lake Manapouri in Fiordland National Park, in the South Island of New Zealand. At 854 MW installed capacity, it is the largest hydroelectric power station in New Zealand, and the second largest power station in New Zealand. The station is noted for the controversy and environmental protests by the Save Manapouri Campaign against raising the level of Lake Manapouri to increase the station's hydraulic head, which galvanised New Zealanders and was one of the foundations of the New Zealand environmental movement.

Tiwai Point lies at the entrance to Bluff Harbour on the southern coast of the South Island of New Zealand. A spit which extends from the western end of the Awarua Plain, it lies between Awarua Bay to the north and Foveaux Strait to the south. It is known for the Tiwai Point Aluminium Smelter, one of the largest industrial facilities in New Zealand.
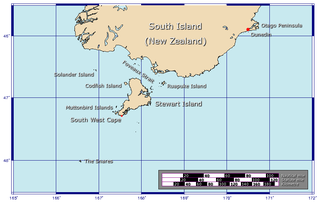
Foveaux Strait is a strait that separates Stewart Island from the South Island of New Zealand. The width of the strait ranges from about 23 to 53 km, and the depth varies between 18 and 46 m. The strait was first charted by an American sealer, Owen Folger Smith. He charted the strait from a whaleboat of the sealing brig Union in 1804.

Manapouri is a small town in Southland / Fiordland, in the southwest corner of the South Island, in New Zealand. The township is the westernmost municipality in New Zealand. Located at the edge of the Fiordland National Park, on the eastern shore of Lake Manapouri, close to its outflow into the Waiau River, tourist boat services are based in the town.
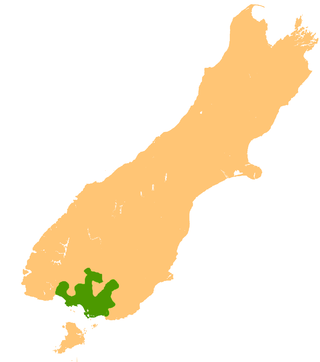
The Southland Plains is a general name given to several areas of low-lying land in the South Island of New Zealand, separated by the rise of the Hokonui Hills in the north. It forms a sizeable area of Southland region and encompasses its two principal settlements the city of Invercargill and the town of Gore. The Southland Plains include some of New Zealand's most fertile farmland.

The Awarua Plain is a large area of wetland to the east of Bluff, New Zealand. Covering an area of around 600 km², the plain stretches for 35 kilometres along the coast of Foveaux Strait. This stretch of coast includes the peninsula of Tiwai Point, Awarua Bay, the Waituna Lagoon, and Toetoes Bay. The Mataura River is the major river responsible for the presence of the Awarua Plain; along with the Ōreti River, it is a remnant of the rivers from the Ice Ages that formed the Southland Plains (Murihiku). In addition, several small streams enter Foveaux Strait along this stretch of coast, mainly via Awarua Bay and Waituna Lagoon.

Toetoes Bay is the easternmost of three large bays lying on the Foveaux Strait coast of Southland, New Zealand, the others being Te Waewae Bay and Oreti Beach. The 240 km Mataura River drains to sea at Toetoes Bay, first passing through the Toetoes Harbour estuary. Thirty kilometres in length, the bay is the southern end of the Awarua Plain, an area of swampy land stretching inland for about fifteen kilometres. The eastern end of the bay is close to Slope Point, the South Island's southernmost point, and the western end of the Catlins.

The Tiwai Point Aluminium Smelter is an aluminium smelter owned by Rio Tinto Group (79.36%) and the Sumitomo Group (20.64%), via a joint venture called New Zealand Aluminium Smelters (NZAS) Limited.
By the end of the year reports from London regarding Napoleon's retreat from Moscow, and from the Bay of Islands regarding the hospitality of the Māori, encourage Samuel Marsden into thinking the time for the establishment of a Christian mission to New Zealand is now imminent.
There is a drastic decline in the number of ships visiting New Zealand from the previous year. An economic depression starts in New South Wales as a result of the escalation of war in Europe and the consequent reduction in the number of convicts being transported. In March news of the Boyd massacre reaches Port Jackson and a punitive expedition is sent to New Zealand and bombards the village of the incorrectly blamed chief, Te Pahi. After this the few whaling ships that later head for New Zealand usually prefer to avoid landing, especially in the Bay of Islands.
Foveaux Strait is the centre of attention for sealing ships. Sealing gangs are dropped along the coast from southern Fiordland to Otago Harbour and on Stewart Island/Rakiura. The Bay of Islands is sometimes on the journey to or from Port Jackson. The Chatham Islands are also visited. A few whalers also operate around New Zealand; some also collect timber from Bay of Islands.

The dredge oyster, Bluff oyster or Chilean oyster, is also known in Chile as ostra verde, is a species of bivalve mollusc in the family Ostreidae.

Stewart Island is New Zealand's third-largest island, located 30 kilometres south of the South Island, across Foveaux Strait. It is a roughly triangular island with a total land area of 1,746 km2 (674 sq mi). Its 164-kilometre (102 mi) coastline is deeply indented by Paterson Inlet (east), Port Pegasus (south), and Mason Bay (west). The island is generally hilly and densely forested. Flightless birds, including penguins, thrive because there are few introduced predators. Almost all the island is owned by the New Zealand government, and over 80 per cent of the island is set aside as the Rakiura National Park.
The Save Aramoana Campaign was formed in 1974 to oppose a proposed aluminium smelter at Aramoana in New Zealand.

Southland is New Zealand's southernmost region. It consists of the southwestern portion of the South Island and includes Stewart Island. Southland is bordered by the culturally similar Otago Region to the north and east, and the West Coast Region in the extreme northwest. The region covers over 3.1 million hectares and spans 3,613 km of coastline. As of June 2023, Southland has a population of 103,900, making it the eleventh-most-populous New Zealand region, and the second-most sparsely populated. Approximately half of the region's population lives in Invercargill, Southland's only city.

Ocean Beach is an industrial area in the Southland Region of New Zealand. For around 100 years it was the site of a freezing works. This closed in 1991, and the site has been redeveloped as an aquaculture facility.















