
The Australian Capital Territory (ACT), known as the Federal Capital Territory (FCT) until 1938, is a federal territory of Australia. Canberra, the capital city of Australia, is located in this territory. It is located in southeastern Australian mainland as an enclave completely within the state of New South Wales. Founded after Federation as the seat of government for the new nation, the territory hosts the headquarters of all important institutions of the Australian Government.

Namadgi National Park is a protected area in the south-west of the Australian Capital Territory (ACT), bordering Kosciuszko National Park in New South Wales. It lies approximately 40 kilometres (25 mi) southwest of Canberra, and occupies approximately 46 percent of the ACT's land area.

Duntroon is a suburb of the city of Canberra in the Australian Capital Territory.

The Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex (CDSCC) is a satellite communication station, part of the Deep Space Network of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), located at Tidbinbilla in the Australian Capital Territory. Opened in 1965, the complex was used for tracking the Apollo Lunar Module, and along with its two sister stations at Goldstone, California and Madrid, Spain is now used for tracking and communicating with NASA's spacecraft, particularly interplanetary missions. Its DSS-43 antenna is the only antenna on Earth that can send commands to Voyager 2. It is managed in Australia by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO) for NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation program (SCaN) at NASA Headquarters in Washington, D.C.

The Australian National Botanic Gardens (ANBG) is a heritage-listed botanical garden located in Acton, Canberra, in the Australian Capital Territory, Australia. Established in 1949, the Gardens is administered by the Australian Government's Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment. The botanic gardens was added to the Commonwealth Heritage List on 22 June 2004.

Narrabundah is a leafy, medium density suburb of Canberra, Australian Capital Territory, located in the inner south of the city.

The National Rose Gardens are a heritage-listed rose gardens located in Parkes, a suburb of Canberra, in the Australian Capital Territory of Australia. The rose gardens were added to the Australian Commonwealth Heritage List on 22 June 2004.

The Queanbeyan River, a perennial stream that is part of the Molonglo catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Monaro and Capital Country regions of New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory, in Australia. The river is 104 kilometres (65 mi) in length with a catchment area of 96,000 hectares. The Queanbeyan River and the Cotter River meet the potable water supply needs of the Canberra and Queanbeyan region and whose water quality is specifically protected under Federal legislation.
The history of the Australian Capital Territory (ACT) as a separate administrative division began in 1911, when it was transferred from New South Wales to the Australian federal government. The territory contains Australia's capital city Canberra and various smaller settlements. Until 1989, it also administered the Jervis Bay Territory, a small coastal region.

The geology of the Australian Capital Territory includes rocks dating from the Ordovician around 480 million years ago, whilst most rocks are from the Silurian. During the Ordovician period the region—along with most of eastern Australia—was part of the ocean floor. The area contains the Pittman Formation consisting largely of Quartz-rich sandstone, siltstone and shale; the Adaminaby Beds and the Acton Shale.

The Orroral Valley tracking station was an Earth station in Australia, supported Earth-orbiting satellites, as part of NASA's Spacecraft Tracking and Data Acquisition Network (STADAN). It was located approximately 50 km south of Canberra, Australian Capital Territory (ACT), and was one of three tracking stations in the ACT, and seven in Australia.

Clematis microphylla is one of 8 Clematis species native to Australia. It occurs in all states and the ACT, but not in the Northern Territory.
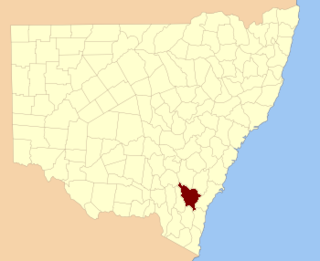
Murray County was one of the original Nineteen Counties in New South Wales and is now one of the 141 Lands administrative divisions of New South Wales. It included the area which is now part of Canberra and as far north as Lake George and Yass. It was originally bounded on the west by the Murrumbidgee River, on the east by the Shoalhaven River and on the north by the Yass River. A large area of the county was transferred to the Commonwealth government in 1909 in the Seat of Government Acceptance Act to make part of the Australian Capital Territory, along with land in Cowley County. Since then, the ACT border is now part of the western boundary. Part of the ACT border is determined by property boundaries in the Parish of Keewong, in the County of Murray; specifically the southern end of portions 177, 218, 211, 36, and 38. This is mentioned in the Seat of Government Acceptance Act of 1909.
The Bendora Gravity Main is a water main located in the Australian Capital Territory, Australia.

Mount Ginini is a mountain with an elevation of 1,762 metres (5,781 ft) AHD in the Brindabella Ranges that is located on the border between the Australian Capital Territory and New South Wales in Australia.

The Lower Molonglo Water Quality Control Centre is a sewerage and waste water treatment facility in the Australian Capital Territory, owned and operated by Icon Water.
Jerrabomberra Creek, a partly perennial stream of the Murrumbidgee catchment within the Murray–Darling basin, is located in the Capital Country region spanning both New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory, Australia.

The National Arboretum Canberra is a 250-hectare (620-acre) arboretum in Canberra, the national capital of Australia, created after the area was burned out as a result of the Christmas 2001 and 2003 Canberra bushfires: The Himalayan Cedar forest lost about one third of its trees, and the commercial Radiata Pine plantation was burned out, allowing the arboretum to be created.
Oakey Hill is a hill near Canberra, Australian Capital Territory. It rises 80 metres (260 ft) above the adjacent south Canberra suburbs of Lyons, Curtin and Weston, and its 66 hectares is one of 33 areas which form Canberra Nature Reserve. The highest point of the hill, 684 metres above sea level, is marked by a survey station.















