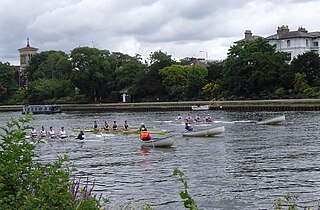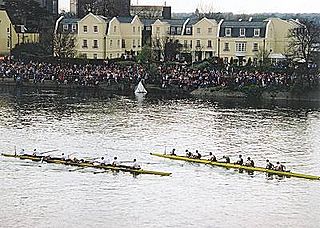Rowing, sometimes called crew in the United States, is the sport of racing boats using oars. It differs from paddling sports in that rowing oars are attached to the boat using oarlocks, while paddles are not connected to the boat. Rowing is divided into two disciplines: sculling and sweep rowing. In sculling, each rower holds two oars—one in each hand, while in sweep rowing each rower holds one oar with both hands. There are several boat classes in which athletes may compete, ranging from single sculls, occupied by one person, to shells with eight rowers and a coxswain, called eights. There are a wide variety of course types and formats of racing, but most elite and championship level racing is conducted on calm water courses 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) long with several lanes marked using buoys.

An oar is an implement used for water-borne propulsion. Oars have a flat blade at one end. Rowers grasp the oar at the other end.

Sculling is the use of oars to propel a boat by moving them through the water on both sides of the craft, or moving one oar over the stern. A long, narrow boat with sliding seats, rigged with two oars per rower may be referred to as a scull, its oars may be referred to as sculls and a person rowing it referred to as sculler.

Rowing is the act of propelling a human-powered watercraft using the sweeping motions of oars to displace water and generate reactional propulsion. Rowing is functionally similar to paddling, but rowing requires oars to be mechanically attached to the boat, and the rower drives the oar like a lever, exerting force in the same direction as the boat's travel; while paddles are completely hand-held and have no attachment to the boat, and are driven like a cantilever, exerting force opposite to the intended direction of the boat.

In watercraft, a racing shell is an extremely narrow, and often comparatively long, rowing boat specifically designed for racing or exercise. It is outfitted with long oars, outriggers to hold the oarlocks away from the boat, and sliding seats. The boat's long length and semicircular cross-section reduce drag to a minimum. This makes the boat both fast and unstable. It must be balanced by the rowers to avoid tipping. Being able to balance – or "set" – the boat while putting maximum effort into the oars is therefore an essential skill of sport rowing.
In competitive rowing, the following specialized terms are important in the corresponding aspects of the sport:

Coastal and offshore rowing is a rowing sport performed at sea. In North America, this sport is often called open water rowing.

In a rowing crew, the coxswain is the member who does not row but steers the boat and faces forward, towards the bow. The coxswain is responsible for steering the boat and coordinating the power and rhythm of the rowers. In some capacities, the coxswain is responsible for implementing the training regimen or race plan. Most coaches cannot communicate to boat/coxswain, so the coxswain is the "coach" in the boat. A coxswain is necessary in the first place because the rowers sit with their backs to the direction of travel.

A coxless pair is a rowing boat used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for two rowers, who propel the boat with sweep oars.

A cox box is an electronic device used in competitive rowing that combines a digital stroke rate monitor, stopwatch, and voice amplifier. It is generally used by a coxswain to monitor the crew's performance, and amplify instructions given by the cox using a microphone and series of wired loudspeakers.
In the sport of rowing, each rower is numbered by boat position in ascending order from the bow to the stern. The person who is seated on the first seat is always the 'bow', the closest to the stern is commonly referred to as the 'stroke'. There are some exceptions to this: Rowers in continental Europe number from stern up to bow. Certain crew members have other informal titles and roles. Stroke seat in most cases is responsible for keeping pace for the boat, while the coxswain is responsible for the steering of the boat.
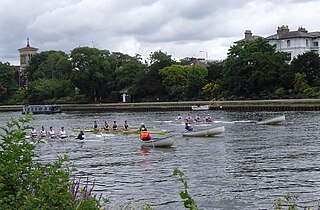
A coxed four, also known as a 4+, is a rowing boat used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for four persons who propel the boat with sweep oars and is steered by a coxswain.

A coxless four is a rowing boat used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for four persons who propel the boat with sweep oars, without a coxswain.

A coxed pair is a rowing boat used in the sport of competitive rowing. It is designed for two persons who propel the boat with sweep oars and is steered by a coxswain.
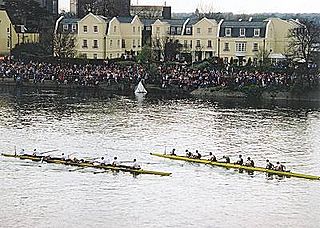
An eight is a rowing boat used in the sport of competitive rowing (crew). It is designed for eight rowers, who propel the boat with sweep oars, and is steered by a coxswain, or "cox".

Sweep rowing is one of two disciplines of the sport of rowing. In sweep rowing each rower has one oar, usually held with both hands. As each rower has only one oar, the rowers have to be paired so that there is an oar on each side of the boat. In the United Kingdom, rowing generally refers to sweep rowing only. The term pulling was also used historically. In the other rowing discipline, sculling, each rower holds two oars, one in each hand.

An octuple scull is a racing shell or a rowing boat used in the sport of rowing. The octuple is directed by a coxswain and propelled by eight rowers who move the boat by sculling with two oars, one in each hand. Like a coxed eight, an octuple is typically 65.2 feet long and weighs 211.2 pounds. Unlike other boats, octuples are seldom seen at higher levels of competitive rowing, usually only being used for those who are newer to the sport. This is because of the high speed of the boat, which can cause greater injury to the ribcage if one lets go of their oar during a race.
David Webster is an Australian national champion rowing coxswain who steered Australian crews at six World Rowing Championships and won two world championship titles in 2010 and 2011.

The 1972 New Zealand eight was a team of Olympic gold medallists in rowing from New Zealand, having previously won the 1971 European Rowing Championships. At the time, the eight was regarded as the blue ribbon class of rowing, and the sport still had amateur-status in New Zealand, unlike many other nations competing in rowing. After a disappointing Olympic performance at the 1968 Summer Olympics by the New Zealand eight, national selectors Rusty Robertson, Don Rowlands, and Fred Strachan were tasked with assembling a new crew. Robertson was also the team's coach. The next time a New Zealand eight competed was at the 1970 World Rowing Championships, where they came third. The team was once again significantly changed for the next rowing season, with the 1971 edition of the European Rowing Championships and other international regattas beforehand seen as the ultimate test for the 1972 Summer Olympics. The team put up an impressive performance, beat the highly favoured East German eight, and became European champion; at the time the win was regarded to hold world championship status. No further changes were made to the team, not even their seating position, for the 1972 season. Despite a shoe-string budget, financial constraints, and all rowers working part-time, the 1971 success was repeated and the team won Olympic gold in Munich. The president of the International Olympic Committee (IOC), Avery Brundage, was a zealous advocate of amateurism; he was so impressed by the New Zealand performance that he insisted on handing out the gold medals himself. During the medal ceremony, much to almost everybody's surprise, "God Defend New Zealand" was played instead of the national anthem, "God Save the Queen". It was the impetus for a campaign to make "God Defend New Zealand" the New Zealand anthem, and in 1977 it was gazetted as having equal status to the traditional anthem.

Stern sculling is the use of a single oar over the stern of a boat to propel it with side-to-side motions that create forward lift in the water. It is distinguished from sculling, which is rowing with two oars on either side of the boat and from sweep rowing, whereby each boat crew member employs a single oar, complemented by another crew member on the opposite side with an oar, usually with each pulling an oar with two hands.
![The Dutch coxed pair at the 1977 World Rowing Championships, Evert Kroes and Peter van de Plas [Wikidata] with coxswain Poul de Haan in the bow Evert Kroes and Peter van de Plas 1977.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/de/Evert_Kroes_and_Peter_van_de_Plas_1977.jpg/220px-Evert_Kroes_and_Peter_van_de_Plas_1977.jpg)