Related Research Articles
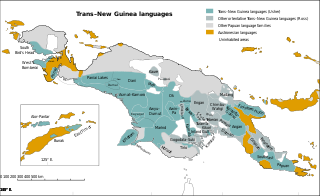
Trans–New Guinea (TNG) is an extensive family of Papuan languages spoken in New Guinea and neighboring islands, perhaps the third-largest language family in the world by number of languages. The core of the family is considered to be established, but its boundaries and overall membership are uncertain. The languages are spoken by around 3 million people. There have been three main proposals as to its internal classification.
Brahman is a term in Hinduism for the metaphysical ultimate reality, the highest unchanging Universal Principle in the universe.
Indo-Pacific is a hypothetical language macrofamily proposed in 1971 by Joseph Greenberg and now believed to be spurious. It grouped together the Papuan languages of New Guinea and Melanesia with the languages of the Andaman Islands and, tentatively, the languages of Tasmania, both of which are remote from New Guinea. The valid cognates Greenberg found turned out to be reflexes of the less extensive Trans–New Guinea family. Recently the Kusunda language, which is generally seen as a language isolate, is also included in the Indo-Pacific proposal.
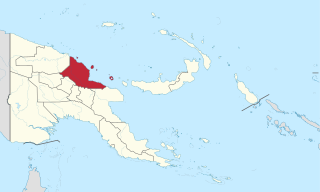
Madang is a province of Papua New Guinea. The province is on the northern coast of mainland Papua New Guinea and has many of the country's highest peaks, active volcanoes and its biggest mix of languages. The capital is the town of Madang.

Madang is the capital of Madang Province and is a town with a population of 27,420 on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. It was first settled by the Germans in the 19th century.
Tauya is a Rai Coast language spoken in the Ramu River valley, Madang Province, Papua New Guinea by approximately 350 people. The Linguistics Department at the University of Manitoba in Winnipeg, Canada, has Tauya language resources.
Ogea or Erima is a Papuan language spoken by approximately 2210 people living in an area 18 kilometers south of the town of Madang, in the Madang Province of Papua New Guinea.
The Numugen (Numagen) languages are a small family of closely related languages in the Madang branch of the Trans–New Guinea languages (TNG) phylum of New Guinea, spoken in the region of the Numagen River.
The Northern Adelbert or Pihom–Isumrud languages are a family of two dozen languages in the Madang stock of New Guinea. The occupy the coastal northern Adelbert Range of mountains, vs. the Southern Adelbert languages, another branch of Madang.
The Yaganon languages are a small family of closely related languages in New Guinea. They were linked with the Rai Coast languages in 1951 by Arthur Capell in his Madang family, but separated out again by Timothy Usher. The family is named after the Yaganon River.
The Rai Coast languages are a family of languages in the Madang stock of New Guinea.

The Madang or Madang–Adelbert Range languages are a language family of Papua New Guinea. They were classified as a branch of Trans–New Guinea by Stephen Wurm, followed by Malcolm Ross. William A. Foley concurs that it is "highly likely" that the Madang languages are part of TNG, although the pronouns, the usual basis for classification in TNG, have been "replaced" in Madang. Timothy Usher finds that Madang is closest to the Upper Yuat River languages and other families to its west, but does not for now address whether this larger group forms part of the TNG family.

The Monumbo or Bogia Bay languages are a pair of closely related languages that constitute a branch of the Torricelli language family. They are spoken in a few coastal villages around Bogia Bay of Bogia District, Madang Province in Papua New Guinea. Unlike all other Torricelli branches except for the Marienberg languages, word order in the Bogia languages is SOV, likely due to contact with Lower Sepik-Ramu and Sepik languages.
Kursav is a divergent and nearly extinct Madang language of the Adelbert Range of Papua New Guinea. It was once placed in the now-defunct Brahman branch of Madang. Daniels (2017) identifies Gants as its closest relative.
Gants, or in native orthography Gaj, is a Madang language of Papua New Guinea.
The Sogeram languages are a family of languages in the Madang stock of New Guinea. They are named after the Sogeram River.

Bundi Rural LLG is a local-level government (LLG) of Madang Province, Papua New Guinea.
Yamben is a Trans–New Guinea language of Madang Province, Papua New Guinea. It was first documented by Andrew Pick in the 2010s and classified by Pick (2019) as a probable primary branch of Madang, though its precise classification is still pending further research. Although surrounded by Croisilles languages, Yamben is not one of them.
Proto-Trans–New Guinea is the reconstructed proto-language ancestral to the Trans–New Guinea languages. Reconstructions have been proposed by Malcolm Ross and Andrew Pawley.

Brahman is a cattle station supplied with an airport near the eastern highlands of Madang Province, Papua New Guinea. It is located 500 km north of Port Moresby and is 128 meters above sea level.
References
- ↑ Brahman Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine , in the 15th edition of Ethnologue
| This Madang languages-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |