
Shopi or Šopi is a regional term, used by a group of people in the Balkans. The areas traditionally inhabited by the Shopi or Šopi is called Shopluk or Šopluk (Шоплук), a mesoregion. Most of the region is located in Western Bulgaria, with smaller parts in Eastern Serbia and Eastern North Macedonia, where the borders of the three countries meet.
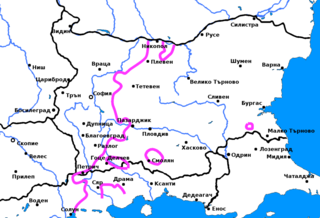
The Northwestern Bulgarian dialects are two closely related dialects of the Bulgarian language, which are located west of the yat boundary and thus are part of the Western Bulgarian dialects. The range of the dialects includes most of northwestern Bulgaria, to the west of the line between Nikopol, Pleven and Mezdra and to the north of the line between Vratsa and Belogradchik. They bear strong resemblance to their neighbouring Eastern Bulgarian dialects and with some exceptions, mainly the pronunciation of yat, have the same phonological and morphological features as the neighbouring subdialects of the Eastern Bulgarian Central Balkan dialect.

The Central Balkan dialect is a Bulgarian dialect that is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. Its range includes most of north-central Bulgaria, as well as the regions of Karlovo, Kazanlak and Plovdiv in southern Bulgaria, all the way down to the northernmost ridges of the Rhodopes. As a result of the mass population movements that affected eastern Bulgaria during the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century, the Central Balkan dialect is now spoken also in vast areas of northeastern Bulgaria. The most significant feature of the dialect is the pronunciation of Old Church Slavonic ѣ (yat) as or, depending on the character of the following syllable. The Central Balkan dialect lies at the foundation of formal Bulgarian. However, it is not identical to the standard language because many of its features derive from the Western Bulgarian dialects, including the Macedonian dialects, or are a compromise between Eastern and Western standard. The Central Balkan dialect includes a number of subdialects, e.g. Troyan, Lovech, Gabrovo, Karlovo, Kalofer, Tryavna, etc. which share many common features and yet have some differences.
The Pirdop dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, which is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. Its range includes the towns of Pirdop, Zlatitsa and Koprivshtitsa, as well as several neighbouring villages. The most significant feature of the dialect, as in all Balkan dialects, is the pronunciation of Old Church Slavonic ѣ (yat) as or, depending on the character of the following syllable. However, the Pirdop dialect also features a number of characteristics which bring it closer to the neighbouring Western Bulgarian dialects, and especially to the Botevgrad dialect and which, in turn, separate it from the rest of the Balkan dialects.
The Panagyurishte dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, which is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. Its range includes the town of Panagyurishte, as well as a number of neighbouring villages. The most significant feature of the dialect, as in all Balkan dialects, is the pronunciation of Old Church Slavonic ѣ (yat) as or, depending on the character of the following syllable.
The Zlatograd dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Rup or Southeastern Bulgarian dialects. The Zlatograd dialect is spoken in the southwestern part of the Eastern Rhodopes, i.e. in the town of Zlatograd, as well as a number of neighbouring villages and towns, e.g. Nedelino, Kirkovo, etc. The Zlatograd dialect is most closely related to the eastern and western Rup dialects, but also shares a number of phonological and morphological characteristics with the Rhodopean dialects. Thus, it is usually considered to be transitional between the two groups.
The Babyak dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Rup or Southeastern Bulgarian dialects. It is spoken in several mountainous villages on the western fringes of the Rhodopes and is thus sandwiched between the Chepino dialect on the east and northeast and the Razlog dialect to the south and west. It shares a number of phonological characteristics with both the Rup and the Southwestern dialects. Because of its specific reflexes of Old Church Slavonic yat, it is generally classified as a Rup dialect but is actually transitional between the two dialectal groups.
The Razlog dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Rup dialects. Its range includes the valley of Razlog in southwestern Bulgaria and its immediate neighbours are the Rup Serres-Nevrokop dialect to the south, the Babyak dialect to the east, the Samokov and Ihtiman dialects to the north and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect to the west. It shares a number of phonological characteristics with both the Rup and the Southwestern dialects. This is the dialect through which the Bulgarian language became known to modern science, because in 1822 the creator of the modern Serbian language Vuk Karadžić published in Vienna Dodatak k sankpeterburgskim sravnitelnim rijechnicima sviju jezika i narijechija s osobitom ogledom Bugarskog jezika ;("An addition to the St. Petersburg comparative dictionaries of all languages and dialects with a particular sample of the Bulgarian language"), in which are placed 273 words, a short grammar, 27 folk songs and 2 chapters of the gospel, which he wrote and said to him pravi bugarin iz Razloga;("a real Bulgarian from Razlog").
The Teteven dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, which is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. It is spoken in the town of Teteven and several neighbouring villages and is almost completely surrounded by the Central Balkan dialect, except on the west where it borders on the Western Bulgarian Botevgrad dialect. The most significant feature of the dialect, as in all Balkan dialects, is the pronunciation of Old Church Slavonic ѣ (yat) as or, depending on the character of the following syllable.
The Botevgrad dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Southwestern Bulgarian dialects, which is spoken in the region of Botevgrad and Etropole in northwestern Bulgaria. It is located on the yat boundary and is closely related to the Eastern Bulgarian Pirdop dialect.
The Ihtiman dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Southwestern Bulgarian dialects, which is spoken in the regions of Ihtiman, Kostenets and Septemvri in central western Bulgaria. It is transitional between the Botevgrad and Samokov dialect.
The Elin Pelin dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Southwestern Bulgarian dialects, which is spoken in the eastern part of the Sofia valley in central western Bulgaria. Its immediate neighbours are the Vratsa dialect to the north, the Botevgrad dialect to the east, the Sofia dialect to the west and the Samokov dialect to the south.
The Sofia dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Northwestern Bulgarian dialects, which is spoken in western part of the Sofia valley by part of the Shopi. Its immediate neighbours are the Vratsa dialect to the north, the Elin Pelin dialect to the east, the Transitional dialects to the west and the Samokov dialect to the south.
The Samokov dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Southwestern Bulgarian dialects, which is spoken in the region of Samokov in central western Bulgaria. Its immediate neighbours are the Sofia dialect and Elin Pelin dialect to the north, the Ihtiman dialect to the east, the Dupnitsa dialect to the west and the Razlog dialect to the south.
The Dupnitsa dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Southwestern Bulgarian dialects, which is spoken in the region of Dupnitsa in central western Bulgaria. It is transitional between the Samokov dialect to the east and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect to the south.
The Kyustendil dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Southwestern Bulgarian dialects, which is spoken in the region of Kyustendil in central western Bulgaria. It borders on the Transitional dialects to the north, the Dupnitsa dialect to the east and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect to the south. It is closely related to the Dupnitsa dialect.

The Transitional Bulgarian dialects are a group of Bulgarian dialects, whose speakers are located west of the yat boundary and are part of the Western Bulgarian dialects. As they have most of the typical characteristics of the North-Western Bulgarian dialects, they are sometimes classified as belonging to this subgroup under the name of Extreme North-Western dialects. On Bulgarian territory, the Transitional dialects occupy a narrow strip of land along the Bulgarian border with Serbia, including the regions of Tran, Breznik, Godech, Chiprovtsi and Belogradchik. They also cross the border to include the dialects or subdialects of the Bulgarian minority in the Western Outlands. The Transitional dialects are part of the Torlak dialectal group also spoken in southeastern Serbia and North Macedonia and are part of the gradual transition from Bulgarian to Serbian. The Bulgarian Transitional dialects and the Serbian Prizren-Timok dialects are loosely characterised by mixed, predominantly Serbian phonology and predominantly Bulgarian morphology. The features described here are characteristic only of the Transitional dialects within Bulgaria.
The Belogradchik dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Transitional dialects, which is spoken on the westernmost northern slopes of the Balkan mountains in northwestern Bulgaria. It borders on the Northwestern Byala Slatina-Pleven and Vidin-Lom dialect and north, the Sofia dialect to the southeast and the Serbian Torlak dialect to the southwest.
The Tran dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Transitional dialects, which is spoken in the regions of Tran and Godech in central western Bulgaria and in the Western Outlands. It borders on the Belogradchik dialect to the north, the Sofia dialect to the east and the Breznik dialect to the south.
The Shumen dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Moesian dialects. It is one of the best preserved Moesian dialects and is spoken in the regions of Shumen and Kaspichan.