
Ya or Ja is a letter of the Cyrillic script, the civil script variant of Old Cyrillic Little Yus, and possibly Iotated A. Among modern Slavic languages, it is used in the East Slavic languages and Bulgarian. It is also used in the Cyrillic alphabets used by Mongolian and many Uralic, Caucasian and Turkic languages of the former Soviet Union.

The Russian alphabet is the script used to write the Russian language. It comes from the Cyrillic script, which was devised in the 9th century for the first Slavic literary language, Old Slavonic. Initially an old variant of the Bulgarian alphabet, it became used in the Kievan Rusʹ since the 10th century to write what would become the modern Russian language.
The history of the Slavic languages stretches over 3000 years, from the point at which the ancestral Proto-Balto-Slavic language broke up into the modern-day Slavic languages which are today natively spoken in Eastern, Central and Southeastern Europe as well as parts of North Asia and Central Asia.

The letter Ъ of the Cyrillic script is known as er golyam in the Bulgarian alphabet, as the hard sign in the modern Russian and Rusyn alphabets, as the debelo jer in pre-reform Serbian orthography, and as ayirish belgisi in the Uzbek Cyrillic alphabet. The letter is called back yer or back jer and yor or jor in the pre-reform Russian orthography, in Old East Slavic, and in Old Church Slavonic.
Numerous Cyrillic alphabets are based on the Cyrillic script. The early Cyrillic alphabet was developed in the 9th century AD and replaced the earlier Glagolitic script developed by the Byzantine theologians Cyril and Methodius. It is the basis of alphabets used in various languages, past and present, Slavic origin, and non-Slavic languages influenced by Russian. As of 2011, around 252 million people in Eurasia use it as the official alphabet for their national languages. About half of them are in Russia. Cyrillic is one of the most-used writing systems in the world. The creator is Saint Clement of Ohrid from the Preslav literary school in the First Bulgarian Empire.
The Moesian dialects are a group of closely related dialects of the Bulgarian language, part of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. The Moesian dialects are spoken in northeastern Bulgaria and in the regions of Karnobat, Aytos, Burgas and Yambol in southern Bulgaria. However, due to the mass population movements that affected eastern Bulgaria during the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century, nowadays, there are very few areas where only Moesian is spoken. In most areas, and especially in southern Bulgaria and Dobruja, Moesian speakers are mixed with speakers speaking Balkan dialects. As a result of this and also due to the influence of the literary language, most features of the Moesian dialects have given way to features typical for the Balkan dialects.

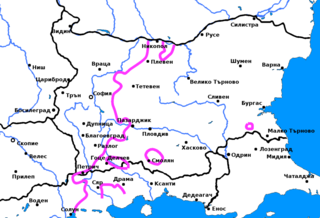
The Northwestern Bulgarian dialects are two closely related dialects of the Bulgarian language, which are located west of the yat boundary and thus are part of the Western Bulgarian dialects. The range of the dialects includes most of northwestern Bulgaria, to the west of the line between Nikopol, Pleven and Mezdra and to the north of the line between Vratsa and Belogradchik. They bear strong resemblance to their neighbouring Eastern Bulgarian dialects and with some exceptions, mainly the pronunciation of yat, have the same phonological and morphological features as the neighbouring subdialects of the Eastern Bulgarian Central Balkan dialect.

The Balkan dialects are the most extensive group of dialects of the Bulgarian language, covering almost half of the present-day territory of Bulgaria. Their range includes north-central Bulgaria and most of the Bulgarian part of Thrace, excluding the Rhodopes, the region of Haskovo and Strandzha. As a result of the mass population movements that affected eastern Bulgaria during the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century, the Balkan dialects are now spoken also in vast areas of northeastern Bulgaria, especially the regions of Dobrich and Varna. The most significant feature of the dialects, as in most Eastern Bulgarian dialects, is the pronunciation of Old Church Slavonic ѣ (yat) as or, depending on the character of the following syllable. The Balkan dialects, and in particular, the Central Balkan dialect, lie at the foundation of formal Bulgarian. However, they are not identical to the standard language because many of its features derive from the Western Bulgarian dialects, including the Macedonian dialects, or are a compromise between Eastern and Western standard.
The Erkech dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, which is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. It originates from two villages in the eastern parts of the Balkan Mountains, Kozichino near Pomorie and Golitsa south of Varna. As a result of the mass population movements that affected eastern Bulgaria during the 19th and the beginning of the 20th century, speakers of the dialect have established numerous colonies in the regions of Provadia, Varna, Novi Pazar, Balchik, Silistra and Pomorie, thus significantly expanding the range of the dialect. The most significant feature of the dialect, as in all Balkan dialects, is the pronunciation of Old Church Slavonic ѣ (yat) as or, depending on the character of the following syllable.
The Pirdop dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, which is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. Its range includes the towns of Pirdop, Zlatitsa and Koprivshtitsa, as well as several neighbouring villages. The most significant feature of the dialect, as in all Balkan dialects, is the pronunciation of Old Church Slavonic ѣ (yat) as or, depending on the character of the following syllable. However, the Pirdop dialect also features a number of characteristics which bring it closer to the neighbouring Western Bulgarian dialects, and especially to the Botevgrad dialect and which, in turn, separate it from the rest of the Balkan dialects.

The Rup dialects, or the Southeastern dialects, are a group of Bulgarian dialects located east of the yat boundary, thus being part of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. The range of the Rup dialects includes the southern part of Thrace, i.e. Strandzha, the region of Haskovo, the Rhodopes and the eastern half of Pirin Macedonia.
The Smolyan dialect or Central Rhodope dialect is a Bulgarian dialect of the Rhodopean group of the Rup dialects. Its range includes most of the Central Rhodopes, i.e. the region of Smolyan. Its immediate neighbours are the Rhodopean Hvoyna dialect to the north, the Serres-Nevrokop dialect and the Razlog dialect to the west and the Turkish dialects of the Turkish population in the Eastern Rhodopes. To the south, the Smolyan dialect crosses the Greek-Bulgarian border and is spoken by much of the Muslim Bulgarian (Pomak) population in Western Thrace. As a result of the rugged mountainous terrain and the century-long isolation of the region from the rest of the country, the Smolyan dialect is the most idiosyncratic of all Bulgarian dialects and is not readily understandable even for its immediate neighbours.
The Hvoyna dialect is a Bulgarian dialect of the Rhodopean group of the Rup dialects. Its range includes the northern part of the Central Rhodopes and the town of Batak in the Western Rhodopes. Its immediate neighbours are the Central Balkan dialect to the north, the Smolyan dialect to the south and the Rhodopean Chepino dialect to the west.
The Chepino dialect is a Bulgarian dialect of the Rhodopean group of the Rup dialects. Its range includes the northwestern Rhodopes, i.e. the towns of Velingrad, Rakitovo and Kostandovo and the villages of Dragichevo and Dorkovo. Its immediate neighbours are the Central Balkan dialect and the Ihtiman dialect to the north, the Babyak dialect to the west and south and the Hvoyna dialect to the east. The Chepino dialect is spoken by both Orthodox and Muslim Bulgarians in the region irrespective of religious affiliation.
The Paulician dialect is a Bulgarian dialect of the Rhodopean group of the Rup dialects. The Paulician dialect is spoken by some 40,000 people, nearly all of them Catholic Bulgarians, in the region of Rakovski in southern Bulgaria and Svishtov in northern Bulgaria, as well as regions in Romania. The language of the Banat Bulgarians, late 17th century Bulgarian Catholic migrants to Banat, is phonologically and morphologically identical to the Paulician dialect. The dialect's name derives from the Paulicians, believed to be the ancestors of the Catholic Banat Bulgarians.
The Zlatograd dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Rup or Southeastern Bulgarian dialects. The Zlatograd dialect is spoken in the southwestern part of the Eastern Rhodopes, i.e. in the town of Zlatograd, as well as a number of neighbouring villages and towns, e.g. Nedelino, Kirkovo, etc. The Zlatograd dialect is most closely related to the eastern and western Rup dialects, but also shares a number of phonological and morphological characteristics with the Rhodopean dialects. Thus, it is usually considered to be transitional between the two groups.
The Razlog dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Rup dialects. Its range includes the valley of Razlog in southwestern Bulgaria and its immediate neighbours are the Rup Serres-Nevrokop dialect to the south, the Babyak dialect to the east, the Samokov and Ihtiman dialects to the north and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect to the west. It shares a number of phonological characteristics with both the Rup and the Southwestern dialects. This is the dialect through which the Bulgarian language became known to modern science, because in 1822 the creator of the modern Serbian language Vuk Karadžić published in Vienna Dodatak k sankpeterburgskim sravnitelnim rijechnicima sviju jezika i narijechija s osobitom ogledom Bugarskog jezika ;("An addition to the St. Petersburg comparative dictionaries of all languages and dialects with a particular sample of the Bulgarian language"), in which are placed 273 words, a short grammar, 27 folk songs and 2 chapters of the gospel, which he wrote and said to him pravi bugarin iz Razloga;("a real Bulgarian from Razlog").
The Teteven dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, which is part of the Balkan group of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. It is spoken in the town of Teteven and several neighbouring villages and is almost completely surrounded by the Central Balkan dialect, except on the west where it borders on the Western Bulgarian Botevgrad dialect. The most significant feature of the dialect, as in all Balkan dialects, is the pronunciation of Old Church Slavonic ѣ (yat) as or, depending on the character of the following syllable.

The Southwestern Bulgarian dialects are a group of Bulgarian dialects which are located west of the yat boundary and are part of the Western Bulgarian dialects. The range of the Southwestern dialects on the territory of Bulgaria includes most of west central and southwestern Bulgaria. The Southwestern dialects border on the Northwestern dialects to the north, the Transitional dialects to the northwest and the Balkan dialects and the Rup dialects to the northeast and southeast, respectively. If the Macedonian language is regarded as a third literary form of Modern Bulgarian, then the Southwestern dialects extend west and southwest to include the Slavic dialects in Vardar Macedonia and the western half of Greek Macedonia. Should the Macedonian language be counted as a separate language, then the southernmost dialect of the group, the Blagoevgrad-Petrich or Pirin dialect, along with the corresponding variety on the Macedonian side of the border, the Maleshevo dialect, constitute a transitional dialect between Bulgarian and Macedonian. A defining characteristic of the Southwestern dialects is the gradual transition from one dialect to another, as well as to dialects which belong to other dialectal groups. For example, the Dupnitsa dialect is transitional to both the Samokov dialect and the Blagoevgrad-Petrich dialect, the Botevgrad dialect is transitional to the Eastern Bulgarian Balkan dialects, and especially to the Pirdop dialect, etc. etc.
The Samokov dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Southwestern Bulgarian dialects, which is spoken in the region of Samokov in central western Bulgaria. Its immediate neighbours are the Sofia dialect and Elin Pelin dialect to the north, the Ihtiman dialect to the east, the Dupnitsa dialect to the west and the Razlog dialect to the south.