
Amoco is a brand of fuel stations operating in the United States and owned by British conglomerate BP since 1998. The Amoco Corporation was an American chemical and oil company, founded by Standard Oil Company in 1889 around a refinery in Whiting, Indiana, and was officially the Standard Oil Company of Indiana until 1985. Originally part of the Standard Oil Company trust, it focused on producing gasoline for the new automobile market. In 1911, as part of the break-up of the Standard Oil trust, it became an independent corporation. Incorporated in Indiana, it was headquartered in Chicago, and formally adopted the name Amoco in 1985. Amoco Corporation merged in 1998, over the course of several years all Amoco and Standard stations were converted to BP. The Amoco name was branded at the gas pump for the highest 93 octane blends. The Deepwater Horizon oil spill of 2010 tarnished the BP brand in the US resulting in a rethinking of US branding. Amoco was resurrected in 2017 beyond merely being a gasoline blend, as service station owners could choose to use the Amoco brand for station branding and supplies purchased from BP in selected areas of the United States markets. This branding decision also allow for an increase in stations without flooding a particular market with a single BP name. This was consistent with marketing at Chevron and ExxonMobil and the utilization of the Chevron/Texaco and Exxon/Mobil brands.
Union Oil Company of California, and its holding company Unocal Corporation, together known as Unocal was a major petroleum explorer and marketer in the late 19th century, through the 20th century, and into the early 21st century. It was headquartered in El Segundo, California, United States.

The Turkmenistan–Afghanistan–Pakistan–India (TAPI) Gas Pipeline, also known as Trans-Afghanistan Pipeline, is a natural gas pipeline being developed by the Galkynysh – TAPI Pipeline Company Limited with participation of the Asian Development Bank. The pipeline will transport natural gas from the Galkynysh Gas Field in Turkmenistan through Afghanistan into Pakistan and then to India. A ceremony to mark the project's initiation was held in Turkmenistan on 13 December 2015, and practical work in Afghanistan began on 11 September 2024. Proponents of the project see it as a modern continuation of the Silk Road.
Talisman Energy Inc. was a Canadian independent petroleum company that existed between 1993 and 2015. The company was created from the assets of BP Canada after British Petroleum divested its 57 percent stake in June 1992. It was one of Canada's largest independent oil and gas companies, and operated globally, with operations in Canada and the United States of America in North America; Colombia, South America; Algeria in North Africa; United Kingdom and Norway in Europe; Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, Papua New Guinea, East Timor and Australia in the Far East; and Kurdistan in the Middle East. Talisman Energy has also built the offshore Beatrice Wind Farm in the North Sea off the coast of Scotland.

The China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) is a major national oil and gas corporation of China and one of the largest integrated energy groups in the world. Its headquarters are in Dongcheng District, Beijing. CNPC was ranked fourth in 2022 Fortune Global 500, a global ranking of the largest corporations by revenue.
ARETI International Group is a private energy company headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. The ARETI group consists of holding companies registered in Switzerland, Cyprus, the United States, Turkmenistan and is involved in the energy industry, real estate and cycling development. The company operates primarily in Switzerland and the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries. ARETI was created by Igor Makarov in 2015 following his sale of Itera International Group of Companies, which was started in 1992 and sold off in 2013, when Itera's main subsidiary, Itera Oil & Gas Company, was acquired by Rosneft prior to any sanctions placed on Rosneft.
Kashagan Field is an offshore oil field in Kazakhstan's zone of the Caspian Sea. The field, discovered in 2000, is located in the northern part of the Caspian Sea close to Atyrau and is considered the world's largest discovery in the last 30 years, combined with the Tengiz Field. When discovered, it was the second largest oil field in the world.

Shah Deniz gas field is the largest natural gas field in Azerbaijan. It is situated in the South Caspian Sea, off the coast of Azerbaijan, approximately 70 kilometres (43 mi) southeast of Baku, at a depth of 600 metres (2,000 ft). The field covers approximately 860 square kilometres (330 sq mi). Stretching out over 140 square kilometres, the reservoir is similar in size and shape to Manhattan Island.
The Afghanistan Oil Pipeline was a project proposed by several oil companies to transport oil from the Caspian region and Central Asia through Afghanistan to Pakistan.
Azeri–Chirag–Gunashli or Azeri–Chirag–Deepwater Gunashli is a complex of oil fields in the Caspian Sea, about 120 kilometres (75 mi) off the coast of Azerbaijan. It consists of the Azeri and Chirag oil fields, and the deepwater portion of the Gunashli oil field. An overall estimate of the area of the development is 432.4 square kilometres (167.0 sq mi). It is developed by the Azerbaijan International Operating Company, a consortium of international oil companies, and operated by BP on behalf of the consortium. The ACG fields have estimated recoverable reserves of about 5 to 6 billion barrels of petroleum. Peak oil production of 885,000 barrels per day (140,700 m3/d) was reached in 2010. However by the first quarter of 2024 production had fallen to 339,000 barrels per day (53,900 m3/d), or approximately one-third of peak value, as the development continued terminal decline. As of 2021, ACG oil accounted for 95% of all Azerbaijani oil exports.
Central Asia Gas Pipeline, Ltd. (CentGas) was a consortium formed in the 1990s to develop a project to build the Trans-Afghanistan Pipeline from Turkmenistan's natural gas fields to Pakistan. The consortium had also considered an extension of the pipeline to the New Delhi area. Regional and political instability proved too great a challenge to overcome and the project eventually was cancelled after Unocal withdrew from the consortium.

The Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline is a proposed subsea pipeline between Türkmenbaşy in Turkmenistan, and Baku in Azerbaijan. According to some proposals it would also include a connection between the Tengiz Field in Kazakhstan, the Sangachal Terminal in Baku, and Türkmenbaşy. The Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline project would transport natural gas from Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan to European Union member countries, circumventing both Russia and Iran. It would do this by feeding the Southern Gas Corridor. This project attracts significant interest since it would connect vast Turkmen gas resources to major consumers Turkey and Europe.
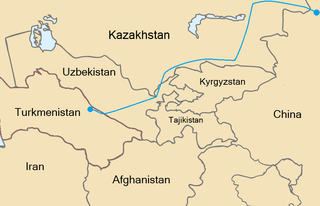
The Central Asia–China gas pipeline is a natural gas pipeline system from Central Asia to Xinjiang in the People's Republic of China. By connecting Turkmenistan to China’s domestic grid, this pipeline makes it possible to transport gas some 7000 km from Turkmenistan to Shanghai. More than half of Turkmen natural gas exports are delivered to China through the pipeline.

BP p.l.c. is a British multinational oil and gas company headquartered in London, England. It is one of the oil and gas "supermajors" and one of the world's largest companies measured by revenues and profits. It is a vertically integrated company operating in all areas of the oil and gas industry, including exploration and extraction, refining, distribution and marketing, power generation, and trading.

Carlos Alberto Bulgheroni was an Argentine businessman prominent in the nation's energy sector, and the country's richest man at the time of his death.

China National Offshore Oil Corporation, or CNOOC Group, is the third-largest national oil company in China, after CNPC and China Petrochemical Corporation. The CNOOC Group focuses on the exploitation, exploration and development of crude oil and natural gas in offshore China, along with its subsidiary COOEC.

The Trans-Anatolian Natural Gas Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline in Turkey. It is the central part of the Southern Gas Corridor, which connects the giant Shah Deniz gas field in Azerbaijan to Europe through the South Caucasus Pipeline and the Trans Adriatic Pipeline. The pipeline has a strategic importance for both Azerbaijan and Turkey. It allows the first Azerbaijani gas exports to Europe, beyond Turkey. It also strengthens the role of Turkey as a regional energy hub.
Alejandro Pedro Bulgheroni is an Argentine billionaire businessman in the oil and gas sector. Following his education at the University of Buenos Aires, he joined his father's company, the Bridas Corporation, founded by the Bulgheroni family in 1948. Following expansion by the company, half of it was sold to the Chinese state-run CNOOC Group in 2010. As of March 2022, his net worth is estimated at US$1.9 billion.

Bangladesh is the sixteenth-largest producer of natural gas in Asia. Gas supplies meet 56% of domestic energy demand. However, the country faces an acute energy crisis in meeting the demands of its vast and growing population. Bangladesh is a net importer of crude oil and petroleum products. The energy sector is dominated by state-owned companies, including Petrobangla and the Bangladesh Petroleum Corporation. Chevron, ConocoPhillips, Equinor, Gazprom and ONGC are major international companies engaged in Bangladesh's hydrocarbon industry, with Chevron's gas fields accounting for 50% of natural gas production.












