
Bridgwater is a historic market town and civil parish in Somerset, England. The town had a population of 41,276 at the 2021 census. Bridgwater is at the edge of the Somerset Levels, in level and well-wooded country. The town lies along both sides of the River Parrett; it has been a major inland port and trading centre since the industrial revolution. Most of its industrial bases still stand today. Its larger neighbour, Taunton, is linked to Bridgwater via a canal, the M5 motorway and the GWR railway line.

The River Parrett flows through the counties of Dorset and Somerset in South West England, from its source in the Thorney Mills springs in the hills around Chedington in Dorset. Flowing northwest through Somerset and the Somerset Levels to its mouth at Burnham-on-Sea, into the Bridgwater Bay nature reserve on the Bristol Channel, the Parrett and its tributaries drain an area of 660 square miles (1,700 km2) – about 50 per cent of Somerset's land area, with a population of 300,000.

Greyfriars Church is an evangelical Anglican church, and former Franciscan friary, in the town centre of Reading in the English county of Berkshire. The church forms part of the Church of England's Diocese of Oxford.

Blackfriars, Gloucester, England, founded about 1239, is one of the most complete surviving Dominican black friaries in England. Now owned by English Heritage and restored in 1960, it is currently leased to Gloucester City Council and used for weddings, concerts, exhibitions, guided tours, filming, educational events and private hires. The former church, since converted into a house, is a Grade I listed building.

The Church and Friary of St Francis, known locally as Gorton Monastery, is a Grade II* listed former Franciscan friary in Gorton, Manchester, England. It was designed by the noted Victorian architect Edward Welby Pugin and built 1866–1872. Gorton Monastery is a noted example of Gothic Revival architecture.

Bridgwater Castle was a castle in the town of Bridgwater, Somerset, England.

Bridgwater and Taunton College is a further education college based in the heart of Somerset, England, with main centres in Bridgwater, Taunton and Cannington. It educates approximately 3000 students between the ages of 16–18 in academic and vocational programmes in addition to several thousand part-time or mature students. The college was founded in 1973, although the history of its predecessor institutions dates to 1891.

Cannington Court in the village of Cannington, Somerset, England was built around 1138 as the lay wing of a Benedictine nunnery, founded by Robert de Courcy. It has been designated as a Grade I listed building.
Buckland Priory was established around 1167 in Lower Durston, Somerset, England.
Ilchester Friary was founded between 1221 and 1260 as a Dominican monastery in Ilchester Somerset, England.

Greyfriars, in Bristol, England, was a Franciscan friary. The name Greyfriars derived from the grey robes worn by the friars. It was founded at some time before 1234, within the town walls and then moved to Lewin's Mead in 1250. The site included extensive gardens surrounded by a stone wall. Following the Dissolution of the Monasteries in the sixteenth century, the premises were leased to the town council in 1541, who desired to use the stone to make repairs to the town walls, and the harbour facilities. In succeeding centuries many different uses have been made of the site, which is currently occupied by an office block and part of Bristol Dental School.
Whitefriars was a Carmelite friary on the lower slopes of St Michael's Hill, Bristol, England. It was established in 1267; in subsequent centuries a friary church was built and extensive gardens developed. The establishment was dissolved in 1538.

Various monasteries and other religious houses have existed at various times during the Middle Ages in the city of Exeter, Devon, England.

The Greyfriars, Lincoln was a Franciscan friary in Lincolnshire, England. The surviving building is the remains of the infirmary of the friary, built of dressed stone and brick and dating from c.1230, with mid-19th-century additions. The clay tile roof of the main building is in a poor condition and the Welsh slate roof of the 19th-century extension has been repaired.
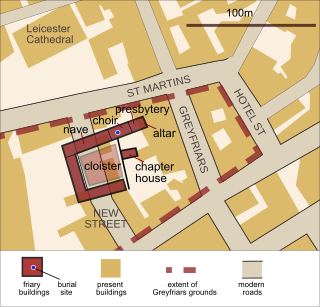
Greyfriars, Leicester, was a friary of the Order of Friars Minor, commonly known as the Franciscans, established on the west side of Leicester by 1250, and dissolved in 1535. Following dissolution the friary was demolished and the site levelled, subdivided, and developed over the following centuries. The locality has retained the name Greyfriars particularly in the streets named "Grey Friars", and the older "Friar Lane".

Longforth Farm, on the outskirts of Wellington, Somerset, England, is the site of a Bronze Age landscape and an extensive medieval structure.

The Chandos Glass Cone in Bridgwater, in the English county of Somerset, was built in 1725 as a kiln for a glassworks. The remains have been scheduled as an ancient monument.

Kinalehin Friary, originally a medieval charterhouse or Carthusian monastery and later a Franciscan friary, is a National Monument located in County Galway, Ireland.

Immaculate Conception Church, also known as the Church of the Immaculate Conception of Mary, is a Roman Catholic parish church in Clevedon, Somerset. It was built from 1886 to 1887 and was designed by Alexander Scoles, an architect and priest who worked in Somerset. It is located on the intersection between Marine Parade, Marine Hill and Wellington Terrace, overlooking the Severn Estuary. It was founded by the Franciscan Order of Friars Minor who continue to serve the parish.

















