Related Research Articles

The London, Brighton and South Coast Railway was a railway company in the United Kingdom from 1846 to 1922. Its territory formed a rough triangle, with London at its apex, practically the whole coastline of Sussex as its base, and a large part of Surrey. It was bounded on its western side by the London and South Western Railway (L&SWR), which provided an alternative route to Portsmouth. On its eastern side the LB&SCR was bounded by the South Eastern Railway (SER)—later one component of the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SE&CR)—which provided an alternative route to Bexhill, St Leonards-on-Sea, and Hastings. The LB&SCR had the most direct routes from London to the south coast seaside resorts of Brighton, Eastbourne, Worthing, Littlehampton and Bognor Regis, and to the ports of Newhaven and Shoreham-by-Sea. It served the inland towns and cities of Chichester, Horsham, East Grinstead and Lewes, and jointly served Croydon, Tunbridge Wells, Dorking and Guildford. At the London end was a complicated suburban and outer-suburban network of lines emanating from London Bridge and Victoria, and shared interests in two cross-London lines.
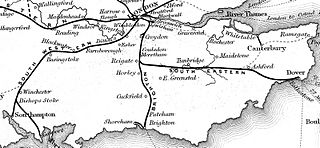
The London and Brighton Railway (L&BR) was a railway company in England which was incorporated in 1837 and survived until 1846. Its railway ran from a junction with the London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) at Norwood – which gives it access from London Bridge, just south of the River Thames in central London. It ran from Norwood to the South Coast at Brighton, together with a branch to Shoreham-by-Sea.

The Brighton Main Line is a major railway line in the United Kingdom that links Brighton, on the south coast of England, with central London. In London the line has two branches, out of London Victoria and London Bridge stations respectively, which join up in Croydon and continue towards Brighton as one line. The line is electrified throughout using the third rail system.

The West Coastway line is a railway line in England linking the conurbations of Brighton/Hove/Littlehampton and Southampton/Portsmouth, with 1.3 million people between them. It has short southward branches to Littlehampton and Bognor Regis, which offer direct services to and from London.
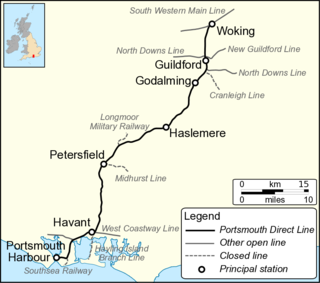
The Portsmouth Direct line is a railway route between Woking in Surrey and Portsmouth Harbour in Hampshire, England. It forms the principal route for passenger trains between London, Guildford and Portsmouth; connections are made to the ferry services which operate between Portsmouth and the Isle of Wight. The final section of line from Havant to Portsmouth is shared with other passenger routes.

Hassocks railway station is on the Brighton Main Line in England, serving the village of Hassocks, West Sussex. It is 43 miles 42 chains (70.0 km) down the line from London Bridge via Redhill and is situated between Burgess Hill and Preston Park. It is managed by Southern.

Worthing railway station is the largest of the five stations serving the town of Worthing in West Sussex. It is 10 miles 46 chains (17.0 km) down the line from Brighton. The station is managed by Govia Thameslink Railway who operate all the services. It is one of the main stations on the West Coastway Line; all timetabled trains stop here.

Lancing railway station is in Lancing in the county of West Sussex, England. It is 8 miles 19 chains (13.3 km) down the line from Brighton. The station is operated by Southern.

Hove railway station serves Hove, in Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is 50 miles 56 chains (81.6 km) measured from London Victoria. The station and the majority of trains serving it are operated by Southern.

Bognor Regis railway station is in the town of Bognor Regis, in the English county of West Sussex. It opened as the terminus of a short branch line in 1864, replacing a more distant station on the Worthing to Chichester main line. Like the town it served, it was known as Bognor until 1929. The junction on the main line is Barnham station, opened on the same day as the branch itself.

Barnham railway station is in Barnham, West Sussex, England around 5 miles (8.0 km) north of Bognor Regis.

Angmering is a railway station on the West Coastway Line, on the border of Angmering and East Preston in the district of Arun. It was opened in 1846. The station itself is situated about 0.6 miles (1 km) away from the centre of Angmering village, and is 15 miles 44 chains (25.0 km) down the line from Brighton. Buses depart for Angmering village hourly, or walking to the village takes about 20 minutes. The station is located near the local secondary school The Angmering School, some of the students of which use the station daily to travel to and from school. Angmering station is also designed to be used by the residents of the nearby villages of Rustington and East Preston, with some of the station's signage actually reading 'Angmering for Rustington and East Preston'.

Southwick railway station serves the town of Southwick in West Sussex, England. It is on the West Coastway Line, 4 miles 30 chains (7.0 km) from Brighton. It is operated by Southern. Its platforms are long enough for eight-coach trains.

Portslade railway station is a railway station located in Portslade-by-Sea in the city of Brighton and Hove, East Sussex, England, but located on the western fringes of the village of Aldrington. It is 2 miles 73 chains (4.7 km) down the line from Brighton.
The Cranleigh line was a railway line in England that connected Guildford in Surrey, with Horsham in West Sussex. Construction of the line was started by an independent company, the Horsham and Guildford Direct Railway, but management failures delayed construction, and the company was taken over by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LBSCR). The LBSCR completed the construction of the line and it was opened in 1865; it was nearly 16 miles in length.
The Steyning Line was a railway branch line that connected the West Sussex market town of Horsham with the port of Shoreham-by-Sea, with connections to Brighton. It was built by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway, and opened in 1861. It was 20 miles in length. It followed the course of the River Adur for much of its extent and was alternatively known as the Adur Valley Line.

The Brighton, Lewes and Hastings Railway was an early railway in southern England that built the East Coastway line running between the three East Sussex towns mentioned in its name. The company existed from February 1844 but only operated trains for a few weeks during June and July 1846 before it was amalgamated with other companies to form the London Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) on 27 July 1846.
The Croydon and Epsom Railway was an early railway in southern England running between the two Surrey towns mentioned in its name. The company was formed March 1844 to operate a new line using the atmospheric principle. However, before its line was opened it was amalgamated with other companies to form the London Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR) on 27 July 1846.
The Portsmouth to Brighton Railway was built by the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway and its immediate predecessor in several stages.
The Mid-Sussex railways were a group of English railway companies that together formed what became the Mid-Sussex line, from Three Bridges through Horsham to Littlehampton, in southern England. After 1938 the Southern Railway operated a regular electric train service ran from London to Bognor Regis and Portsmouth using the marketing brand "Mid-Sussex Line", leading to an informal consensus. The Mid-Sussex Railway company ran from Horsham to Petworth, and the Mid-Sussex Junction line of the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LBSCR) extended from the Petworth line to Littlehampton. The Three Bridges to Horsham branch of the LBSCR was at first the sole access from the north to the Mid-Sussex railways, although a line from Leatherhead was used later.
References
- ↑ Turner, John Howard (1977). The London Brighton and South Coast Railway: 1 Origins and Formation. London: Batsford. pp. 206–12. ISBN 0-7134-0275-X.
- ↑ Turner, JT Howard (1977). The London, Brighton & South Coast Railway 1 :Origins & Formation (First ed.). London: BT Batsford Ltd. p. 212. ISBN 0-7134-0275X.
- ↑ White, H.P. (1961). a regional history of the railways of Great Britain: II. Southern England. London: Phoenix House. p. 99.