Related Research Articles

Digitaria is a genus of plants in the grass family native to tropical and warm temperate regions but can occur in tropical, subtropical, and cooler temperate regions as well. Common names include crabgrass, finger-grass, and fonio. They are slender monocotyledonous annual and perennial lawn, pasture, and forage plants; some are often considered lawn pests. Digitus is the Latin word for "finger", and they are distinguished by the long, finger-like inflorescences they produce.

Aricia agestis, the brown argus, is a butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It is found throughout the Palearctic realm, north to northern Jutland (Denmark) and east to Siberia and the Tian Shan.

Ellenborough Park is a park situated in the centre of Weston-super-Mare, North Somerset, England.
This article gives an overview of the plant communities formed by vegetation of open habitats in the British National Vegetation Classification system.
NVC community SD12 is one of the 16 sand-dune communities in the British National Vegetation Classification system.
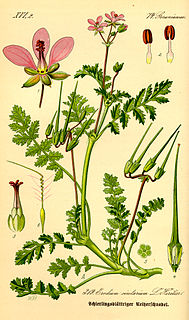
Erodium cicutarium, also known as common stork's-bill, redstem filaree, redstem stork's bill or pinweed, is a herbaceous annual – or in warm climates, biennial – member of the family Geraniaceae of flowering plants. It is native to Macaronesia, temperate Eurasia and north and northeast Africa, and was introduced to North America in the eighteenth century, where it has since become naturalized, particularly of the deserts and arid grasslands of the southwestern United States.

Stephens's kangaroo rat is a species of rodent in the family Heteromyidae. It is endemic to the Southern California region of the United States, primarily in western Riverside County. The species is named after American zoologist Frank Stephens (1849–1937).

Erodium moschatum is a species of flowering plant in the geranium family known by the common names musk stork's-bill and whitestem filaree. This is a weedy annual or biennial herb which is native to much of Eurasia and North Africa but can be found on most continents where it is an introduced species. The young plant starts with a flat rosette of compound leaves, each leaf up to 15 centimeters long with many oval-shaped highly lobed and toothed leaflets along a central vein which is hairy, white, and stemlike. The plant grows to a maximum of about half a meter in height with plentiful fuzzy green foliage. The small flowers have five sepals behind five purple or lavender petals, each petal just over a centimeter long. The filaree fruit has a small, glandular body with a long green style up to 4 centimeters in length.

Digitaria ischaemum is a species of crabgrass known by the common names smooth crabgrass and small crabgrass. It is native to Europe and Asia, but it is known throughout much of the warm temperate world as an introduced species and often a common roadside and garden weed. It is an annual grass producing an inflorescence with two or more narrow branches lined with tiny spikelets.
British NVC community OV3 is one of the open habitat communities in the British National Vegetation Classification system. It is one of six arable weed and track-side communities of light, less-fertile acid soils.
British NVC community OV6 is one of the open habitat communities in the British National Vegetation Classification system. It is one of six arable weed and track-side communities of light, less-fertile acid soils.
British NVC community OV8 is one of the open habitat communities in the British National Vegetation Classification system. It is one of eight arable weed and wasteland communities of fertile loams and clays.
British NVC community OV14 is one of the open habitat communities in the British National Vegetation Classification system. It is one of eight arable weed and wasteland communities of fertile loams and clays.

Wingletang Down is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) on the southern side of the island of St Agnes in the Isles of Scilly, England, UK, which is noted for its biological characteristics. The site is managed by the Isles of Scilly Wildlife Trust and is within the Isles of Scilly Heritage Coast and the Isles of Scilly Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. It is the only site in Great Britain and Ireland for the small fern, least adder's–tongue. As of 11 September 2009 the SSSI was considered to be in ″unconditional recovering″ condition because European gorse and bramble are at unacceptable levels.
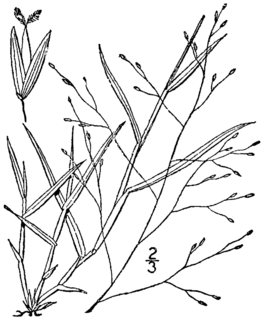
Digitaria cognata is a species of grass known by the common names fall witchgrass, Carolina crabgrass, and mountain hairgrass.

Digitaria ciliaris is a species of grass known by the common names southern crabgrass, tropical finger-grass, tropical crabgrass or summer grass.
Common stork's-bill is a common name for several plants and may refer to:

Alnmouth Saltmarsh and Dunes is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Northumberland, England. It is the largest saltflat on the north-east coast, located on the south bank of the River Aln estuary, and notable for the varied plant community found on the interface between the saltflats and the dunes. It overlaps with and forms part of the much larger Northumberland Shore SSSI.
Bamburgh Coast and Hills is the name given to a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) on the coast of north Northumberland, England. The site is one of the longest-standing SSSIs in England, having been listed since 1954, and displays the interaction of a fluid magma rock, now known as the Whin Sill, interacting with older sedimentary rock. Coastal erosion at the site enables sections of the geological strata to be seen. In turn, the soil associated with the Whin Sill gives rise to a distinct pattern of vegetation which on its own merits is at this site found notable.

Ischaemum rugosum, also known as saramollagrass, is a flowering plant belonging to the grass family Poaceae in the genus Ischaemum, and is native to tropical and temperate regions of Asia, growing in marshes and other wet habitats. It is a vigorous annual, and is an invasive species in South America and Madagascar. It reaches heights of up to 1 m and is primarily recognized by the ridged surface of its sessile spikelet’s lower glume. Despite its historic importance as fodder in Asia, the grass has become a major weed in mid-latitude rice paddies throughout Asia and South America.
References
Rodwell, John S, ed. (March 2000). Maritime communities and vegetation of open habitats. British Plant Communities. Vol. 5. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-39167-2.