
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (−OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, C
6H
5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.

Phenol, or Benzenol, is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile. The molecule consists of a phenyl group bonded to a hydroxy group. Mildly acidic, it requires careful handling because it can cause chemical burns.

In organic chemistry, the phenyl group, or phenyl ring, is a cyclic group of atoms with the formula C6H5, and is often represented by the symbol Ph. The phenyl group is closely related to benzene and can be viewed as a benzene ring, minus a hydrogen, which may be replaced by some other element or compound to serve as a functional group. A phenyl group has six carbon atoms bonded together in a hexagonal planar ring, five of which are bonded to individual hydrogen atoms, with the remaining carbon bonded to a substituent. Phenyl groups are commonplace in organic chemistry. Although often depicted with alternating double and single bonds, the phenyl group is chemically aromatic and has equal bond lengths between carbon atoms in the ring.
Furan is a heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic ring with four carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as furans.
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications.

Bromobenzene is the simplest of the bromobenzenes, consisting of a benzene ring substituted with one bromine atom. Its chemical formula is C6H5Br. It is a colourless liquid although older samples can appear yellow. It is a reagent in organic synthesis.
The Hofmann rearrangement is the organic reaction of a primary amide to a primary amine with one less carbon atom. The reaction involves oxidation of the nitrogen followed by rearrangement of the carbonyl and nitrogen to give an isocyanate intermediate. The reaction can form a wide range of products, including alkyl and aryl amines.
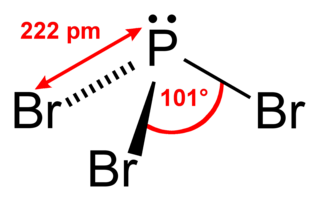
Phosphorus tribromide is a colourless liquid with the formula PBr3. The liquid fumes in moist air due to hydrolysis and has a penetrating odour. It is used in the laboratory for the conversion of alcohols to alkyl bromides.
The Sandmeyer reaction is a chemical reaction used to synthesize aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts using copper salts as reagents or catalysts. It is an example of a radical-nucleophilic aromatic substitution. The Sandmeyer reaction provides a method through which one can perform unique transformations on benzene, such as halogenation, cyanation, trifluoromethylation, and hydroxylation.
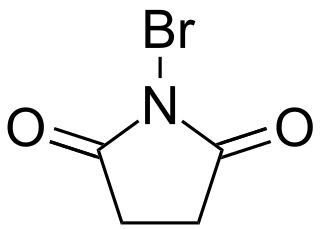
N-Bromosuccinimide or NBS is a chemical reagent used in radical substitution, electrophilic addition, and electrophilic substitution reactions in organic chemistry. NBS can be a convenient source of Br•, the bromine radical.
In organic chemistry, hydroboration refers to the addition of a hydrogen-boron bond to certain double and triple bonds involving carbon. This chemical reaction is useful in the organic synthesis of organic compounds.
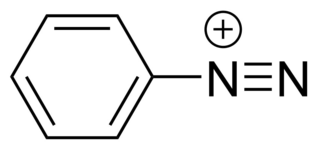
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group [R−N+≡N]X− where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide.
The Wohl–Ziegler reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the allylic or benzylic bromination of hydrocarbons using an N-bromosuccinimide and a radical initiator.

Thiophenol is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H5SH, sometimes abbreviated as PhSH. This foul-smelling colorless liquid is the simplest aromatic thiol. The chemical structures of thiophenol and its derivatives are analogous to phenols. An exception is the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the aromatic ring is replaced by a sulfur atom. The prefix thio- implies a sulfur-containing compound and when used before a root word name for a compound which would normally contain an oxygen atom, in the case of 'thiol' that the alcohol oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom.
The Hunsdiecker reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry whereby silver salts of carboxylic acids react with a halogen to produce an organic halide. It is an example of both a decarboxylation and a halogenation reaction as the product has one fewer carbon atoms than the starting material and a halogen atom is introduced its place. A catalytic approach has been developed.
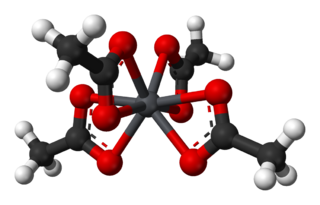
Lead(IV) acetate or lead tetraacetate is an metalorganic compound with chemical formula Pb(C2H3O2)4. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in nonpolar, organic solvents, indicating that it is not a salt. It is degraded by moisture and is typically stored with additional acetic acid. The compound is used in organic synthesis.

A boronic acid is an organic compound related to boric acid in which one of the three hydroxyl groups is replaced by an alkyl or aryl group. As a compound containing a carbon–boron bond, members of this class thus belong to the larger class of organoboranes.
Organobromine chemistry is the study of the synthesis and properties of organobromine compounds, also called organobromides, which are organic compounds that contain carbon bonded to bromine. The most pervasive is the naturally produced bromomethane.

Oxazoline is a five-membered heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C3H5NO. It is the parent of a family of compounds called oxazolines, which contain non-hydrogenic substituents on carbon and/or nitrogen. Oxazolines are the unsaturated analogues of oxazolidines, and they are isomeric with isoxazolines, where the N and O are directly bonded. Two isomers of oxazoline are known, depending on the location of the double bond.

In organic chemistry, a benzylidene acetal is the functional group with the structural formula C6H5CH(OR)2 (R = alkyl, aryl). Benzylidene acetals are used as protecting groups in glycochemistry. These compounds can also be oxidized to carboxylic acids in order to open important biological molecules, such as glycosaminoglycans, to other routes of synthesis. They arise from the reaction of a 1,2- or 1,3-diols with benzaldehyde. Other aromatic aldehydes are also used.














