
Bruceanols are quassinoids isolated from Brucea antidysenterica . [1] [2]

Bruceanols are quassinoids isolated from Brucea antidysenterica . [1] [2]
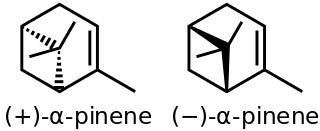
α-Pinene is an organic compound of the terpene class, one of two isomers of pinene. It is an alkene and it contains a reactive four-membered ring. It is found in the oils of many species of many coniferous trees, notably the pine. It is also found in the essential oil of rosemary and Satureja myrtifolia. Both enantiomers are known in nature; (1S,5S)- or (−)-α-pinene is more common in European pines, whereas the (1R,5R)- or (+)-α-isomer is more common in North America. The racemic mixture is present in some oils such as eucalyptus oil and orange peel oil.
Herkinorin is an opioid analgesic that is an analogue of the natural product Salvinorin A. It was discovered in 2005 during structure-activity relationship studies into neoclerodane diterpenes, the family of chemical compounds of which Salvinorin A is a member.

Thelephoric acid is a terphenylquinone pigment that is found in several fungi, such as Omphalotus subilludens and Polyozellus multiplex. Thelephoric acid has been shown to inhibit prolyl endopeptidase, an enzyme that has a role in processing proteins in Alzheimer's disease. Chemicals that inhibit prolyl endopeptidase have attracted research interest due to their potential therapeutic effects. It is derived from atromentin, and its precursor can be from cyclovariegatin. Fragmentation patterns have suggested that polymers of thelephoric acid exists.
Flavonolignans are natural phenols composed of a part flavonoid and a part phenylpropane.

δ-Viniferin is a resveratrol dehydrodimer. It is an isomer of epsilon-viniferin. It can be isolated from stressed grapevine leaves. It is also found in plant cell cultures and wine. It can also be found in Rheum maximowiczii.

Justicidin A is a organic compound isolated from Justicia procumbens. It is classified as a lignan. The compound may possess cytotoxic effects.

Quassinoids are degraded triterpene lactones of the Simaroubaceae plant family grouped into C-18, C-19, C-20, C-22 and C-25 types. The prototypical member of the group, quassin, was first described in the 19th century from plants of the genus Quassia from which it gets its name. It was isolated in 1937 and its structure elucidated in 1961.
Penicillium herquei is an anamorph, filamentous species of the genus of Penicillium which produces citreorosein, emodin, hualyzin, herquline B, janthinone, citrinin and duclauxin,.

Brucea javanica is a shrub in the family Simaroubaceae. The specific epithet javanica is from the Latin, meaning "of Java". Other common names in English include Java brucea and kosam.
Streptomyces flavoviridis is a bacterium species from the genus of Streptomyces which has been isolated from soil. Streptomyces flavoviridis produces phleomycin and zorbamycin.

Gutolactone is a chemical compound extracted from Simaba guianensis and has displayed antimalarial properties in vitro.

The phomoxanthones are a loosely defined class of natural products. The two founding members of this class are phomoxanthone A and phomoxanthone B. Other compounds were later also classified as phomoxanthones, although a unifying nomenclature has not yet been established. The structure of all phomoxanthones is derived from a dimer of two covalently linked tetrahydroxanthones, and they differ mainly in the position of this link as well as in the acetylation status of their hydroxy groups. The phomoxanthones are structurally closely related to other tetrahydroxanthone dimers such as the secalonic acids and the eumitrins. While most phomoxanthones were discovered in fungi of the genus Phomopsis, most notably in the species Phomopsis longicolla, some have also been found in Penicillium sp.

Bruceanol A is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol B is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol C is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol D is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol E is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol F is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol G is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol H is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.
| | This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |