
Aporphine is an alkaloid that forms the core of a class of quinoline alkaloids. It can exist in either of two enantiomeric forms, (R)-aporphine and (S)-aporphine.

Brucea is a genus of plant in the family Simaroubaceae. It is named for the Scottish scholar and explorer James Bruce.
Hannoa is a genus of plant in the family Simaroubaceae. It contains the following species :

Granzyme B is a serine protease that in humans is encoded by the GZMB gene. Granzyme B is expressed by cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and natural killer (NK) cells.

Enediynes are organic compounds containing two triple bonds and one double bond.

Kinamycins are a group of bacterial polyketide secondary metabolites containing a diazo group. Kinamycins are known for their cytotoxicity and are considered of interest for potential use in anti-cancer therapies.

Acutissimin A is a flavono-ellagitannin, a type of tannin formed from the linking of a flavonoid with an ellagitannin.
Solitomab is an artificial bispecific monoclonal antibody that is being investigated as an anti-cancer drug. It is a fusion protein consisting of two single-chain variable fragments (scFvs) of different antibodies on a single peptide chain of about 55 kilodaltons. One of the scFvs binds to T cells via the CD3 receptor, and the other to EpCAM as a tumor antigen against gastrointestinal, lung, and other cancers.

Bruceanols are quassinoids isolated from Brucea antidysenterica.

Quassinoids are degraded triterpene lactones of the Simaroubaceae plant family grouped into C-18, C-19, C-20, C-22 and C-25 types. The prototypical member of the group, quassin, was first described in the 19th century from plants of the genus Quassia from which it gets its name. It was isolated in 1937 and its structure elucidated in 1961.
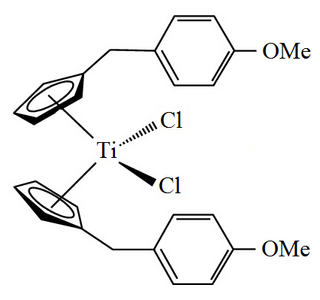
Titanocene Y also known as bis[(p-methoxybenzyl)cyclopentadienyl]titanium(IV) dichloride or dichloridobis(η5- cyclopentadienyl)titanium is an organotitanium compound that has been investigated for use as an anticancer drug.
Cytokine-induced killer cells (CIK) cells are a group of immune effector cells featuring a mixed T- and natural killer (NK) cell-like phenotype. They are generated by ex vivo incubation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) or cord blood mononuclear cells with interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), anti-CD3 antibody, recombinant human interleukin (IL-) 1 and recombinant human interleukin (IL)-2.

Brucea javanica is a shrub in the family Simaroubaceae. The specific epithet javanica is from the Latin, meaning "of Java". Other common names in English include Java brucea and kosam.

C-1027 or Lidamycin is an antitumor antibiotic consisting of a complex of an enediyne chromophore and an apoprotein. It shows antibiotic activity against most Gram-positive bacteria. It is one of the most potent cytotoxic molecules known, due to its induction of a higher ratio of DNA double-strand breaks than single-strand breaks.

Bruceanol A is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol B is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol D is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol E is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol G is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol H is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

















