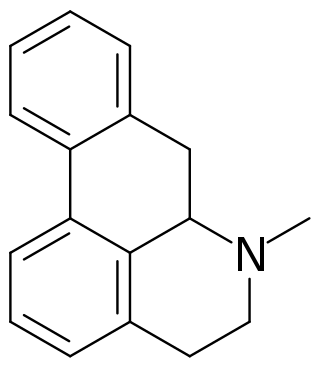
Aporphine is an alkaloid with the chemical formula C17H17N. It is the core chemical substructure of the aporphine alkaloids, a subclass of quinoline alkaloids. It can exist in either of two enantiomeric forms, (R)-aporphine and (S)-aporphine.

Halomon is a polyhalogenated monoterpene first isolated from the marine red algae Portieria hornemannii. Halomon has attracted research interest because of its promising profile of selective cytotoxicity that suggests its potential use as an antitumor agent.

Enediynes are organic compounds containing two triple bonds and one double bond.

Acutissimin A is a flavono-ellagitannin, a type of tannin formed from the linking of a flavonoid with an ellagitannin.

Withanolides are a group of at least 300 naturally occurring steroids built on an ergostane skeleton. They occur as secondary metabolites primarily in genera of the Nightshade family, for example in the tomatillo.
Cylindrocyclophanes are a class of cyclophane, a group of aromatic hydrocarbons composed of two benzene rings attached in a unique structure. Cylindrocyclophanes were the first cyclophanes found in nature, isolated from a species of cyanobacteria, and have proven to be an interesting group of compounds to study due to their unusual molecular structure and intriguing biological possibilities, especially its cytotoxicity to some cancer cell lines.

Bruceanols are quassinoids isolated from Brucea antidysenterica.

Eudistomins are β-carboline derivatives, isolated from ascidians, like Ritterella sigillinoides, Lissoclinum fragile, or Pseudodistoma aureum.
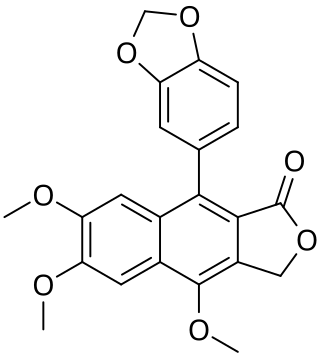
Justicidin A is a organic compound isolated from Justicia procumbens. It is classified as a lignan. The compound may possess cytotoxic effects.

Quassinoids are degraded triterpene lactones of the Simaroubaceae plant family grouped into C-18, C-19, C-20, C-22 and C-25 types. The prototypical member of the group, quassin, was first described in the 19th century from plants of the genus Quassia from which it gets its name. It was isolated in 1937 and its structure elucidated in 1961.

Brucea javanica is a shrub in the family Simaroubaceae. The specific epithet javanica is from the Latin, meaning "of Java". Other common names in English include Java brucea and kosam.

C-1027 or Lidamycin is an antitumor antibiotic consisting of a complex of an enediyne chromophore and an apoprotein. It shows antibiotic activity against most Gram-positive bacteria. It is one of the most potent cytotoxic molecules known, due to its induction of a higher ratio of DNA double-strand breaks than single-strand breaks.

Bruceanol A is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol B is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol C is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol D is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol E is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol F is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceanol H is a cytotoxic quassinoid isolated from Brucea antidysenterica with potential antitumor and antileukemic properties.

Bruceantin is a chemical compound that was first isolated from the plant Brucea antidysenterica in 1973. Chemically, it is classified as a secotriterpenoid and a quassinoid.



















