
Choctaw mythology is part of the culture of the Choctaw, a Native American tribe originally occupying a large territory in the present-day Southeastern United States: much of the states of Mississippi, Alabama, and Louisiana. In the 19th century, the Choctaw were known to European Americans as one of the "Five Civilized Tribes" even though controversy surrounds their removal.
The Abenaki people are an indigenous peoples of the Americas located in the Northeastern Woodlands region. Their religious beliefs are part of the Midewiwin tradition, with ceremonies led by medicine keepers, called Medeoulin or Mdawinno.

Barton Broad is a large lake that forms part of the River Ant which gives its name to a 164-hectare (410-acre) nature reserve north-east of Norwich in Norfolk. The reserve is owned and managed by the Norfolk Wildlife Trust. It is part of the Ant Broads and Marshes Site of Special Scientific Interest and National Nature Reserve, and part of it is in the Ant Marshes Nature Conservation Review site, Grade I. It is part of the Broadland Ramsar site and Special Protection Area, and The Broads Special Area of Conservation.
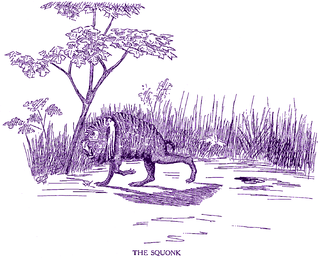
The squonk is a mythical creature that is reputed to live in the hemlock forests of northern Pennsylvania in the United States.

In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants. More in general, the word can be used for any low-lying and seasonally waterlogged terrain. In Europe and in agricultural literature low-lying meadows that require draining and embanked polderlands are also referred to as marshes or marshland.

The St. Johns River is the longest river in the U.S. state of Florida and is the most significant one for commercial and recreational use. At 310 miles (500 km) long, it flows north and winds through or borders 12 counties. The drop in elevation from headwaters to mouth is less than 30 feet (9 m); like most Florida waterways, the St. Johns has a very slow flow speed of 0.3 mph (0.13 m/s), and is often described as "lazy".

Lake Bogoria is a saline, alkaline lake that lies in a volcanic region in a half-graben basin south of Lake Baringo, Kenya, a little north of the equator. Lake Bogoria, like Lake Nakuru, Lake Elementeita, and Lake Magadi further south in the Rift Valley, and Lake Logipi to the north, is periodically home to one of the world's largest populations of lesser flamingos. The lake is a Ramsar site and Lake Bogoria National Reserve has been a protected National Reserve since November 29, 1973.

The Apatani people are an ethnic group who live in the Ziro valley of Arunachal Pradesh's Lower Subansiri region.

The Hula Valley is an agricultural region in northern Israel with abundant fresh water that used to be Lake Hula before it was drained. It is a major stopover for birds migrating along the Great Rift Valley between Africa, Europe, and Asia.

The Pontine Marshes is an approximately quadrangular area of former marshland in the Lazio Region of central Italy, extending along the coast southeast of Rome about 45 km (28 mi) from just east of Anzio to Terracina, varying in distance inland between the Tyrrhenian Sea and the Volscian Mountains from 15 to 25 km. The northwestern border runs approximately from the mouth of the river Astura along the river and from its upper reaches to Cori in the Monti Lepini.
Sanitation in ancient Rome, acquired from the Etruscans, was very advanced compared to other ancient cities and provided water supply and sanitation services to residents of Rome. Although there were many sewers, public latrines, baths and other sanitation infrastructure, disease was still rampant. The baths are known to symbolise the "great hygiene of Rome".

Before drainage, the Everglades, a region of tropical wetlands in southern Florida, were an interwoven mesh of marshes and prairies covering 4,000 square miles (10,000 km2). The Everglades is both a vast watershed that has historically extended from Lake Okeechobee 100 miles (160 km) south to Florida Bay, and many interconnected ecosystems within a geographic boundary. It is such a unique meeting of water, land, and climate that the use of either singular or plural to refer to the Everglades is appropriate. When Marjory Stoneman Douglas wrote her definitive description of the region in 1947, she used the metaphor "River of Grass" to explain the blending of water and plant life.
The Apatanis who inhabit a tranquil pine clad valley called Ziro at the core of Lower Subansiri District of Arunachal Pradesh, are famous for their unique practice of wet rice cultivation. They are also known for their sustainable agricultural practices and the agricultural cycles govern their everyday lives. The agricultural festival of Dree is the highlight in this cycle.

The Warner Lakes are a chain of shallow lakes and marshes in the Warner Valley of eastern Lake County, Oregon, United States. The lakes extend the length of the valley, covering approximately 90,000 acres (360 km2).

Ralph William Burdick Izzard, OBE was an English journalist, author, adventurer and, during World War II, a British Naval Intelligence officer.
Apatani is a Tani language, a branch of the Sino-Tibetan languages, spoken in India.
Paleontology in Colorado refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Colorado. The geologic column of Colorado spans about one third of Earth's history. Fossils can be found almost everywhere in the state but are not evenly distributed among all the ages of the state's rocks. During the early Paleozoic, Colorado was covered by a warm shallow sea that would come to be home to creatures like brachiopods, conodonts, ostracoderms, sharks and trilobites. This sea withdrew from the state between the Silurian and early Devonian leaving a gap in the local rock record. It returned during the Carboniferous. Areas of the state not submerged were richly vegetated and inhabited by amphibians that left behind footprints that would later fossilize. During the Permian, the sea withdrew and alluvial fans and sand dunes spread across the state. Many trace fossils are known from these deposits.

Aiyangiyang is a basin in southern Turkana, Kenya, southeast of Lodwar. It is known by nomadic pastoralists for its seasonal water availability, and is an important archaeological and paleontological site with artifacts and remains from the African Middle and Late Stone Ages.
In Slavic mythology, bolotnik, balotnik, bolotyanik or błotnik is a male swamp spirit. There are many descriptions of bolotnik. Usually he was portrayed as a man or an old man who has big, frog-like eyes, a green beard and long hair. His body is covered with dirt, algae and fish scales. The legends from the Vitebsk Governorate of Russia said that bolotnik is a dirty, fat, eyeless creature that motionlessly sits at the bottom of the swamp. In some accounts bolotnik is also said to have long arms and a tail. Just like the majority of Slavic water spirits, he would lure and drag people into the water if they get close to the edge. It is believed that bolotnik has neither wife nor children; in the other legends he is married to bolotnitsa, a female swamp spirit.

Tage Rita is an agricultural engineer from Ziro Valley and is India's first kiwi wine brewer. In 2018, she was honored with the Women Transforming India Awards, organized by the United Nations and NITI Aayog.














