
Social dynamics is the study of the behavior of groups that results from the interactions of individual group members as well to the study of the relationship between individual interactions and group level behaviors.
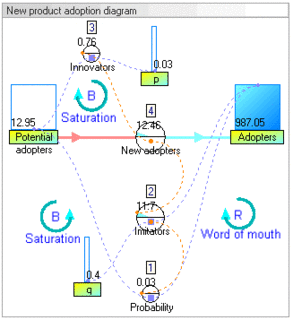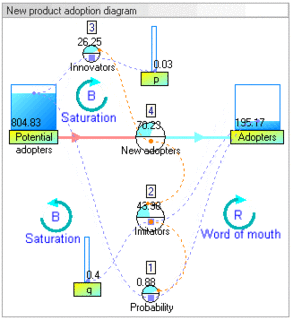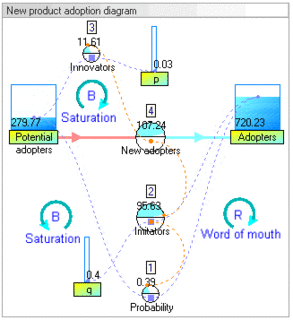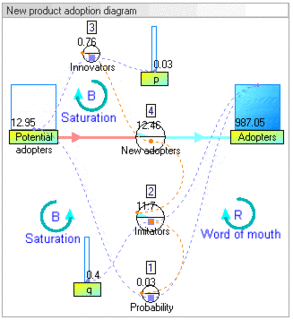
System dynamics (SD) is an approach to understanding the nonlinear behaviour of complex systems over time using stocks, flows, internal feedback loops, table functions and time delays.

Jay Wright Forrester was a pioneering American computer engineer and systems scientist. He is credited with being one of the inventors of magnetic core memory, the predominant form of random-access computer memory during the most explosive years of digital computer development. It was part of a family of related technologies which bridged the gap between vacuum tubes and semiconductors by exploiting the magnetic properties of materials to perform switching and amplification.

Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of or the outcome of a real-world or physical system. Since they allow to check the reliability of chosen mathematical models, computer simulations have become a useful tool for the mathematical modeling of many natural systems in physics, astrophysics, climatology, chemistry, biology and manufacturing, as well as human systems in economics, psychology, social science, health care and engineering. Simulation of a system is represented as the running of the system's model. It can be used to explore and gain new insights into new technology and to estimate the performance of systems too complex for analytical solutions.
The New England Complex Systems Institute (NECSI) is an independent American research institution and think tank dedicated to advancing analytics and its application to the challenges of society, and the interaction of complex systems with the environment. NECSI offers educational programs, conducts research, and hosts the International Conference on Complex Systems. It was founded in 1996 and is located in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Systems science is an interdisciplinary field that studies the nature of systems—from simple to complex—in nature, society, cognition, engineering, technology and science itself. To systems scientists, the world can be understood as a system of systems. The field aims to develop interdisciplinary foundations that are applicable in a variety of areas, such as psychology, biology, medicine, communication, business management, technology, computer science, engineering, and social sciences.

Computational sociology is a branch of sociology that uses computationally intensive methods to analyze and model social phenomena. Using computer simulations, artificial intelligence, complex statistical methods, and analytic approaches like social network analysis, computational sociology develops and tests theories of complex social processes through bottom-up modeling of social interactions.
An agent-based model (ABM) is a class of computational models for simulating the actions and interactions of autonomous agents with a view to assessing their effects on the system as a whole. It combines elements of game theory, complex systems, emergence, computational sociology, multi-agent systems, and evolutionary programming. Monte Carlo methods are used to introduce randomness. Particularly within ecology, ABMs are also called individual-based models (IBMs), and individuals within IBMs may be simpler than fully autonomous agents within ABMs. A review of recent literature on individual-based models, agent-based models, and multiagent systems shows that ABMs are used on non-computing related scientific domains including biology, ecology and social science. Agent-based modeling is related to, but distinct from, the concept of multi-agent systems or multi-agent simulation in that the goal of ABM is to search for explanatory insight into the collective behavior of agents obeying simple rules, typically in natural systems, rather than in designing agents or solving specific practical or engineering problems.
Computational science, also known as scientific computing or scientific computation (SC), is a rapidly growing field that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex problems. It is an area of science which spans many disciplines, but at its core, it involves the development of models and simulations to understand natural systems.
John David Sterman is the Jay W. Forrester Professor of Management, and the current director of the MIT System Dynamics Group at the MIT Sloan School of Management. He is also co-faculty at the New England Complex Systems Institute. He is mostly considered as the current leader of the System Dynamics school of thought. He is the author of "Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World".
The beer distribution game is a type of gamification that is used to experience typical coordination problems of a supply chain process. It reflects a role-play simulation where several participants play with each other. The game represents a supply chain with a non-coordinated process where problems arise due to lack of information sharing. This game outlines the importance of information sharing, supply chain management and collaboration throughout a supply chain process. Due to lack of information, suppliers, manufacturers, sales people and customers often have an incomplete understanding of what the real demand of an order is. The most interesting part of the game is that each group has no control over another part of the supply chain. Therefore, each group has only significant control over their own part of the supply chain. Each group can highly influence the entire supply chain by ordering too much or too little which can lead to a bullwhip effect. Therefore, the order taking of a group also highly depends on decisions of the other groups.
Computer simulation is a prominent method in organizational studies and strategic management. While there are many uses for computer simulation, most academics in the fields of strategic management and organizational studies have used computer simulation to understand how organizations or firms operate. More recently, however, researchers have also started to apply computer simulation to understand organizational behaviour at a more micro-level, focusing on individual and interpersonal cognition and behavior such as team working.

AnyLogic is a multimethod simulation modeling tool developed by The AnyLogic Company. It supports agent-based, discrete event, and system dynamics simulation methodologies. AnyLogic is a cross-platform simulation software because it works on Windows, macOS and Linux.

Systems modeling or system modeling is the interdisciplinary study of the use of models to conceptualize and construct systems in business and IT development.
DYNAMO is a historically important simulation language and accompanying graphical notation developed within the system dynamics analytical framework. It was originally for industrial dynamics but was soon extended to other applications, including population and resource studies and urban planning.
Attractiveness Principle is one of System Dynamics archetypes. System archetypes describe common patterns of behavior in dynamic complex systems. Attractiveness principle is a variation of Limits to Growth archetype, with restrictions caused by multiple limits. The limiting factors here are each of different character and usually cannot be dealt with the same way and/or they cannot be all addressed.
The environmental sustainability problem has proven difficult to solve. The modern environmental movement has attempted to solve the problem in a large variety of ways. But little progress has been made, as shown by severe ecological footprint overshoot and lack of sufficient progress on the climate change problem. Something within the human system is preventing change to a sustainable mode of behavior. That system trait is systemic change resistance. Change resistance is also known as organizational resistance, barriers to change, or policy resistance.
Hazhir Rahmandad is an Iranian American Scientist and Engineer. Dr. Rahmandad is a dynamic modeling expert. His research applies dynamic modeling to a broad range of problems in strategy, organizational learning, and public health.
Vensim is a simulation software developed by Ventana Systems. It primarily supports continuous simulation, with some discrete event and agent-based modelling capabilities. It is available commercially and as a free "Personal Learning Edition".







