
The Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) was designed as a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer system, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. It was originally designed as a successor to PCI-type connections for video cards. Since 2004, AGP has been progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express (PCIe); by mid-2008, PCI Express cards dominated the market and only a few AGP models were available, with GPU manufacturers and add-in board partners eventually dropping support for the interface in favor of PCI Express.
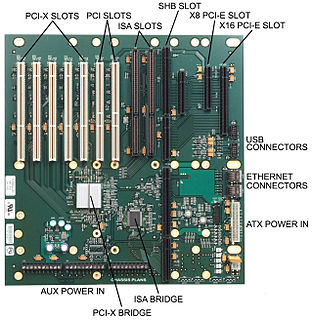
A backplane is a group of electrical connectors in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors, forming a computer bus. It is used as a backbone to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete computer system. Backplanes commonly use a printed circuit board, but wire-wrapped backplanes have also been used in minicomputers and high-reliability applications.

A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use.

In computing, an expansion card, also known as an expansion board, adapter card or accessory card, is a printed circuit board that can be inserted into an electrical connector, or expansion slot, on a computer motherboard, backplane or riser card to add functionality to a computer system via the expansion bus.
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport (LDT), is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001. The HyperTransport Consortium is in charge of promoting and developing HyperTransport technology.

PCI Express, officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for personal computers' graphics cards, hard drives, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections. PCIe has numerous improvements over the older standards, including higher maximum system bus throughput, lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint, better performance scaling for bus devices, a more detailed error detection and reporting mechanism, and native hot-swap functionality. More recent revisions of the PCIe standard provide hardware support for I/O virtualization.

Data acquisition is the process of sampling signals that measure real world physical conditions and converting the resulting samples into digital numeric values that can be manipulated by a computer. Data acquisition systems, abbreviated by the initialisms DAS or DAQ, typically convert analog waveforms into digital values for processing. The components of data acquisition systems include:

A single-board computer (SBC) is a complete computer built on a single circuit board, with microprocessor(s), memory, input/output (I/O) and other features required of a functional computer. Single-board computers are commonly made as demonstration or development systems, for educational systems, or for use as embedded computer controllers. Many types of home computers or portable computers integrate all their functions onto a single printed circuit board.

Electronic test equipment is used to create signals and capture responses from electronic devices under test (DUTs). In this way, the proper operation of the DUT can be proven or faults in the device can be traced. Use of electronic test equipment is essential to any serious work on electronics systems.
LAN eXtensions for Instrumentation (LXI) is a standard developed by the LXI Consortium, a consortium that maintains the LXI specification and promotes the LXI Standard. The LXI standard defines the communication protocols for instrumentation and data acquisition systems using Ethernet. Ethernet is a ubiquitous communication standard providing a versatile interface, the LXI standard describes how to use the Ethernet standards for test and measurement applications in a way that promotes simple interoperability between instruments. The LXI Consortium ensures LXI compliant instrumentation developed by various vendors work together with no communication or setup issues. The LXI Consortium ensures that the LXI standard complements other test and measurement control systems, such as GPIB and PXI systems.

ExpressCard, initially called NEWCARD, is an interface to connect peripheral devices to a computer, usually a laptop computer. The ExpressCard technical standard specifies the design of slots built into the computer and of expansion cards to insert in the slots. The cards contain electronic circuits and sometimes connectors for external devices. The ExpressCard standard replaces the PC Card standards.

In computing, a POST card is a plug-in diagnostic interface card that displays progress and error codes generated during power-on self-test (POST) of a computer. It is used to troubleshoot computers that do not start up.
The VXI bus architecture is an open standard platform for automated test based upon VMEbus. VXI stands for VME eXtensions for Instrumentation, defining additional bus lines for timing and triggering as well as mechanical requirements and standard protocols for configuration, message-based communication, multi-chassis extension, and other features. In 2004, the 2eVME extension was added to the VXI bus specification, giving it a maximum data rate of 160 MB/s.

Automatic test equipment or automated test equipment (ATE) is any apparatus that performs tests on a device, known as the device under test (DUT), equipment under test (EUT) or unit under test (UUT), using automation to quickly perform measurements and evaluate the test results. An ATE can be a simple computer-controlled digital multimeter, or a complicated system containing dozens of complex test instruments capable of automatically testing and diagnosing faults in sophisticated electronic packaged parts or on wafer testing, including system on chips and integrated circuits.

PCI eXtensions for Instrumentation (PXI) is one of several modular electronic instrumentation platforms in current use. These platforms are used as a basis for building electronic test equipment, automation systems, and modular laboratory instruments. PXI is based on industry-standard computer buses and permits flexibility in building equipment. Often modules are fitted with custom software to manage the system.
The AMD 700 chipset series is a set of chipsets designed by ATI for AMD Phenom processors to be sold under the AMD brand. Several members were launched in the end of 2007 and the first half of 2008, others launched throughout the rest of 2008.
Pickering Interfaces is a test and measurement company headquartered in Clacton-on-Sea, United Kingdom. Pickering designs, manufactures and markets a range of switching, simulation and cabling products in the LXI, PXI, and PCI platforms. These products are sold into the functional test, hardware-in-the-loop simulation (HILS) and design verifications markets.
In computing, the form factor is the specification of a motherboard – the dimensions, power supply type, location of mounting holes, number of ports on the back panel, etc. Specifically, in the IBM PC compatible industry, standard form factors ensure that parts are interchangeable across competing vendors and generations of technology, while in enterprise computing, form factors ensure that server modules fit into existing rackmount systems. Traditionally, the most significant specification is for that of the motherboard, which generally dictates the overall size of the case. Small form factors have been developed and implemented.
M-Modules are a mezzanine standard mainly used in industrial computers. Being mezzanines, they are always plugged on a carrier PCB that supports this format. The modules communicate with their carrier over a dedicated bus, and can have all kinds of special functions.
An instrument driver, in the context of test and measurement (T&M) application development, is a set of software routines that simplifies remote instrument control. Instrument drivers are specified by the IVI Foundation and define an I/O abstraction layer using the virtual instrument software architecture (VISA). The VISA hardware abstraction layer provides an interface-independent communication channel to T&M instruments. Furthermore, the instrument drivers encapsulate the Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments (SCPI) commands, which are an ASCII-based set of commands for reading and writing instrument settings and measurement data. This standard allows an abstract way of using various programming languages to program remote-control applications instead of using SCPI commands. An instrument driver usually has a well-defined API.











