An electronic oscillator is an electronic circuit that produces a periodic, oscillating or alternating current (AC) signal, usually a sine wave, square wave or a triangle wave, powered by a direct current (DC) source. Oscillators are found in many electronic devices, such as radio receivers, television sets, radio and television broadcast transmitters, computers, computer peripherals, cellphones, radar, and many other devices.

An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal. It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a proportionally greater amplitude signal at its output. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain: the ratio of output voltage, current, or power to input. An amplifier is defined as a circuit that has a power gain greater than one.

An operational amplifier is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential that is typically 100,000 times larger than the potential difference between its input terminals. The operational amplifier traces its origin and name to analog computers, where they were used to perform mathematical operations in linear, non-linear, and frequency-dependent circuits.

In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an analog input voltage or current to a digital number representing the magnitude of the voltage or current. Typically the digital output is a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities.

Data acquisition is the process of sampling signals that measure real-world physical conditions and converting the resulting samples into digital numeric values that can be manipulated by a computer. Data acquisition systems, abbreviated by the acronyms DAS,DAQ, or DAU, typically convert analog waveforms into digital values for processing. The components of data acquisition systems include:

A power supply is an electrical device that supplies electric power to an electrical load. The main purpose of a power supply is to convert electric current from a source to the correct voltage, current, and frequency to power the load. As a result, power supplies are sometimes referred to as electric power converters. Some power supplies are separate standalone pieces of equipment, while others are built into the load appliances that they power. Examples of the latter include power supplies found in desktop computers and consumer electronics devices. Other functions that power supplies may perform include limiting the current drawn by the load to safe levels, shutting off the current in the event of an electrical fault, power conditioning to prevent electronic noise or voltage surges on the input from reaching the load, power-factor correction, and storing energy so it can continue to power the load in the event of a temporary interruption in the source power.
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another. Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and control systems, where electrical signals are converted to and from other physical quantities. The process of converting one form of energy to another is known as transduction.

A preamplifier, also known as a preamp, is an electronic amplifier that converts a weak electrical signal into an output signal strong enough to be noise-tolerant and strong enough for further processing, or for sending to a power amplifier and a loudspeaker. Without this, the final signal would be noisy or distorted. They are typically used to amplify signals from analog sensors such as microphones and pickups. Because of this, the preamplifier is often placed close to the sensor to reduce the effects of noise and interference.
In electronics, an analog multiplier is a device that takes two analog signals and produces an output which is their product. Such circuits can be used to implement related functions such as squares, and square roots.

An opto-isolator is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits by using light. Opto-isolators prevent high voltages from affecting the system receiving the signal. Commercially available opto-isolators withstand input-to-output voltages up to 10 kV and voltage transients with speeds up to 25 kV/μs.

An electronic component is any basic discrete electronic device or physical entity part of an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not to be confused with electrical elements, which are conceptual abstractions representing idealized electronic components and elements. A datasheet for an electronic component is a technical document that provides detailed information about the component's specifications, characteristics, and performance.

A class-D amplifier or switching amplifier is an electronic amplifier in which the amplifying devices operate as electronic switches, and not as linear gain devices as in other amplifiers. They operate by rapidly switching back and forth between the supply rails, using pulse-width modulation, pulse-density modulation, or related techniques to produce a pulse train output. This passes through a simple low-pass filter which blocks the high-frequency pulses and provides analog output current and voltage. Because they are always either in fully on or fully off modes, little energy is dissipated in the transistors and efficiency can exceed 90%.

A charge amplifier is an electronic current integrator that produces a voltage output proportional to the integrated value of the input current, or the total charge injected.
A flash ADC is a type of analog-to-digital converter that uses a linear voltage ladder with a comparator at each "rung" of the ladder to compare the input voltage to successive reference voltages. Often these reference ladders are constructed of many resistors; however, modern implementations show that capacitive voltage division is also possible. The output of these comparators is generally fed into a digital encoder, which converts the inputs into a binary value.
A fully differential amplifier (FDA) is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with differential inputs and differential outputs. In its ordinary usage, the output of the FDA is controlled by two feedback paths which, because of the amplifier's high gain, almost completely determine the output voltage for any given input.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to electronics:
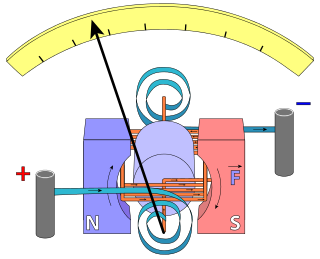
In electrical engineering, current sensing is any one of several techniques used to measure electric current. The measurement of current ranges from picoamps to tens of thousands of amperes. The selection of a current sensing method depends on requirements such as magnitude, accuracy, bandwidth, robustness, cost, isolation or size. The current value may be directly displayed by an instrument, or converted to digital form for use by a monitoring or control system.
This glossary of electrical and electronics engineering is a list of definitions of terms and concepts related specifically to electrical engineering and electronics engineering. For terms related to engineering in general, see Glossary of engineering.
In electronics, power amplifier classes are letter symbols applied to different power amplifier types. The class gives a broad indication of an amplifier's characteristics and performance. The classes are related to the time period that the active amplifier device is passing current, expressed as a fraction of the period of a signal waveform applied to the input. A class A amplifier is conducting through all the period of the signal; Class B only for one-half the input period, class C for much less than half the input period. A Class D amplifier operates its output device in a switching manner; the fraction of the time that the device is conducting is adjusted so a pulse-width modulation output is obtained from the stage.
A voltage-controlled resistor (VCR) is a three-terminal active device with one input port and two output ports. The input-port voltage controls the value of the resistor between the output ports. VCRs are most often built with field-effect transistors (FETs). Two types of FETs are often used: the JFET and the MOSFET. There are both floating voltage-controlled resistors and grounded voltage-controlled resistors. Floating VCRs can be placed between two passive or active components. Grounded VCRs, the more common and less complicated design, require that one port of the voltage-controlled resistor be grounded.










