C3 Collaborating for Health [1] is a global, not-for-profit non-governmental organisation, based in London, that exists to find solutions to fight the epidemic of non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
C3 Collaborating for Health [1] is a global, not-for-profit non-governmental organisation, based in London, that exists to find solutions to fight the epidemic of non-communicable diseases (NCDs).
C3’s focus is on the main risk factors – tobacco use, physical inactivity, and poor diet (including the harmful use of alcohol) – which between them cause the majority of many of the major NCDs – cardiovascular disease (heart disease and stroke), type 2 diabetes, chronic lung disease and cancers.
The United Nations Political Declaration on NCDs (September 2011) [2] calls for a 'whole of society' approach to tackling NCDs. To this end, C3 works with a range of organisations that affect public health and prevention of NCDs, including health professionals and local community leaders, businesses, NGOs, researchers, planners and young people.
C3 has produced a number of reports (e.g. on the benefits of physical activity for health) and also raises awareness of the importance of tackling NCDs and the risk factors through other media, e.g.:
C3 was founded in 2009 by Christine Hancock, former general secretary of the Royal College of Nursing and past president of the International Council of Nurses. C3 is a registered charity (no. 1135930) and a company limited by guarantee (no. 6941278), registered in England and Wales.
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. Health can be promoted by encouraging healthful activities, such as regular physical exercise and adequate sleep, and by reducing or avoiding unhealthful activities or situations, such as smoking or excessive stress. Some factors affecting health are due to individual choices, such as whether to engage in a high-risk behavior, while others are due to structural causes, such as whether the society is arranged in a way that makes it easier or harder for people to get necessary healthcare services. Still, other factors are beyond both individual and group choices, such as genetic disorders.

India's population in 2021 as per World Bank is 1.39 billion. Being the world's most populous country and one of its fastest-growing economies, India experiences both challenges and opportunities in context of public health. India is a hub for pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries; world-class scientists, clinical trials and hospitals yet country faces daunting public health challenges like child undernutrition, high rates of neonatal and maternal mortality, growth in noncommunicable diseases, high rates of road traffic accidents and other health related issues.
Workplace wellness, also known as corporate wellbeing outside the United States, is a broad term used to describe activities, programs, and/or organizational policies designed to support healthy behavior in the workplace. This often involves health education, medical screenings, weight management programs, and onsite fitness programs or facilities. It can also include flex-time for exercise, providing onsite kitchen and eating areas, offering healthy food options in vending machines, holding "walk and talk" meetings, and offering financial and other incentives for participation.

A non-communicable disease (NCD) is a disease that is not transmissible directly from one person to another. NCDs include Parkinson's disease, autoimmune diseases, strokes, heart diseases, cancers, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, osteoarthritis, osteoporosis, Alzheimer's disease, cataracts, and others. NCDs may be chronic or acute. Most are non-infectious, although there are some non-communicable infectious diseases, such as parasitic diseases in which the parasite's life cycle does not include direct host-to-host transmission.
An environmental health officer (EHO), also referred to as an environmental health practitioner (EHP) or public health inspector, is a person responsible for carrying out measures to protect public health, which includes the administration and enforcement of legislation related to environmental health and safety hazards.

World Diabetes Day (WDD) is the primary global awareness campaign focusing on diabetes mellitus and is held on 14 November each year.
Nutrition transition is the shift in dietary consumption and energy expenditure that coincides with economic, demographic, and epidemiological changes. Specifically the term is used for the transition of developing countries from traditional diets high in cereal and fiber to more Western-pattern diets high in sugars, fat, and animal-source food.
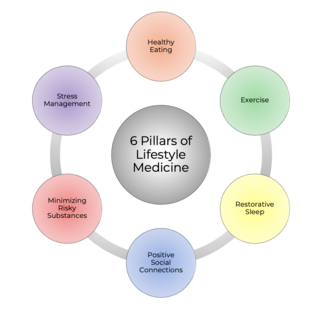
Lifestyle medicine (LM) is a branch of medicine focused on preventive healthcare and self-care dealing with prevention, research, education, and treatment of disorders caused by lifestyle factors and preventable causes of death such as nutrition, physical inactivity, chronic stress, and self-destructive behaviors including the consumption of tobacco products and drug or alcohol abuse. The goal of LM is to improve individuals' health and wellbeing by applying the 6 pillars of lifestyle medicine (nutrition, regular physical activity, restorative sleep, stress management, avoidance of risky substances, and positive social connection) to prevent chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity. By focusing on these 6 areas to improve health, LM can prevent 80% of chronic illnesses and non-communicable diseases (NCD).
The St. Vincent Declaration is a set of goals for the health care of people with diabetes mellitus published as the product of an international conference held in St. Vincent, Italy, on 10–12 October 1989.

The Northern Dimension Partnership in Public Health and Social Well-being (NDPHS) is an international networking platform for strengthening professional connections, sharing and co-creating knowledge, and developing joint activities in public health and social well-being. The Partnership is served by the NDPHS Secretariat that was established in 2012 as an international legal entity hosted by the Swedish Government located in Stockholm and funded jointly by the Partner Countries.
Malawi ranks 170th out of 174 in the World Health Organization lifespan tables; 88% of the population live on less than £2.40 per day; and 50% are below the poverty line.
Occupational health nursing is a specialty nursing practice that provides for and delivers health and safety programs and services to workers, worker populations, and community groups. The practice focuses on promotion, maintenance and restoration of health, prevention of illness and injury, and protection from work‐related and environmental hazards. Occupational health nurses (OHNs) aim to combine knowledge of health and business to balance safe and healthful work environments and a "healthy" bottom line.
Zambia is a landlocked country in Sub Saharan Africa which experiences a burden of both communicable and non-communicable diseases. In line with WHO agenda for equity in health, it has adopted the Universal Health Coverage agenda to mitigate the challenges faced within the health sector. The Ministry of Health (MOH) provides information pertaining to Zambian health. The main focus of the Ministry of Health has been provision of uninterrupted care with emphasis on health systems strengthening and services via the primary health care approach.

Brunei's healthcare system is managed by the Brunei Ministry of Health and funded by the General Treasury. It consists of around 15 health centers, ten clinics and 22 maternal facilities, considered to be of reasonable standard. There are also two private hospitals. Cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes are the leading cause of death in the country, with life expectancy around 75 years, a vast improvement from 1961. Brunei's human development index (HCI) improved from 0.81 in 2002 to 0.83 in 2021, expanding at an average annual rate of 0.14%. According to the UN's Human Development Report 2020, the HCI for girls in the country is greater than for boys, though aren't enough statistics in Brunei to break down HCI by socioeconomic classes. Brunei is the second country in Southeast Asia after Singapore to be rated 47th out of 189 nations on the UN HDI 2019 and has maintained its position in the Very High Human Development category. Being a culturally taboo subject, the rate of suicide has not been investigated.
Public health nursing, also known as community health nursing is a nursing specialty focused on public health. The term was coined by Lillian Wald of the Henry Street Settlement, or, Public health nurses (PHNs) or community health nurses "integrate community involvement and knowledge about the entire population with personal, clinical understandings of the health and illness experiences of individuals and families within the population." Public health nursing in the United States traces back to a nurse named Lillian Wald who, in 1893, established the Henry Street Settlement in New York City and coined the expression "public health nurse". A Public or Community Health Nurse is expected to comply with the duties and limitations of the American Nurse Association (ANA) publication Public Health Nursing: Scope and Standards of Practice.

Franklin Marshall Matthews White is a Canadian public health scientist focused on capacity building for international and global education, research and development. He advocates:
"Public health...must not be left to the international community to define; it is...the responsibility of the countries themselves to define their priorities. The global agenda should be viewed as complementary at best."
"Health is mostly made in homes, communities and workplaces and only a minority of ill health can be repaired in clinics and hospitals."
"Nations (must) assess their public health human resource needs and develop their ability to deliver this capacity, and not depend on other countries to supply it."
“Public health and primary health care are the cornerstones of sustainable health systems, and this should be reflected in the health policies and professional education systems of all nations.”
The United Nations Interagency Task Force on the Prevention and Control of Non-communicable Diseases (UNIATF), hereafter referred to as the Task Force, was established by the United Nations Secretary-General in 2013. Non-communicable diseases (NCDs), also known as chronic diseases, include cardiovascular diseases, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes. The role of the Task Force is to bring relevant actors from across the United Nations (UN) system and national governments together to develop whole-of-government, whole-of-society approaches for the prevention and control of NCDs. Following the establishment of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in 2015, the Task Force's scope of work was expanded to include “NCD related Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)” such as addressing mental health conditions, violence, injuries, nutrition and environmental issues that contribute to the global burden of NCDs. The Task Force promotes multisectoral action for the prevention and control of NCDs, supports countries to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and supports countries to move towards Universal Health Coverage (UHC). The work of the Task Force includes implementing the Global Joint Programme to conduct investment cases, coordinating interagency joint programmes and facilitating thematic working groups. The World Health Organization acts as a Secretariat for the Task Force.

Princess Dina Mired is a Jordanian humanitarian and health activist. She is a leading global advocate for cancer control and non-communicable diseases (NCDs). She was the President of the Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) from 2018 to 2020 and was the first Arab Muslim elected to lead in such a prestigious global post. Princess Dina is the former Director-General of the King Hussein Cancer Foundation. Princess Dina Mired was also recognized as one of the 100 Influential Women in Oncology by OncoDaily.

Sustainable Development Goal 3, regarding "Good Health and Well-being", is one of the 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations in 2015. The official wording is: "To ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all at all ages." The targets of SDG 3 focus on various aspects of healthy life and healthy lifestyle. Progress towards the targets is measured using twenty-one indicators.

Ama de-Graft Aikins is a British-Ghanaian Social Psychologist who is currently a British Academy Global Professor at University College London's Institute of Advanced Studies. Her research focuses primarily on the psychosocial and structural drivers of Africa's chronic non-communicable disease burden, but she also has interests in arts and health, and the history of psychology in Africa and its intersections with critical theory and African Studies. She has held teaching and research positions at the University of Cambridge, London School of Economics and Political Science and the University of Ghana. In 2015, she became the first female full professor of psychology at the University of Ghana, where she has a tenured position.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty |title= (help)[ title missing ]