In chemistry, an ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid in which at least one –OH (hydroxyl) group is replaced by an –O–alkyl (alkoxy) group. Usually, esters are derived from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides, which are fatty acid esters of glycerol, are important esters in biology, being one of the main classes of lipids, and making up the bulk of animal fats and vegetable oils. Esters with low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and found in essential oils and pheromones. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties, while polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties. Esters usually have a sweet smell and are considered high-quality solvents for a broad array of plastics, plasticizers, resins, and lacquers. They are also one of the largest classes of synthetic lubricants on the commercial market.

In chemistry, a salt is an ionic compound that can be formed by the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. Salts are composed of related numbers of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral. These component ions can be inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate ; and can be monatomic, such as fluoride (F−), or polyatomic, such as sulfate.

An acetate is a salt formed by the combination of acetic acid with an alkaline, earthy, metallic or nonmetallic and other base. "Acetate" also describes the conjugate base or ion typically found in aqueous solution and written with the chemical formula C
2H
3O−
2. The neutral molecules formed by the combination of the acetate ion and a positive ion are also commonly called "acetates". The simplest of these is hydrogen acetate with corresponding salts, esters, and the polyatomic anion CH
3CO−
2, or CH
3COO−
.
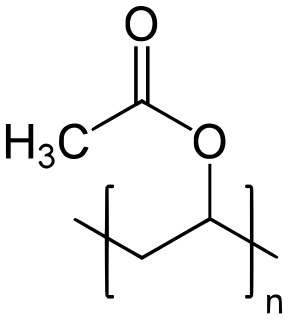
Poly(vinyl acetate) (PVA, PVAc, poly(ethenyl ethanoate): best known as wood glue, white glue, carpenter's glue, school glue, Elmer's glue in the US, or PVA glue) is an aliphatic rubbery synthetic polymer with the formula (C4H6O2)n. It belongs to the polyvinyl esters family, with the general formula -[RCOOCHCH2]-. It is a type of thermoplastic. There is considerable confusion between the glue as purchased, an aqueous emulsion of mostly vinyl acetate monomer, and the subsequent dried and polymerized PVAc that is the true thermoplastic polymer.

Cellulose acetate is the acetate ester of cellulose. It was first prepared in 1865. Cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some coatings, and as a frame material for eyeglasses; it is also used as a synthetic fiber in the manufacture of cigarette filters and playing cards. In photographic film, cellulose acetate replaced nitrate film in the 1950s, being far less flammable and cheaper to produce.

Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH
3–COO–CH
2–CH
3, simplified to C
4H
8O
2. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell and is used in glues, nail polish removers, decaffeinating tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent. The combined annual production in 1985 of Japan, North America, and Europe was about 400,000 tonnes. In 2004, an estimated 1.3 million tonnes were produced worldwide.

Methyl acetate, also known as MeOAc, acetic acid methyl ester or methyl ethanoate, is a carboxylate ester with the formula CH3COOCH3. It is a flammable liquid with a characteristically pleasant smell reminiscent of some glues and nail polish removers. Methyl acetate is occasionally used as a solvent, being weakly polar and lipophilic, but its close relative ethyl acetate is a more common solvent being less toxic and less soluble in water. Methyl acetate has a solubility of 25% in water at room temperature. At elevated temperature its solubility in water is much higher. Methyl acetate is not stable in the presence of strong aqueous bases or aqueous acids. Methyl acetate is not considered as a VOC.

Acetic anhydride, or ethanoic anhydride, is the chemical compound with the formula (CH3CO)2O. Commonly abbreviated Ac2O, it is the simplest isolable anhydride of a carboxylic acid and is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is a colorless liquid that smells strongly of acetic acid, which is formed by its reaction with moisture in the air.

Sodium acetate, CH3COONa, also abbreviated NaOAc, is the sodium salt of acetic acid. This colorless deliquescent salt has a wide range of uses.

n-Butyl acetate, also known as butyl ethanoate, is an ester that is a colorless, flammable liquid at room temperature. It is found in many types of fruit, where along with other chemicals, it imparts characteristic flavors and has a sweet smell of banana or apple. It is used as a synthetic fruit flavoring in foods such as candy, ice cream, cheeses, and baked goods. Butyl acetate is often used as a high-boiling solvent of moderate polarity.

Iron(II) acetate is a coordination complex with formula Fe(C2H3O2)2. It is a white solid, although impure samples can be slightly colored. A light green tetrahydrate is also known, which is highly soluble in water.
Ammonium acetate, also known as spirit of Mindererus in aqueous solution, is a chemical compound with the formula NH4CH3CO2. It is a white, hygroscopic solid and can be derived from the reaction of ammonia and acetic acid. It is available commercially.

Isoamyl acetate, also known as isopentyl acetate, is an organic compound that is the ester formed from isoamyl alcohol and acetic acid. It is a colorless liquid that is only slightly soluble in water, but very soluble in most organic solvents. Isoamyl acetate has a strong odor which is also described as similar to both banana and pear. Pure isoamyl acetate, or mixtures of isoamyl acetate, amyl acetate, and other flavors may be referred to as Banana oil.

Potassium acetate (CH3COOK) is the potassium salt of acetic acid.

γ-Valerolactone (GVL) is an organic compound with the formula C5H8O2. This colourless liquid is one of the more common lactones. GVL is chiral but is usually used as the racemate. It is readily obtained from cellulosic biomass and is a potential fuel and green solvent.

Aceburic acid (INN), also known as 4-acetoxybutanoic acid or 4-hydroxybutyric acid acetate, is drug described as an analgesic which was never marketed. It is the acetyl ester of gamma-hydroxybutyrate, and based on its structural relation to GHB, is likely to behave as a prodrug to it.

Acetic acid, systematically named ethanoic acid, is a colourless liquid organic compound with the chemical formula CH3COOH (also written as CH3CO2H or C2H4O2). When undiluted, it is sometimes called glacial acetic acid. Vinegar is no less than 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water. Acetic acid has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell. In addition to household vinegar, it is mainly produced as a precursor to polyvinyl acetate and cellulose acetate. It is classified as a weak acid since it only partially dissociates in solution, but concentrated acetic acid is corrosive and can attack the skin.

Barium acetate (Ba(C2H3O2)2) is the salt of barium(II) and acetic acid.

γ-Hydroxyvaleric acid (GHV), also known as 4-methyl-GHB, is a designer drug related to γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). It is sometimes seen on the grey market as a legal alternative to GHB, but with lower potency and higher toxicity, properties which have tended to limit its recreational use.